Govt Panel Recommends Overarching Agency to Grade Varsities, including IITs
26-08-2023
12:31 PM

What’s in today’s article?
- Why in News?
- About National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC)
- Objectives of NAAC
- What is Assessment & Accreditation?
- How Accreditation Process is Carried Out?
- Institutions Accredited in India
- What are the Benefits of Being NAAC-Accredited?
- News Summary
- Recommendations of the Dr. K. Radhakrishnan Committee
Why in News?
- A committee, formed by the Union government, has recommended that the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) be brought under the ambit of a proposed Accreditation agency.
- So far, IITs have never been accredited by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC), which is the existing agency that grades India’s colleges and universities.

About National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC)
- NAAC is an autonomous body established by the University Grants Commission (UGC).
- It was established in 1994 on the basis of recommendations made under the National Education Policy (1986).
- It is registered under the Karnataka Societies Registration Act of 1960.
- Vision:
- To make quality the defining element of higher education in India through a combination of self and external quality evaluation, promotion and sustenance initiatives.
- Headquarters: Bengaluru
Objectives of NAAC
- To arrange for periodic assessment and accreditation of institutions of higher education or units thereof, or specific academic programmes or projects;
- To stimulate the academic environment for promotion of quality of teaching-learning and research in higher education institutions;
- To encourage self-evaluation, accountability, autonomy and innovations in higher education;
- To undertake quality-related research studies, consultancy and training programmes.
What is Assessment & Accreditation?
- Assessment is the performance evaluation of an institution or its units based on certain established criteria.
- Accreditation is the certification of quality for a fixed period, which in the case of NAAC is five years.
· The University Grants Commission (UGC) through a gazette notification in January 2013, has made it mandatory for Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs) to undergo accreditation.
How Accreditation Process is Carried Out?
- The process of Assessment and Accreditation broadly consists of –
- Online submission of Institutional Information for Quality Assessment (IIQA) and Self-Study Report (SSR).
- Data Validation and Verification (DVV) by NAAC.
- Student Satisfaction Survey (SSS) by NAAC.
- Peer Team Visit.
- Institutional Grading.
Institutions Accredited in India
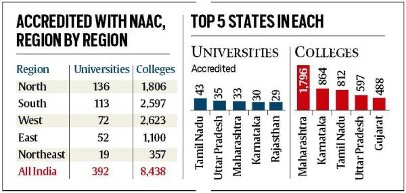
Image Caption: Institutions Accredited in India
- There are 1,043 universities and 42,343 colleges listed on the portal of the All India Survey on Higher Education.
- Out of these, 392 universities and 8,483 colleges are NAAC-accredited.
- Region-wise, the northern states have the highest number of accredited universities at 136, followed by the south (113), the west (72), the east (52) and the Northeast (19).
- Among the states, Maharashtra accounts for the highest number of accredited colleges at 1,796.
- Tamil Nadu has the most accredited universities (43).
What are the Benefits of Being NAAC-Accredited?
- Through a multi-layered process steered by the NAAC, a higher education institution gets to know whether it meets certain standards of quality set by the evaluator in terms of curriculum, faculty, infrastructure, research and financial well-being among others.
- Based on these parameters, the NAAC gives institutions grades ranging from A++ to C. If an institution is graded D, it means it is not accredited.
- Apart from recognition, being accredited also helps institutions attract capital as funding agencies look for objective data for performance funding.
- It helps an institution know its strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities through an informed review process.
- NAAC accreditation helps students going for higher education abroad as many global higher education authorities insist on recognition and accreditation of the institution where the student has studied.
News Summary
- In November 2022, Central government had constituted a High Level Committee, under the Chairmanship of Dr. K. Radhakrishnan, for strengthening the Assessment & Accreditation processes and preparing a road map for the National Accreditation Council envisioned in the National Education Policy, 2020.
- The committee recently submitted its report to the government.
Recommendations of the Dr. K. Radhakrishnan Committee
- The committee has recommended that the IITs should be brought under the ambit of NAAC.
- Currently, IITs follow their internal systems for periodic peer evaluation and assessment of programmes.
- Binary Accreditation System –
- Currently, NAAC follows an eight-point grading system under which institutes are rated A++, A+, A, B++, B+, B, C and D based on data submitted by institutes and their verification by expert teams during campus visits.
- The committee has suggested that under the new system, institutes be certified as “Accredited” or “Not Accredited (for those who are far below the standards for accreditation)”.
- A separate category of “Awaiting Accreditation” will cover institutes which are “close to the threshold level” or accreditation.
- The committee has also proposed that the entire accreditation process be made less dependent on inspections by teams of experts by adopting the mechanism of “crowdsourcing”.
- The idea now is to get the inputs submitted by the institutes vetted by a “carefully chosen set of audience with diverse association with the concerned institutes”.
- This set of audience may include students (including PhD and postdoctoral scholars), faculty, staff, alumni, official visitors such as selection committee members, employers of the students, etc.
- National Accreditation Council (NAAC) –
- Lastly, the Radhakrishnan committee has proposed that instead of having separate bodies for accrediting institutes and courses, one overarching agency be set up.
- The proposed National Accreditation Council (NAAC), envisaged by the NEP, should also subsume the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF), which ranks higher education institutes.
- The educational system should make transition to the proposed accreditation regime by December 2023.
Q1) What is the role of UGC (University Grants Commission)?
Determining and maintaining standards of teaching, examination and research in universities. Framing regulations on minimum standards of education. Monitoring developments in the field of collegiate and university education; disbursing grants to the universities and colleges.
Q2) What is All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE)?
All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) was set up in November 1945 as a national-level Apex Advisory Body to conduct a survey on the facilities available for technical education and to promote development in the country in a coordinated and integrated manner.
Source: Govt panel recommends overarching agency to grade varsities, including IITs | ET
