National Conference on Digitization, Paperless Courts and e-Initiatives
26-08-2023
12:28 PM
1 min read

What’s in today’s article?
- Why in News?
- What is the e-Courts Integrated Mission Mode Project?
- What are the Major Initiatives Launched under the Project?
- The National Conference on Digitization, Paperless Courts and e-Initiatives
- New Initiative - “Neutral Citation for the Indian Judiciary”
Why in News?
- To explore the possible ways of use of technology in the legal system a National Conference on Digitization, Paperless Courts and e-Initiatives has been organized by the High Court of Orissa in the Odisha Judicial Academy, Cuttack.
- Implementation of the Action Plan of Phase-III of e-Courts Project of the Supreme Court of India is the focal point of the conference.

What is the e-Courts Integrated Mission Mode Project?
- As part of the National e-Governance Plan, the Project has been under implementation (under the aegis of the e-Committee SC) since 2007 for ICT development of the Indian Judiciary.
- It is a Pan-India Project, monitored and funded by the Department of Justice, Ministry of Law and Justice, Government of India, for the District Courts across the country.
- It is based on the National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the Indian Judiciary-2005.
- The Project envisages:
- To provide efficient and time-bound citizen centric services delivery.
- To develop, install and implement decision support systems in courts.
- To automate the processes to provide transparency in accessibility of information.
- To enhance judicial productivity, to make the justice delivery system affordable, accessible, cost effective, predictable, reliable and transparent.
- The Phase I of e-Courts was concluded in 2015 in which 14,249 Court sites were computerised. Under Phase II, 18,735 District and Subordinate courts have been computerised so far.
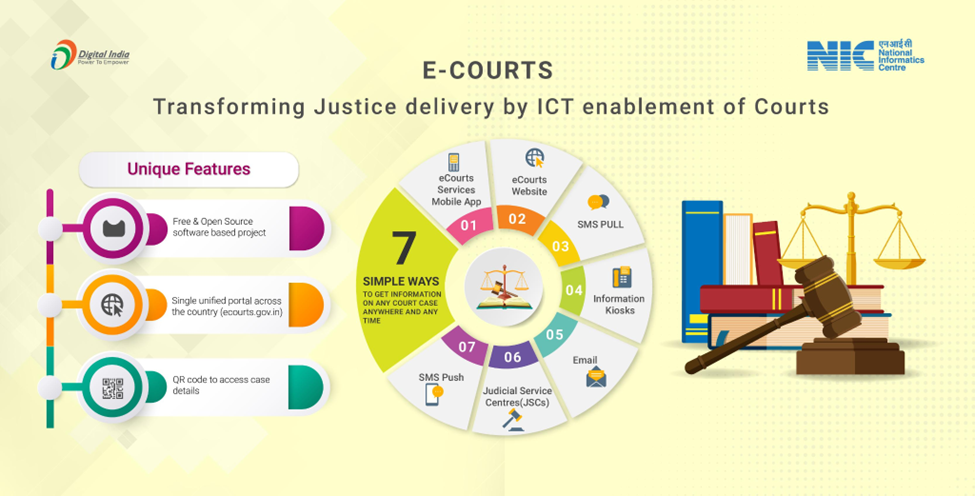
What are some of the Major Initiatives Launched under the Project?
- Case Information Software (CIS) based on customised Free and Open-Source Software (FOSS) has been developed.
- National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG) is a flagship project launched in 2015 for monitoring pendency and disposal of the cases in HCs and Subordinate Courts.
- Virtual Courts (as of July 2022, there are 20 Virtual Courts in 16 States/UTs) and using Video Conferencing.
- An e-Filing system has been rolled out for the electronic filing of legal papers with advanced features like online submission of Vakalatnama, e-Signing, online video recording of oath, etc.
- E-Sewa Kendras: To make justice delivery inclusive and to mitigate handicaps caused by digital divide, e-Sewa Kendras have been rolled out to provide e-filing services to lawyers and litigants.
The National Conference on Digitization, Paperless Courts and e-Initiatives:
- About:
- The conference is primarily aimed at discussing how to implement the National Action Plan of Phase-III of e-Courts Project.
- The conference was inaugurated by the Chief Justice of India (CJI) and attended by all the HCs of the country, the delegates from the Department of Justice and the e-Committee, SC.
- Highlights of the CJI’s speech on the occasion:
- ICT Initiatives like virtual hearing, live streaming, e-Filing, Paperless Courts, digitisation of case records, etc., which gave fillip to the legal system after the Covid pandemic are no longer new and it’s time to effect a complete transformation of judiciary.
- Amid a demand to set up benches of Orissa HC, CJI said that the technology has obliterated the need for benches of the HC.
- He hailed Orissa HC’s efforts to set up virtual courts in 20 of the state’s 30 districts, where lawyers can address the HC from their districts.
- Recommendations:
- There is the need for the judiciary to build its own resources in the field of ICT instead of depending on the private agencies.
- The issue of data integrity and security highlights the need for framing of a Comprehensive Judicial Data Security Policy for protecting the confidential details of the citizens.
- Training of Judges, Judicial Officers, Court staff, lawyers and their clerks on ICT initiatives.
New Initiative - “Neutral Citation for the Indian Judiciary”:
- Case law reporting is an integral part of the legal system. However, different law reports adopt different patterns to identify a case law which often leads to confusion.
- Inaugurated on the occasion by the CJI, Neutral Citations is an initiative (of CJI D.Y Chandrachud) aimed at evolving a uniform and secure methodology for identifying and citing decisions of the orders and judgments of the SC and HCs.
- Case laws, which were so far accessible only to the subscription holders of private law reporters, would now be available to everyone free of cost through Neutral Citations.
Q1) What is the National e-Governance Plan?
It is an initiative of the Government of India (approved in 2006) to make all government services available to the citizens of India via electronic media. It was formulated by the Department of Electronics and Information Technology and Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances.
Q2) What is the mandate of the e-Committee, Supreme Court of India?
It is the governing body charged with overseeing the e-Courts Project conceptualized under the “National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the Indian Judiciary-2005”.
Source: SC is not Supreme Court of Tilak Marg, it is apex court of India, by India, for India: CJI
