National Income data: India’s GDP expanded 6.1% in 2022-23’s last quarter
26-08-2023
12:32 PM
1 min read

What’s in today’s article?
- Why in News?
- Key Economic Terminologies
- The Recently Released Data
- Takeaways from the Recent Data
Why in News?
- According to the provisional national income data released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), India’s gross domestic product (GDP) growth accelerated to 6.1% in the January to March 2023 quarter.
- This has lifted the economy’s growth rate in 2022-23 to 7.2% from the 7% estimated earlier.

Key Economic Terminologies:
- GDP and GVA are the two main ways to ascertain the country’s economic performance that measures national income.
- GDP:
- The GDP is a monetary measure of all final products and services (those purchased by the final user) produced in a country over a certain period.
- The GDP accomplishes this by adding total expenditures in the economy, examining who spent how much, thus, measuring the economy's overall "demand."
- 4 key engines of GDP growth: (GDP = C + I + G + NX)
- Consumption (C)/Private Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE): The biggest engine is consumption demand from private individuals.
- Investment (I)/Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF): The second-biggest engine is the investment demand generated by private sector businesses.
- Government (G)/Government Final Consumption Expenditure (GFCE): The third engine (~11%) is the demand for goods and services generated by the government.
- Net Exports (NX) = Exports minus imports.
- Gross value added (GVA):
- It calculates the same national income from the supply side, by adding up all the value added (value of output minus the value of its intermediary inputs) across different sectors.
- This value added is shared among the primary factors of production, labour and capital.
- By looking at the GVA growth one can understand which sector of the economy is robust and which is struggling.
- How are GDP and GVA related? GDP = (GVA) + (Taxes earned by the government) — (Subsidies provided by the government). If the taxes > subsidies it provides, the GDP will be higher than GVA.
The Recently Released Data:
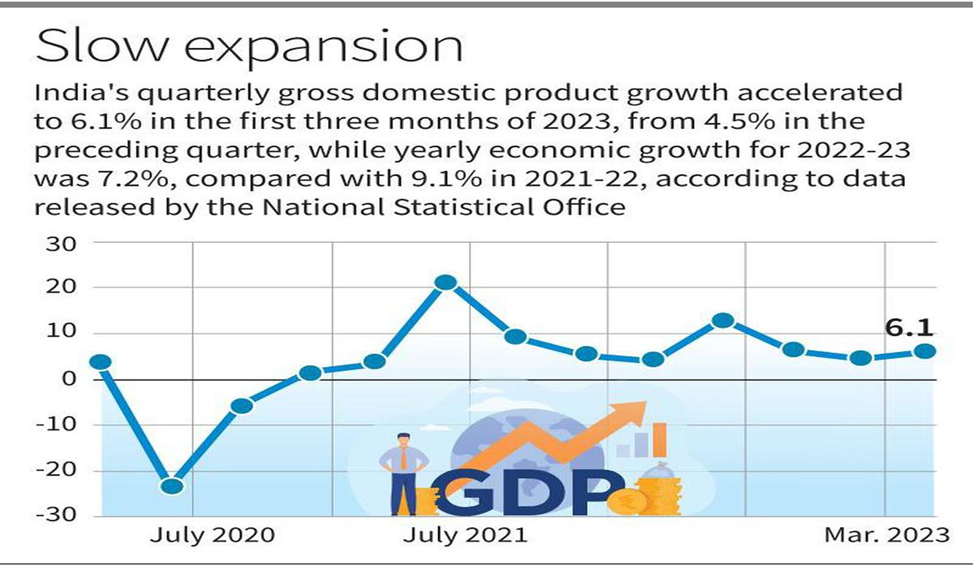
GDP:
- India’s 6.1% GDP growth was the fastest among major economies in the fourth quarter and the prospects look better for this year than they did four months ago.
- GVA:
- It is estimated to have risen 7% in 2022-23, compared to 8.8% in 2021-22, with manufacturing GVA growth sliding to just 1.3% from 11.1% a year ago.
- Economists noted that though several sectors delivered a positive surprise, consumption remained weak and the overall growth pattern remains uneven.
- Agri, services growth:
- The agricultural GVA grew 4%, up from 3.5% in the previous year.
- The financial, real estate and professional services sectors saw their GVA grow 7.1%, compared to 4.7% in 2021-22.
- The GVA of the trade, hotels, transport, and communication sectors, as well as services related to broadcasting grew 14%, marginally faster than in the previous year.
- This means the current economic outcomes are boosted by the farm and services sector.
Takeaways from the Recent Data:
- The 2022-23 GDP growth figures underscored the resilience of the Indian economy amidst global challenges.
- Exports of goods and services accounted for 23.5% of GDP, the highest since 2014-15.
- The private consumption hit the highest level since 2006-07 at 58.5% and gross fixed capital formation is at the highest point (34% of GDP) since 2013-14.
- GVA from the employment-intensive construction sector grew 10% in 2022-23, from 14.8% in 2021-22.
- However, the phenomenon of pent-up demand that lifted services through last year and this fiscal year’s first two months will not be strong, and private sector investment has to pick up.
Q1) What is pent-up demand?
Pent-up demand refers to a situation where demand for a service or product is unusually strong. Economists generally use the term to describe the general public's return to consumerism following a period of decreased spending.
Q2) What is the difference between GDP and GVA?
GVA is the value added to the product to enhance the various aspects of the product whereas GDP is the total amount of products produced in the country.
Source: India’s GDP expanded 6.1% in 2022-23’s last quarter | IE
