SC Ruling on Agnipath Scheme
26-08-2023
12:24 PM

What’s in today’s article?
- Why in news?
- What is the Agnipath scheme?
- News Summary: SC ruling on Agnipath scheme
- What is the background of the case?
- What is the doctrine of promissory estoppel?
- How does the doctrine of promissory estoppel relate to the Agnipath case?
- What was the observation of the apex court on this matter?
Why in news?
- The Supreme Court dismissed petitions challenging the Delhi High Court judgment which upheld the Agnipath scheme for recruitment to the armed forces.

What is the Agnipath scheme?
- About
- Agnipath scheme is a central government scheme launched in 2022 for recruitment to the armed forces.
- It is a recruitment process for individuals below the rank of officer, with the goal of deploying fitter, younger troops on the front lines, many of whom will be on four-year contracts.
- The armed forces would also have the option to retain some of the best 'Agniveers.'
- Eligibility
- Candidates between the age of 17.5 years to 21 years will be eligible for enrolling in the Agnipath scheme.
- Girls under the given age limit are open for the agnipath entry, while there is no such reservation for women under this scheme.
- The recruitment standards will remain the same, and recruitment will be done twice a year through rallies.
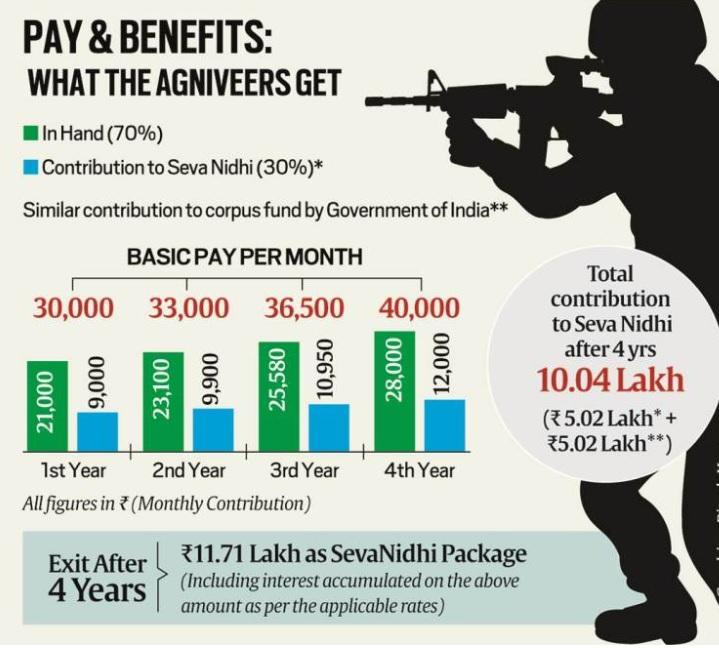
- Pay & Benefits of Agniveers
-
Image Caption: Pay & Benefits of Agniveers
News Summary: SC ruling on Agnipath scheme
What is the background of the case?
- Various petitions were filed in the apex court challenging the Delhi High Court judgment which upheld the Agnipath scheme.
- Some of the petitioners included candidates who were shortlisted in the earlier recruitment process to Army and Air Force.
- Names of some of these candidates had appeared in a provisional list for recruitment to Air Force but the recruitment process was cancelled when Agnipath scheme was notified.
- There was written exam, physical test, medical exam conducted under the old recruitment process.
- After which a provisional selection list was published with the ranks.
- Against this backdrop, the petitioners argued that the government must be directed to complete the old process citing the doctrine of promissory estoppel.
What is the doctrine of promissory estoppel?
- About
- The doctrine of promissory estoppel is an equitable doctrine evolved by equity to prevent injustice.
- The doctrine is a legal principle that prevents a person from going back on a promise made to another person, even if the promise is not supported by consideration.
- It is based upon principles of justice, fair play, and good conscience.
- Conditions when this doctrine may apply
- In a 1981 decision in Chhaganlal Keshavalal Mehta v. Patel Narandas Haribhai, the SC lists out a checklist for when the doctrine can be applied.
- First, there must be a clear and unambiguous promise.
- Second, the plaintiff must have acted relying reasonably on that promise.
- Third, the plaintiff must have suffered a loss.
- This doctrine is often used in contract law cases, but it can also apply in other areas of law, such as property law or tort law.
- In a 1981 decision in Chhaganlal Keshavalal Mehta v. Patel Narandas Haribhai, the SC lists out a checklist for when the doctrine can be applied.
- The doctrine of promissory estoppel and contract
- The doctrine of promissory estoppel is not the same as a contract, and it does not create a contract between the parties.
- Rather, it is a principle that can be used to enforce a promise in certain circumstances.
How does the doctrine of promissory estoppel relate to the Agnipath case?
- In the present case, the petitioners’ argument invoking the doctrine essentially means that the government’s actions of putting up a shortlist etc would be a promise made by it.
- The candidates acted based on that promise and they refused other jobs in CRPF, BSF etc. Hence, they must be compensated for their loss.
What was the observation of the apex court on this matter?
- The promissory estoppel is always subject to overarching public interest.
- The court also observed that this is not a contract matter where promissory estoppel in public law was applied.
- It is a public employment and that the question of applying this principle will not arise in this case.
Q1) What is a contract between two parties?
A contract between two parties is a legally binding agreement that sets out the rights and obligations of both parties. It can be in writing, verbal or implied by conduct. A contract typically includes several key elements, such as the offer, acceptance, consideration, and intention to create legal relations. An offer is a proposal made by one party to another, while acceptance is the other party's agreement to the terms of the offer.
Q2) What is a tort law?
Tort law is an area of law that deals with civil wrongs committed by one party that causes harm or injury to another party. The term "tort" comes from the French word for "wrong" or "injury." Tort law provides a legal framework for individuals or entities who have suffered harm or injury as a result of the wrongful conduct of another party.
Source: SC ruling on Agnipath scheme: What does promissory estoppel under contract law mean? | Mondaq | Vikaspedia | Indian Express