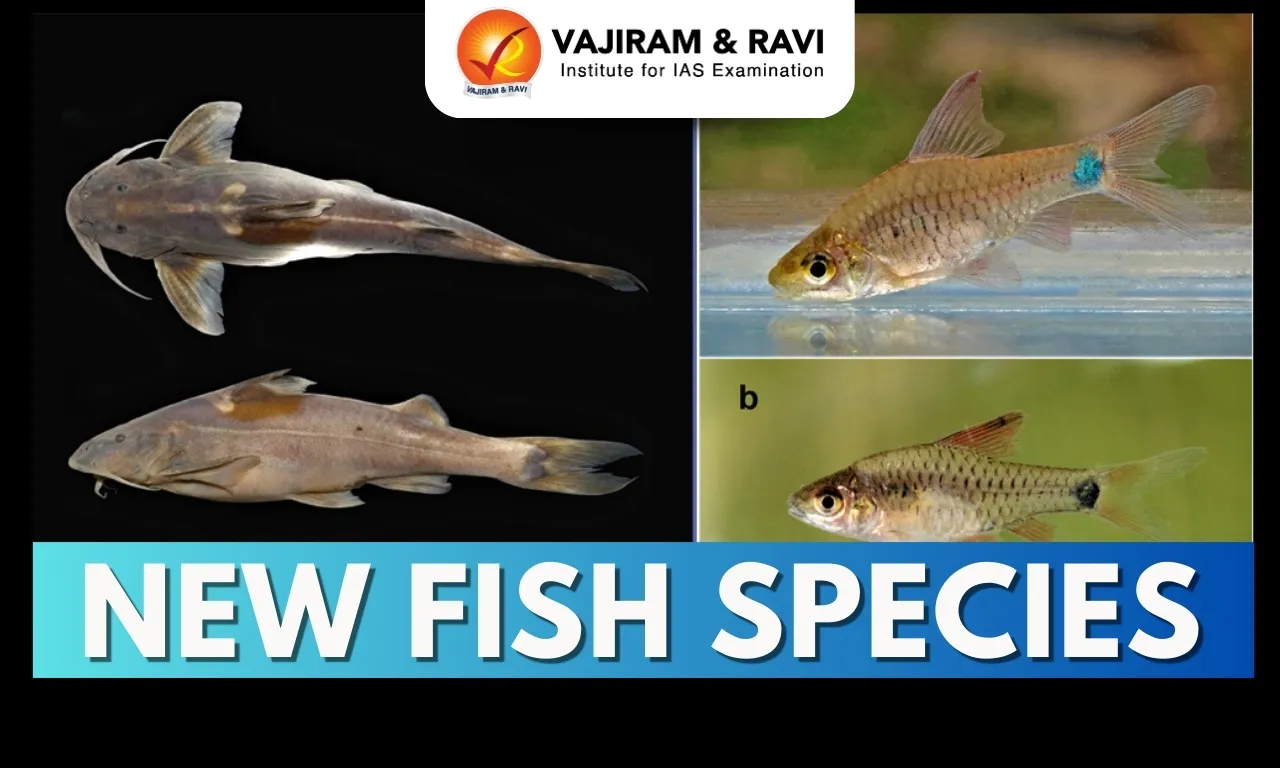
Ahilyabai Holkar Latest News
The Prime Minister will take part in a ‘Mahila Sashaktikaran Maha Sammelan’ event in Bhopal on the occasion of the 300th birth anniversary of legendary queen Ahilyabai Holkar.
About Ahilyabai Holkar
- Maharani Ahilyabai Holkar (31 May 1725 – 13 August 1795) was a ruler of the Malwa territory, a part of the Maratha Confederacy, from 1767 to 1795.
- She served first as regent and then as ruler of the Holkar dynasty with its seats at Maheshwar and Indore in central India, in a period considered the zenith of the Holkar dynasty.
- Under her rule Malwa enjoyed relative peace, prosperity, and stability, and her capital, Maheshwar, was turned into an oasis of literary, musical, artistic, and industrial pursuits.
- She passed away on August 13, 1795, at the age of seventy.
- Upon her death, Ahilyabai was succeeded by Tukoji Rao Holkar, who abdicated in his son Jaswant Rao’s favor two years later.
- Jaswant Rao was the last Holkar ruler to remain independent until his 1804 defeat by and subsequent peace with the British.
- Titles:
- She is known as Punyashlok (“One as Pure as the Sacred Chants”).
- John Keay, the British historian, gave the queen the title of ‘The Philosopher Queen’.
Ahilyabai Holkar Military Contribution
- She was military-trained under her father-in-law, Malhar Rao Holkar, and personally led armies into battle.
- Ahilyabai appointed Malhar Rao’s adopted son, Tukoji Rao Holkar, the commander of the Holkar army.
- She engaged the Frenchman Chevelier Dudrenec in 1792 to help modernize her army by raising four battalions.
Ahilyabai Holkar Administration
- She earned a reputation for administering justice fairly during her rule, without partiality or partisanship. Ex: She sentenced her only son, found guilty of a capital offense, to death by being crushed by an elephant.
- She established courts for justice and arbitration in citizens’ disputes.
- She also made some landmark decisions during her reign, including the removal of traditional law confiscating the property of childless widows.
- She was known for being accessible to all her subjects and held daily audiences where people could approach her.
- Breaking another norm of the time, Ahilyabai did not observe the custom of purdah (seclusion of women).
Ahilyabai Holkar Cultural Contribution
- She welcomed stalwarts such as Marathi poet Moropant, Shahir Ananta Gandhi, and Sanskrit scholar Khushali Ram into her capital.
- She made Maheshwar (literally, “abode of Lord Shiva”) her capital and offered employment to several craftsmen, artists, and sculptors.
- She was a great pioneer and builder of Hindu temples.
- She built hundreds of temples and Dharmashalas throughout India.
- Her most notable contribution was the renovation and repair of the famous Kashi Vishwanath Temple in 1780.
- Ahilyabai also helped construct multiple forts, roads, wells, and rest houses.
- Promotion of craft: She established a textile industry in Maheshwar, which today is very famous for its Maheshwari sarees.
Ahilyabai Holkar FAQs
Q1: Which major temple did Ahilyabai Holkar renovate in 1780?
Ans: Kashi Vishwanath Temple
Q2: In which region of India did Ahilyabai Holkar rule?
Ans: Ahilyabai Holkar ruled over the Malwa region of central India, with her capital at Maheshwar (in present-day Madhya Pradesh).
Q3: Who ruled after Ahilyabai Holkar?
Ans: Ahilyabai was succeeded by Tukoji Rao Holkar, who abdicated in his son Jaswant Rao’s favor two years later.
Source: DH
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ UPSC will release the UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Tags: ahilyabai holkar prelims pointers upsc current affairs upsc prelims current affairs