What is the Earth’s innermost inner core?
26-08-2023
10:19 AM
1 min read
Overview:
Seismologists at The Australian National University(ANU) recently documented the evidence of a distinct fifth layer of earth at the centremost part of Earth— the “innermost inner core”.
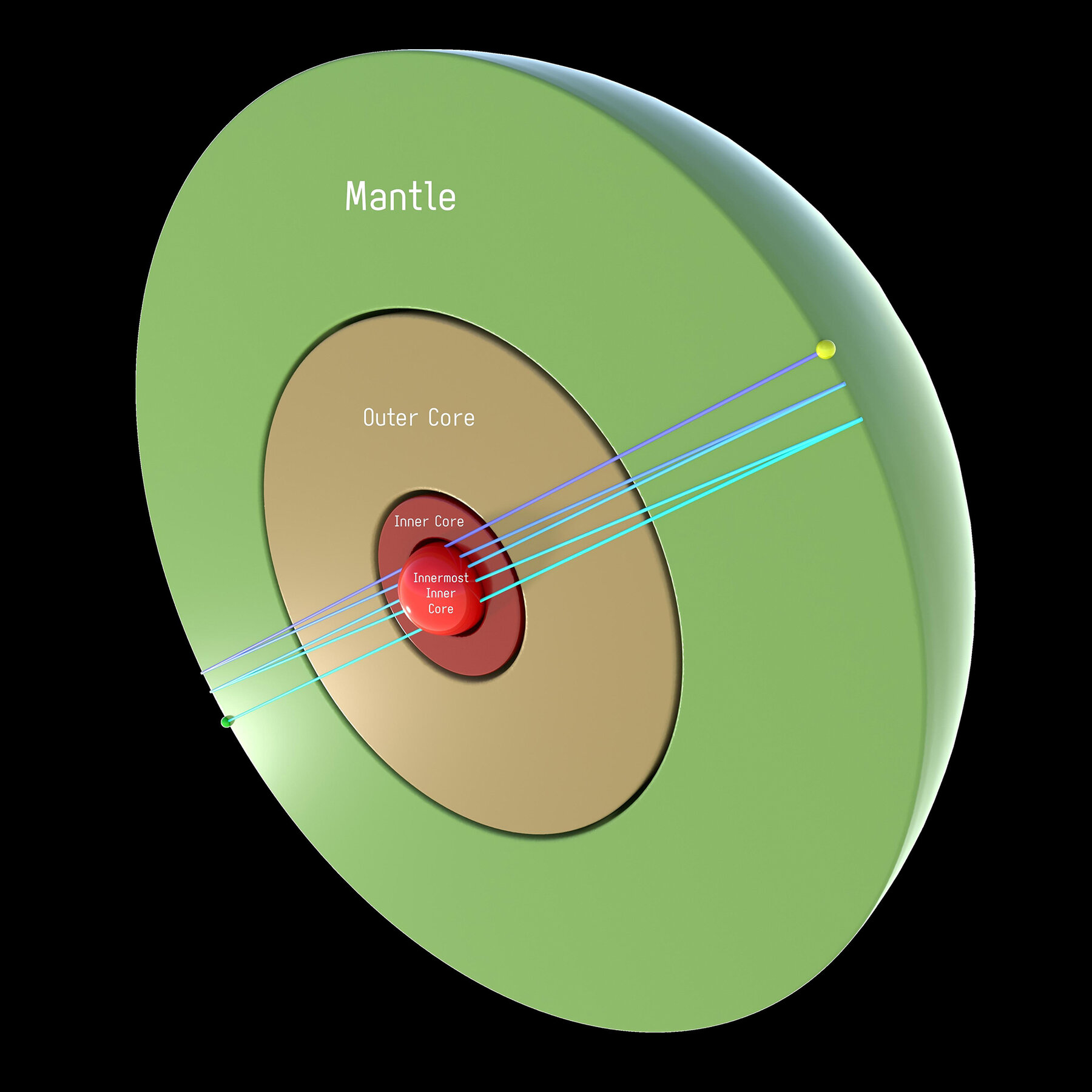
About Earth’s innermost inner core (IMIC):
- It is a 400-mile-wide (644-kilometer-wide) ball of metal.
- IMIC exists in a solid state as an alloy of iron and nickel because of the extreme pressure at the center of the Earth.
- Its temperature is estimated to be about 5,500-6,000 degrees (Celsius/9,930-10,830 Fahrenheit), similar to the sun's surface temperature.
- It has a distinct anisotropy, which is a property of a substance that allows it to take on different characteristics depending on the angle from which it’s approached.
- The concept of the innermost part of the inner core was first proposed in 2002 by seismologists from Harvard University— Miaki Ishii and Adam Dziewonski.

About the Inner core of the Earth:
- It is a solid metallic ball made mainly of iron.
- The inner core is solid due to the pressure caused by the weight put on it by the Earth’s other top layers.
- It is distinct from the outer core, which is a liquid.
- Radius:
- The inner core has an average radius of 1220 km.
- The boundary between the inner and outer core is located at approximately 5150 km below the surface of the Earth.
- This boundary is called the Lehman Seismic Discontinuity.
Temperature: Inner core temperatures reach extraordinary levels, estimated to be between 7,200–8,500ºF (4,000–4,700ºC).
Properties:
- It is predicted to have very high thermal and electrical conductivity.
- The inner core generates its own magnetic field and spins a bit faster than the rest of the planet.
Q1) What are the different layers of earth?
The structure of the earth is divided into four major components: the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core. Each layer has a unique chemical composition, physical state, and can impact life on Earth's surface
