What’s in today’s article?
- Why in news?
- What is Quad Grouping?
- What are the objectives of the Quad?
- Evolution of Quad
- News Summary: Quad Ministerial Meeting
- Key highlights of the joint statement issued at the end of Quad Ministerial Meeting
Why in News?
- India hosted the Quad foreign ministers’ meeting, which discussed the overall situation in the Indo-Pacific in the backdrop of increasing Chinese assertiveness in the region.
What is Quad Grouping?
- The grouping of four democracies –India, Australia, US and Japan– is known as the quadrilateral security dialogue or quad.
- The aim of this grouping is to ensure a free and open international order based on the rule of law in the Indo- Pacific.
What are the objectives of the Quad?
- The group’s primary objectives include
- maritime security,
- combating the Covid-19 crisis, especially vis-à-vis vaccine diplomacy,
- addressing the risks of climate change,
- creating an ecosystem for investment in the region and
- boosting technological innovation.
Evolution of Quad
- Following the Indian Ocean tsunami, India, Japan, Australia, and the US created an informal alliance to collaborate on disaster relief efforts.
- Quad as a formal group was first mooted by Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe in 2007.
- However, due to Chinese resistance and reluctance shown by India, it could not move ahead.
- Later, during the 2017 ASEAN Summits, all four former members re-joined negotiations to revive the quadrilateral alliance.
- The Quad was upgraded to the ministerial level in September 2019.
- In March 2021, the first-ever summit of QUAD leaders took place virtually.
- It was participated by the PMs/Presidents of all the member countries. The summit was hosted by US.
- Later, in September 2021, the first in-person meeting of Quad leaders was hosted by the US.
News Summary: Quad Ministerial Meeting
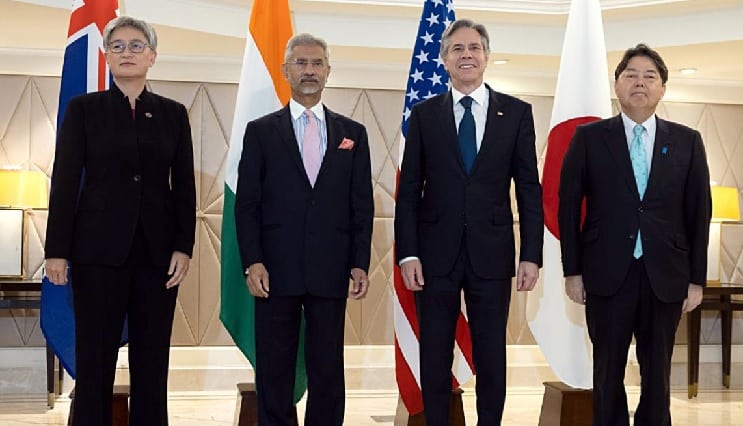
- The meeting of the Quad Foreign Ministers was hosted by India on 03 March 2023 in New Delhi.
- The meeting was chaired by EAM, S. Jaishankar, and saw the participation of Foreign Minsters of Australia and Japan and the Secretary of State of the USA.
- At the end of the meeting, the participating leaders issued a joint statement.
Key highlights of the joint statement issued at the end of Quad Ministerial Meeting
- Highlighted the situation in Ukraine
- The joint statement underscored the need for a comprehensive, just and lasting peace in Ukraine in accordance with international law.
- It called for respect for sovereignty, territorial integrity, transparency and peaceful resolution of disputes.
- This is the first reference to the Ukraine war in a joint statement of the Quad Foreign Ministers.
- It means the grouping, which had so far been concentrating mostly on the aggressive Chinese behaviour in the Indo-Pacific, has broadened its scope to include Russia.
- Called for greater Quad collaboration
- The statement called for greater Quad collaboration in support of the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific.
- It opposed any unilateral actions that seek to change the status quo or increase tensions in the area.
- This statement is understood to indicate recent tensions over Taiwan.
- Mentioned South and East China Seas
- The joint statement expressed serious concern at the militarization of disputed features, the dangerous use of coast guard vessels and maritime militia, and efforts to disrupt other countries’ offshore resource exploitation activities.
- This was mentioned in reference to actions in the South and East China Seas.
- It also hit out at China for blocking listing of terrorists at the UN.
- Criticised both Russia and China
- India joined other Quad members in calling for a just and lasting peace in Ukraine, and respect for a rules-based order in the South and East China Seas.
- This is the first such statement by the grouping that is seen to criticise both Russia and China.
- About Quad Maritime Security Working Group
- The statement announced that the “Quad Maritime Security Working Group” would meet in Washington later this month.
- This working group Working Group is a collaborative effort between the members of Quad to ensure a free and open Indo-Pacific region by promoting security and stability in the maritime domain.
- The group was established in 2020 as part of Quad.
- It focuses on a range of issues related to maritime security, including maritime domain awareness, maritime security architecture, and interoperability among the four navies.
- New working group on counter-terrorism
- The participating leaders also agreed to set up a new working group on counter-terrorism.
- This working group will explore cooperation amongst the Quad, and with Indo-Pacific partners, to counter new and emerging forms of terrorism, radicalisation to violence and violent extremism.
- Its first meeting is expected to be held in the United States in 2023.
Q1) What is the South China Sea?
The South China Sea is a marginal sea that is located in the Pacific Ocean bordered by China to the north, Vietnam to the west, the Philippines to the east, Malaysia and Brunei to the south, and Taiwan to the north-northeast. The sea is a major shipping route, connecting the Indian Ocean with the Western Pacific Ocean, and it is also rich in natural resources such as oil and gas deposits, fisheries, and minerals.
Q2) What is ASEAN?
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN, was established on 8 August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand, with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by the Founding Fathers of ASEAN: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
It is a regional organization that brings together disparate neighbors to address economic and security issues, but the group’s impact remains limited.
Source: Quad Foreign Ministers take aim at Russia and China | Ministry of External Affairs | US Department of State | Indian Express