Thrombectomy Latest News
The Technology Development Board (TDB), under the Centre’s Department of Science and Technology (DST), recently announced financial support for the development of India’s first indigenous thrombectomy device for stroke care.
About Thrombectomy
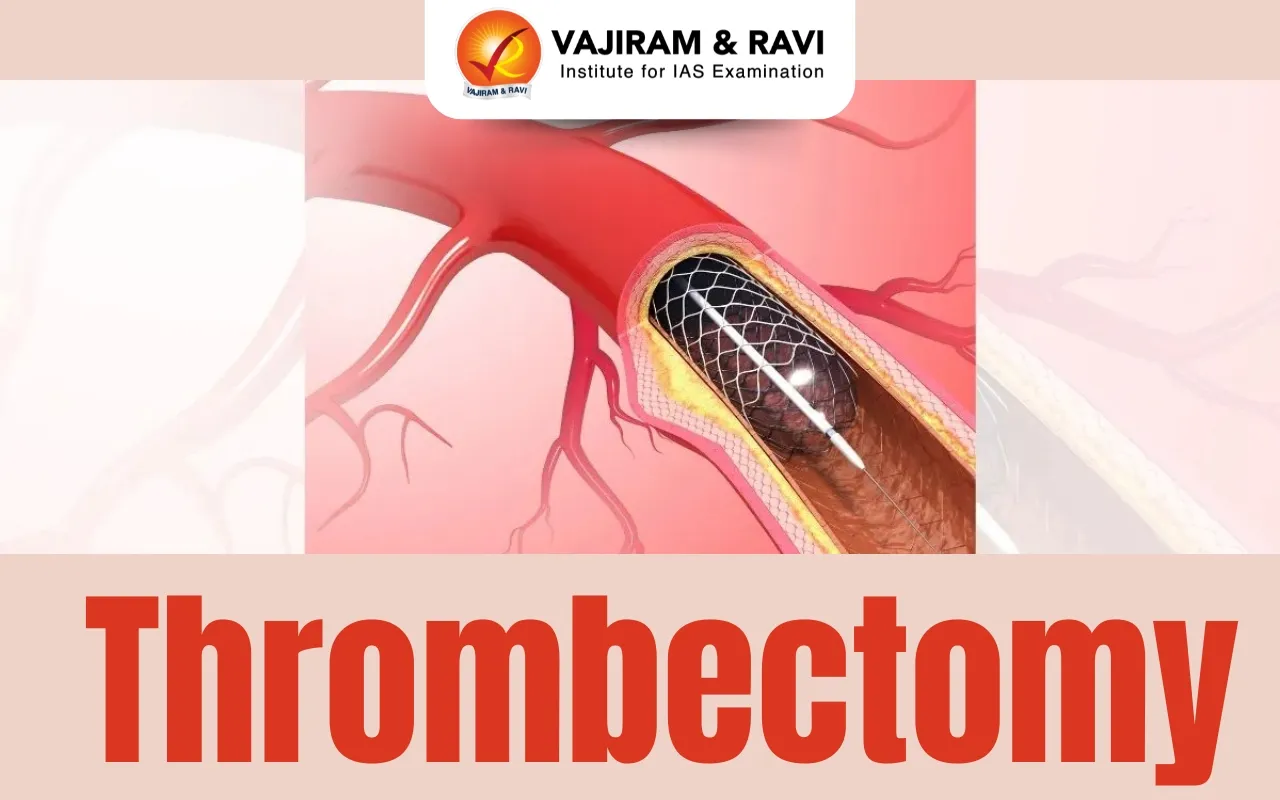
- A thrombectomy is a surgical or interventional treatment to remove blood clots in an artery or vein to help restore blood flow through your blood vessel.
- A blood clot, also known as a thrombus, can obstruct blood flow, leading to tissue damage or even death.
- Some of the most common places for blood clots to occur are your legs, arms, intestines, brain, lungs, and heart.
- Thrombectomies are performed to restore blood flow and prevent serious consequences.
- Sometimes a thrombectomy must be performed within a matter of hours to prevent life- or limb-threatening complications from occurring.
- There are two large categories of thrombectomies:
- Surgical (open) Thrombectomy:
- During a surgical thrombectomy, your surgeon makes an incision to get to your blocked blood vessel, cuts open your blood vessel, removes the blood clot using a balloon, and then repairs the blood vessel.
- Percutaneous (minimally invasive) Thrombectomy:
- During a mechanical thrombectomy, your surgeon introduces special devices through catheters that can either macerate or suction out clots from within your blood vessel.
- When there’s a residual clot left, your surgeon will infuse the area with local clot-dissolving medicines.
- Surgical (open) Thrombectomy:
Thrombectomy FAQs
Q1. What is the main goal of a thrombectomy?
Ans. To remove blood clots and restore blood flow.
Q2. What is the main difference between surgical and percutaneous thrombectomy?
Ans. The use of open surgery vs. catheters.
Q3. During a surgical thrombectomy, how is the clot typically removed?
Ans. By cutting open the vessel and extracting it using a balloon.
Source: BS