Hydrogen Peroxide Latest News
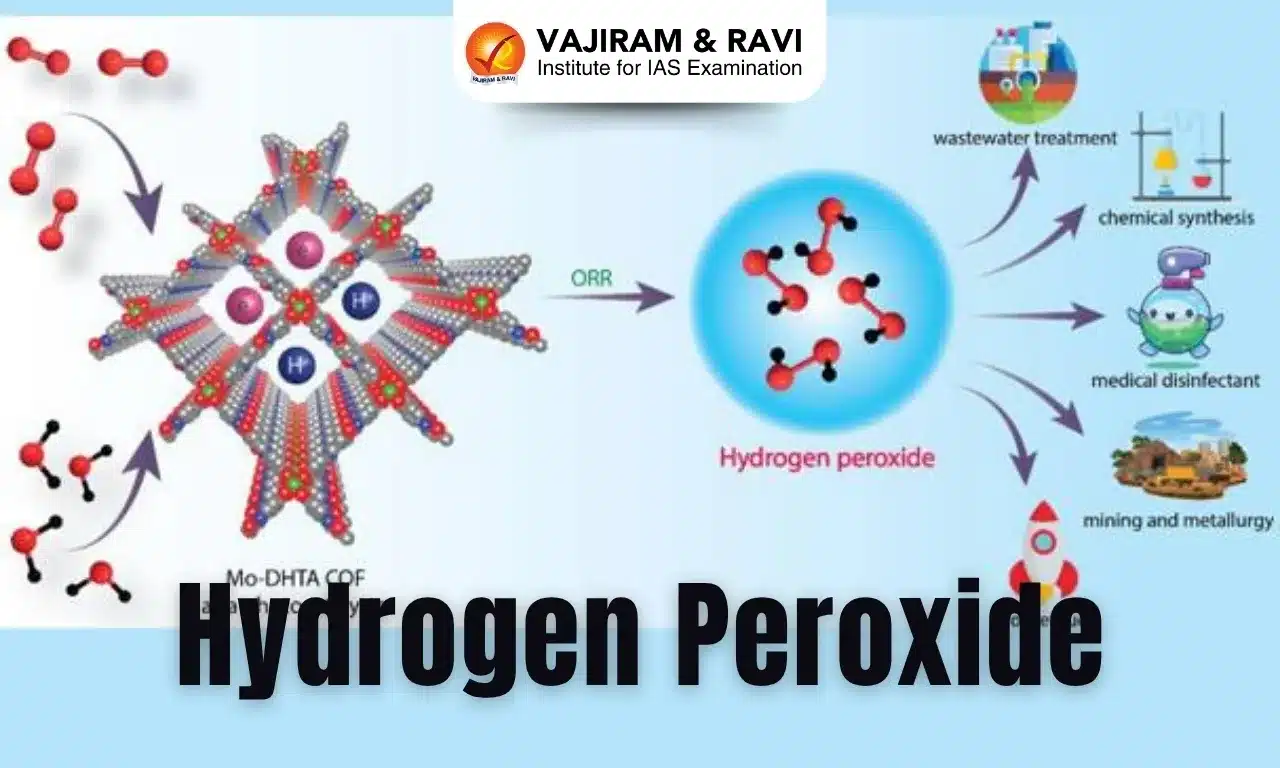
Recently, scientists have developed a novel approach for using a cutting-edge material called Mo-DHTA COF, short for dimolybdenum paddlewheel-embedded covalent organic framework for synthesizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) directly from water and sunlight.
About Hydrogen Peroxide
- It is a colorless liquid at room temperature with a bitter taste.
- Small amounts of gaseous hydrogen peroxide occur naturally in the air.
Features of Hydrogen Peroxide
- It is known for its eco-friendly nature of degrading or breaking down into only water and oxygen.
- Hydrogen peroxide is unstable, decomposing readily to oxygen and water with release of heat.
- It is nonflammable; it is a powerful oxidizing agent that can cause spontaneous combustion when it comes in contact with organic material.
- Hydrogen peroxide is found in many households at low concentrations (3-9%) for medicinal applications and as a clothes and hair bleach.
- It is a key component in sustainable chemical processes. However, its conventional production methods are energy-intensive, environmentally hazardous, and costly.
Applications of Hydrogen Peroxide
- It is a vital oxidizing agent with broad applications in chemical synthesis, sterilization, wastewater treatment, and fuel cells.
- In industry, hydrogen peroxide in higher concentrations is used as a bleach for textiles and paper, as a component of rocket fuels, and for producing foam rubber and organic chemicals.
Source: PIB
Hydrogen Peroxide FAQs
Q1: What is hydrogen peroxide and its uses?
Ans: Hydrogen peroxide is used for hair bleaching and for oxidation in permanent hair dyes and in oral hygiene products such as mouth-rinses and dentifrices as well as in tooth bleaching products.
Q2: What is hydrogen peroxide also known as?
Ans: Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) – also known as oxygenated water – is a gas widely used as a bleaching agent in paper plants and the textile industry.