Rainwater Harvesting is a water management practice that includes collecting and storing rainwater using different methods and systems. Rainwater harvesting is practiced to reduce water scarcity, manage stormwater runoff, and provide sustainable water resources for use. In this article, we are going to cover the principles and practices of rainwater harvesting, its importance, objectives and methods and techniques used in rural and urban areas.
Rainwater Harvesting System
Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting and storing rainwater that runs off from natural or artificial catchment areas such as rooftops, compounds, rock surfaces, hill slopes, or prepared land surfaces.
It typically involves capturing rainwater from rooftops or surface runoff, channeling it into tanks, cisterns, or recharge pits, and using it for drinking, irrigation, domestic use, or groundwater recharge. This system reduces dependency on traditional water supply sources, helps prevent flooding, and minimizes soil erosion.
Rainwater Harvesting Objectives
The method of Rainwater Harvesting has the following objectives:
- Minimizes the surface water runoff and soil erosion.
- Increases the availability of water for domestic, industrial and agricultural purposes.
- Improves aquifer levels through artificial recharge techniques.
- Helps in managing stormwater by controlling flooding, soil erosion and drainage problems.
- Helps in providing irrigation support in drought-prone regions.
- Decreases dependency on reducing pressure on traditional as well as municipal water supply systems.
- Encourages an eco-friendly, self-reliant water management method.
Rainwater Harvesting Types
There are multiple types of rainwater harvesting methods. These include:
- Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting- Rainwater is collected from rooftops and either stored in tanks or directed to recharge groundwater.
- Surface Runoff Harvesting- Rainwater is captured from roads, gardens and open fields and stored in reservoirs, ponds or proper storage structures.
- Check Dams- Checks dams are like small barriers constructed across streams to slow water flow and recharge groundwater.
- Recharge Pits- Shallow excavations are filled with porous material to allow percolation into aquifers.
- Percolation Tanks- Depression tanks that store runoff and recharge groundwater naturally.
Rainwater Harvesting Methods
Rainwater Harvesting is practised using the following methods-
- Recharge Pits & Trenches- Pits and Trenches are filled with gravel/sand in order to allow the infiltration into aquifers.
- Percolation Tanks- Huge depressions are created for gradual seepage of stored water.
- Check Dams- Slow stream flow to allow and help in groundwater recharge.
- Borewell & Dugwell Recharge- Agricultural techniques help in reducing runoff, prevent erosion and retain soil moisture.
Rainwater Harvesting Techniques
Rainwater Harvesting is practised in both rural and urban areas using multiple techniques. These techniques and practises include:
- Rainwater Harvesting in urban areas is practised using the following methods-
- Recharge Pit allows rainwater infiltration to aquifers.
- Recharge Trenches- The Long trenches are filled with porous material to harvest surface runoff.
- The Tubewell Recharge system uses rainwater to recharge deeper aquifers through tubewells.
- Techniques used in Rural Areas-
- Gully Plugs – Built across gullies to store rainwater temporarily.
- Contour Bunds – Embankments along contours to retain runoff and conserve soil moisture.
- Dugwell Recharge – Using old wells for rainwater recharge.
- Percolation Tanks – Created on permeable land for large-scale recharge.
- Check Dams/Cement Plugs – Store stream water and allow controlled overflow.
- Recharge Shafts – Recharge unconfined aquifers beneath poorly permeable layers.
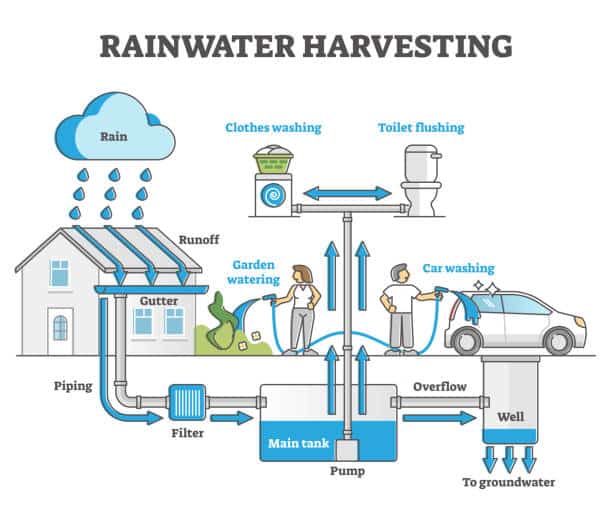
Rainwater Harvesting Diagram
The following diagram represents the process of Rainwater Harvesting:
Rainwater Harvesting Significance
Rainwater Harvesting methods implementations are important due to the following reasons:
- Reduce Runoff Loss – Controls excess runoff during monsoons.
- Meet Rising Demand – Helps cope with urbanization and industrial water needs.
- Agriculture & Food Security – Provides irrigation in rain-fed areas.
- Empowering Women – Reduces burden of fetching water in water-scarce areas.
- Reduce Soil Erosion & Flooding – Controls stormwater flow in cities.
- Increase Groundwater Levels – Provides long-term water sustainability in implementing water harvesting.
Rainwater Harvesting Project
The Rainwater Harvesting Project was launched in order to collect and store rainwater for daily work uses like irrigation and balancing groundwater levels.
- The project includes setting up systems to collect rainwater from rooftops and other surfaces, channeling them into gutters and developing storage for them in tanks and underground reservoirs.
- This project helps in managing problems like water scarcity, reducing the burdens of traditional water sources and promoting environmental conservation.
- Provides a reliable water supply especially in areas affected by droughts and water shortages.
Rainwater Harvesting Traditional Methods in India
Traditional systems of rainwater harvesting highlight India’s sustainable water wisdom and continue to inspire modern water conservation practices:
- Zing (Ladakh) – Collecting glacial meltwater.
- Kul (Himachal/Jammu) – Mountain water channels.
- Naula (Uttarakhand) – Small step ponds.
- Apatani (Arunachal Pradesh) – Terraced water channels.
- Zabo/Ruza (Nagaland) – Runoff impounding.
- Bamboo Drip Irrigation (Meghalaya) – Bamboo pipes for water flow.
- Johads (Rajasthan) – Earthen check dams.
- Tankas & Kunds (Rajasthan) – Underground storage tanks.
- Eri (Tamil Nadu) – Flood-control and groundwater recharge tanks.
- Surangams (Kerala, Karnataka) – Tunnel-based water systems.
- Bhandara Phad (Maharashtra) – Community-managed check dams.
- Pat System (Madhya Pradesh) – Diversion channels from streams.
Rainwater Harvesting FAQs
Q1: What is rainwater harvesting?
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting, storing, and using rainwater for domestic, agricultural, and industrial purposes.
Q2: What are the 7 types of rainwater harvesting?
Ans: The 7 types are: rooftop harvesting, surface runoff harvesting, recharge pits, recharge trenches, percolation tanks, check dams, and rain barrels.
Q3: What is the importance of rainwater harvesting?
Ans: It conserves water, reduces groundwater depletion, prevents flooding, and ensures sustainable water availability.
Q4: What is the Eri Rainwater Harvesting method?
Ans: The Eri method, traditional to Tamil Nadu, uses small interconnected tanks (eris) to store rainwater, recharge groundwater, and prevent floods.
Q5: What is the significance of Rainwater Harvesting?
Ans: It promotes water security, reduces dependence on external water sources, and supports ecological balance.



