The Kuznets Curve is one of the most important concepts in economics used to explain the relationship between economic growth and income inequality. Proposed by economist Simon Kuznets, this theory helps policymakers understand how income distribution changes as an economy develops. Over time, the idea was also extended to environmental studies, leading to the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC).
This article explains the Kuznets Curve in detail, its relationship with income inequality, environmental implications, and criticisms.
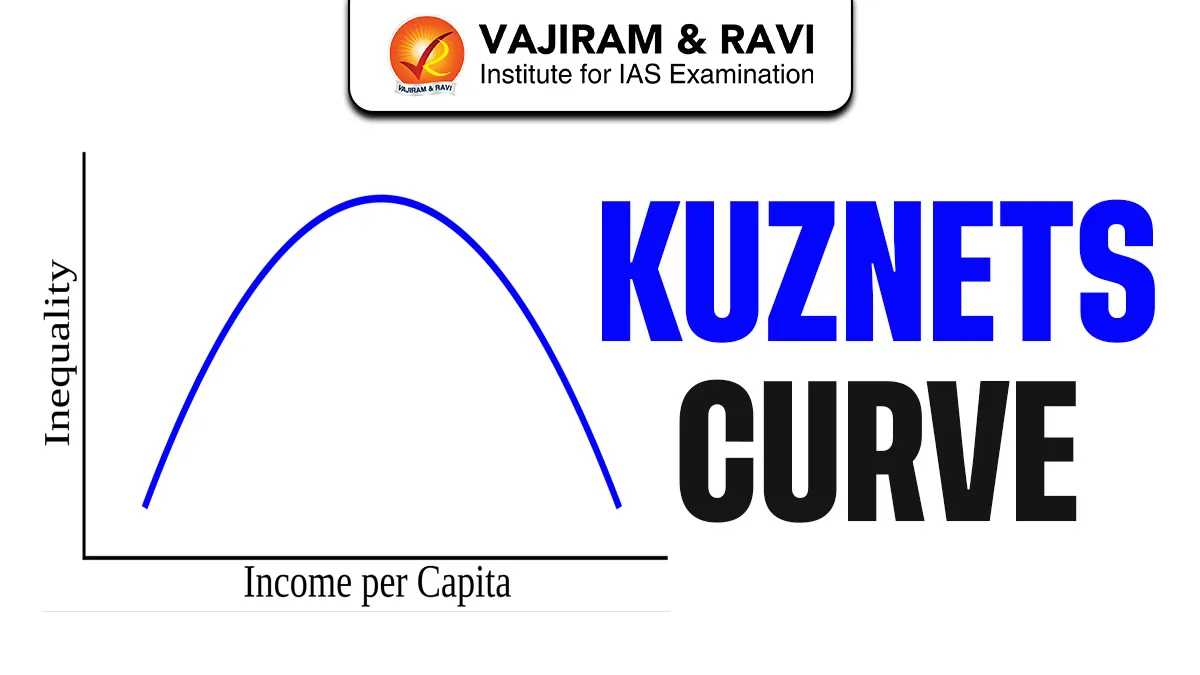
What is Kuznets Curve?
The Kuznets Curve is a theoretical model that shows an inverted U-shaped relationship between economic development and income inequality.
According to this theory, when a country begins to develop, income inequality first increases, but after reaching a certain level of economic growth, inequality starts decreasing. This happens due to structural transformation, urbanization, and better access to education and welfare policies.
Kuznets Curve and Income Inequality
The Kuznets Curve explains how income inequality changes at different stages of economic development. It suggests that inequality does not remain constant but follows a predictable pattern as an economy grows.
- The Kuznets Curve shows an inverted U-shaped relationship between economic growth and income inequality.
- In the early stage of development, income inequality is low because most people depend on
- agriculture and earn similar incomes.
- During industrialization, inequality rises as urban and industrial sectors grow faster than rural areas.
- Skilled workers and capital owners earn more, widening the income gap.
- With further development, education, welfare policies, and social security expand.
- Government intervention and economic diversification help reduce inequality.
- Thus, in the long run, income inequality declines as the economy becomes more developed and inclusive.
Environmental Kuznets Curve
- The Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) explains the relationship between economic growth and environmental degradation.
- It shows an inverted U-shaped curve, similar to the Kuznets Curve for income inequality.
- In the early stage of development, pollution increases due to industrialization and lack of environmental regulations.
- As income rises, industrial expansion and urbanization lead to higher emissions and resource exploitation.
- At higher income levels, countries adopt cleaner technologies and stricter environmental laws.
- Increased public awareness and investment in renewable energy help reduce pollution.
- Thus, environmental degradation first rises and then declines with sustained economic development.
Criticism of Kuznets Curve
The Kuznets Curve has been widely debated because it oversimplifies the relationship between economic growth and income inequality.
- The Kuznets Curve is not universally applicable, as many developing countries continue to face rising inequality despite economic growth.
- It is based on limited historical data from a few developed countries, making it less relevant for modern economies.
- The theory ignores the role of government policies, such as taxation, welfare programs, and labor laws, in reducing inequality.
- Economic growth alone does not ensure equitable income distribution; political and social factors also matter.
- Globalisation and technological change often increase income gaps, contradicting the Kuznets hypothesis.
- In many cases, inequality does not decline automatically and requires active state intervention.
Kuznets Curve FAQs
Q1: Who proposed the Kuznets Curve?
Ans: Simon Kuznets proposed the Kuznets Curve in 1955.
Q2: What does the Kuznets Curve show?
Ans: It shows the relationship between economic growth and income inequality, represented by an inverted U-shape.
Q3: What is the Environmental Kuznets Curve?
Ans: It explains the relationship between economic development and environmental degradation, suggesting pollution rises first and then falls.
Q4: Is the Kuznets Curve valid today?
Ans: Partially. It applies in some cases, but modern economies show mixed results due to policy and globalization.
Q5: Why is the Kuznets Curve important?
Ans: It helps policymakers understand how economic growth affects inequality and guides inclusive development strategies.