Kyasanur Forest Disease Latest News
A 29-year-old man in Karnataka has tragically lost his life recently after contracting Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), commonly known as monkey fever, bringing fresh attention to a disease that often goes unnoticed until it turns fatal.
About Kyasanur Forest Disease
- It is a tick-borne viral haemorrhagic disease mostly found in southern India.
- The disease was first reported from the Kyasanur Forest of Karnataka in India in 1957; hence, it is known as KFD.
- The causal agent, KFD Virus (family Flaviviridae, genus Flavivirus), is a member of the tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) complex.
- It is also known as “monkey disease/monkey fever” because of its association with monkey deaths.
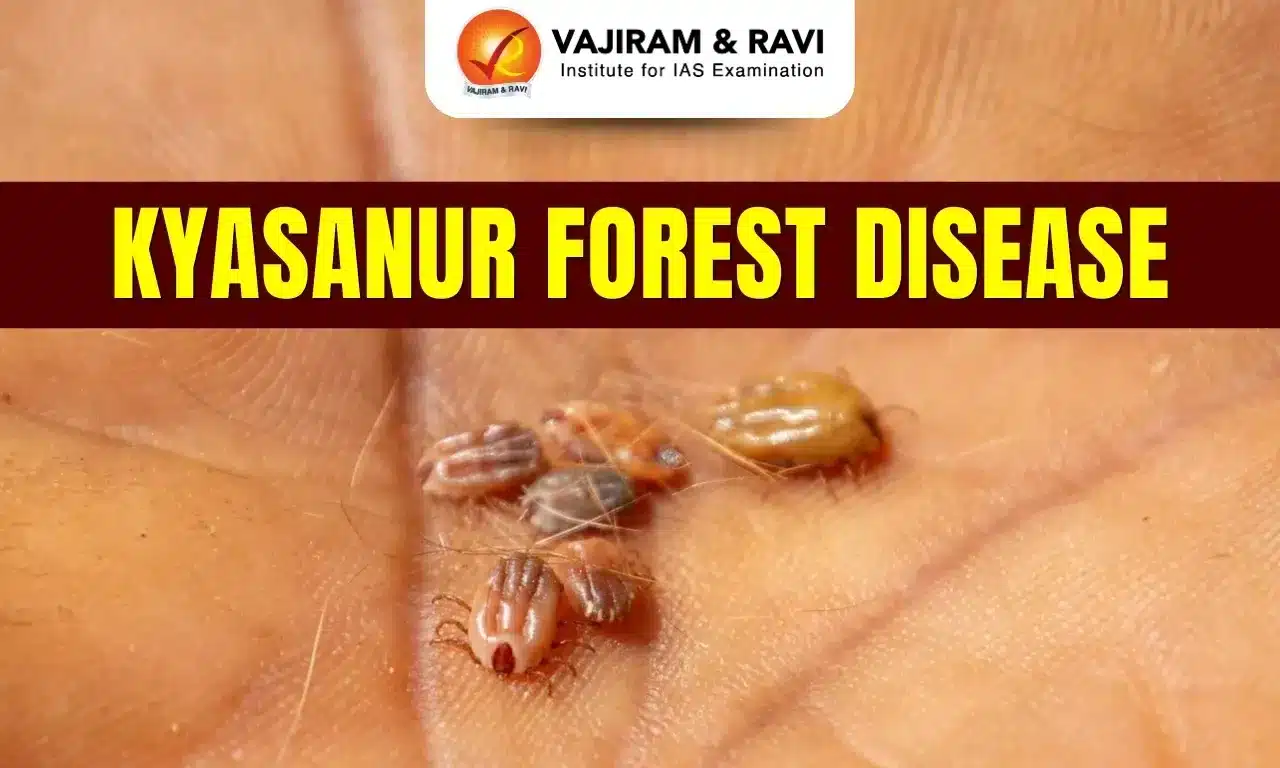
Kyasanur Forest Disease Transmission
- Hard ticks (Hemaphysalis spinigera) spread the KFD virus to people and to animals, like monkeys and rodents.
- Transmission to humans may occur after a tick bite or contact with an infected animal, most importantly a sick or recently dead monkey.
- KFD does not spread between people.
- The epidemic period usually begins in October or November and peaks from January to April, then declines by May and June.
Kyasanur Forest Disease Symptoms
- Sudden onset of high-grade fever, prostration, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and occasionally neurological and haemorrhagic manifestations.
- Between 5 and 10% of people who are known to be affected by KFD die.
Kyasanur Forest Disease Treatment
- There is no cure for KFD.
- Supportive care is crucial, including fluid balance, providing oxygen, managing blood pressure, and treating additional infections.
- With quick medical care, many patients recover from KFD without complications.
Kyasanur Forest Disease Vaccine
A vaccine for KFD is available and recommended in the parts of India where KFD is found.
Source: TOI
Kyasanur Forest Disease FAQs
Q1: What is Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD)?
Ans: It is a tick-borne viral haemorrhagic disease found mainly in southern India.
Q2: Where was Kyasanur Forest Disease first reported?
Ans: In the Kyasanur Forest of Karnataka.
Q3: Why is Kyasanur Forest Disease also called “monkey disease” or “monkey fever”?
Ans: Because it is associated with deaths of monkeys.
Q4: Which vector transmits Kyasanur Forest Disease?
Ans: Hard ticks, mainly Hemaphysalis spinigera.
Q5: Can Kyasanur Forest Disease spread from person to person?
Ans: No, it does not spread between humans.