Molybdenum Disulfide Latest News
Scientists recently developed an electronic system using molybdenum disulphide only a few atoms thick; high-energy particles pass through it without causing damage.
About Molybdenum Disulfide
- Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is an inorganic compound made up of sulfur and molybdenum.
- It exists in nature in the mineral molybdenite.
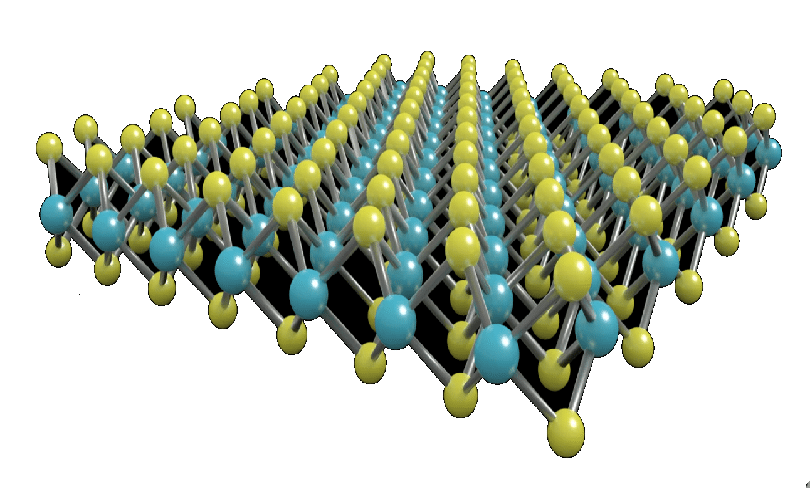
- In its bulk form, it appears as a dark, shiny solid.
- It belongs to a class of materials called 'transition metal dichalcogenides' (TMDCs).
- Materials in this class have the chemical formula MX₂, where M is a transition metal atom (groups 4-12 in the periodic table) and X is a chalcogen (group 16).
- Its crystals have a hexagonal layered structure that is similar to graphite.
- Like most mineral salts, MoS2 has a high melting point, but it begins to sublime at a relatively low 450 ºC. This property is useful for purifying the compound.
- Because of its layered structure, hexagonal MoS2, like graphite, is an excellent solid lubricant.
- It can be used as surface coatings on machine parts (e.g., in the aerospace industry), in two-stroke engines (the type used for motorcycles), and in gun barrels (to reduce friction between the bullet and the barrel).
- Unlike graphite, MoS2 does not depend on adsorbed water or other vapors for its lubricant properties.
- It can be used at temperatures as high as 350 ºC in oxidizing environments and up to 1100 ºC in nonoxidizing environments.
- Its stability makes it useful in high-temperature applications in which oils and greases are not practical.
- MoS2 is highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion, making it an effective lubricant for high-humidity and saltwater environments.
- In addition to its lubricating properties, MoS2 is a semiconductor.
Source: TH
Molybdenum Disulfide FAQs
Q1: What is molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂)?
Ans: Molybdenum disulfide is an inorganic compound composed of molybdenum and sulfur.
Q2: In which mineral form does molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) occur naturally?
Ans: It occurs naturally as the mineral molybdenite.
Q3: To which class of materials does molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) belong?
Ans: MoS₂ belongs to the transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) class.
Q4: What is the crystal structure of molybdenum disulfide?
Ans: MoS₂ has a hexagonal layered crystal structure, similar to graphite.
Q5: Why is molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) an effective solid lubricant?
Ans: Its layered structure allows easy sliding of layers, reducing friction.