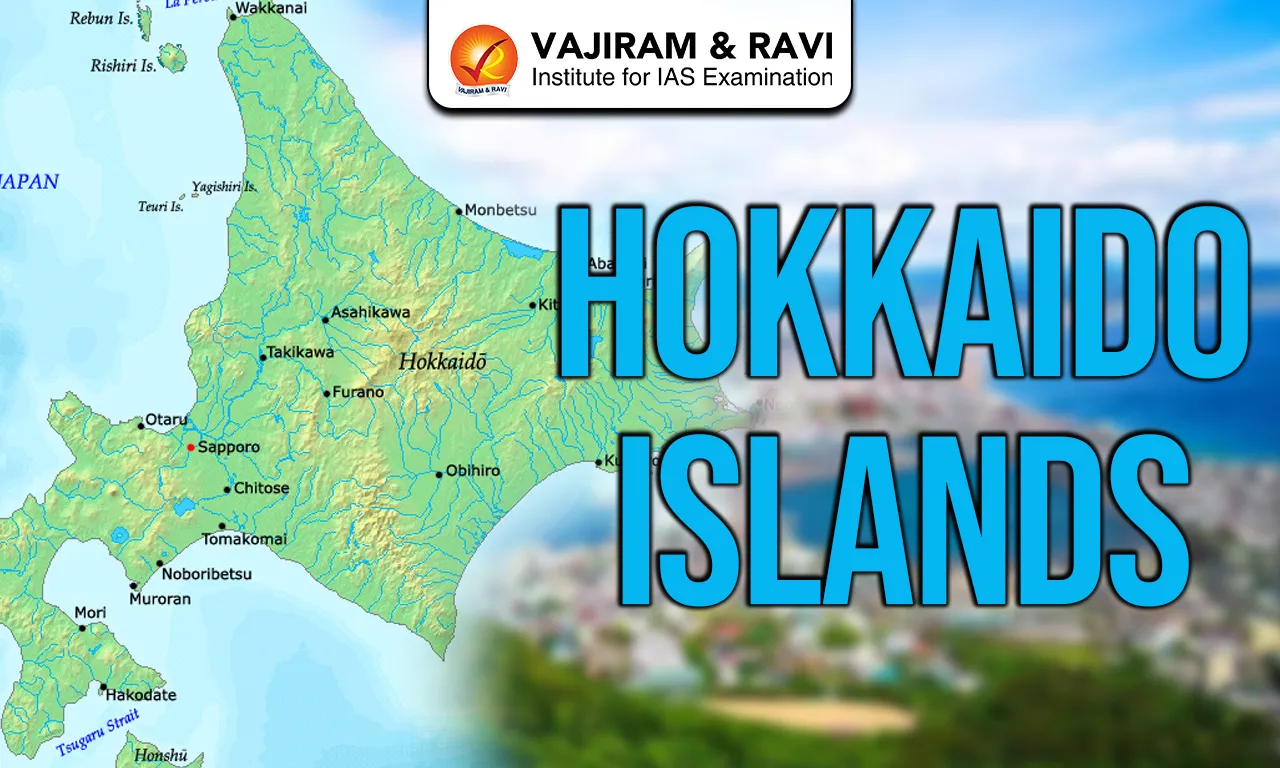
Hokkaido Islands are Japan’s northernmost and second largest island, covering 83,423.84 km² and ranking 21st globally by area. It lies north of Honshu, separated by the Tsugaru Strait and close to Russia across the La Pérouse Strait. The island is bordered by the Sea of Japan to the west, the Sea of Okhotsk to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the east and south. Sapporo City is located on the Ishikari River and serves as the administrative headquarters. Hokkaido forms a key part of the Japanese Archipelago.
Also Read: Lakshadweep Islands
Hokkaido Islands Features
The major highlighting features of the Hokkaido Islands have been listed below:
- Position in Japanese Archipelago: Hokkaido is the northernmost of Japan’s five main islands within the 14,125 Islands of the Japanese Archipelago.
- Location: It lies near Russia’s Sakhalin Oblast and forms the northern arc of Japan’s island chain stretching over 3,000 km.
- Surrounding Water Bodies: The island is bordered by the Sea of Japan in the west, the Sea of Okhotsk in the north and the Pacific Ocean in the east and south. Key straits include Tsugaru Strait, La Pérouse Strait and Nemuro Strait.
- Area and Relief: With 83,423.84 km² area, it is Japan’s second largest island. The interior is mountainous with volcanic plateaux. Major plains include Ishikari 3,800 km², Tokachi 3,600 km², Kushiro 2,510 km² and Sarobetsu 200 km².
- Rivers: The Ishikari River flows through Sapporo city of Hokkaido.
- Wetlands: Kushiro Wetland is Japan’s largest wetland and a Ramsar site since 1980. Other wetlands include Lake Utonai and Lake Akkeshi.
- Climate: Hokkaido has a sub arctic climate with 8°C annual average temperature and 1,150 mm rainfall. January averages -9°C in Asahikawa; August averages 21°C. Snowfall reaches 11 metres in western mountains.
- Recent Climate Change: In April 2024, Sapporo recorded 26°C, its earliest summer day. Japan’s temperature has risen 1.28°C per century since 1898. Sea ice in the Sea of Okhotsk has reduced thickness by 30% in 30 years.
- Biodiversity: The island has three lineages of Ussuri brown bear, Asia’s largest population outside Russia. Species include Steller’s sea eagle, Yezo sika deer, Ezo red fox and Sakhalin fir.
- Geological Activity: Major earthquakes include 7.7 magnitude in 1993, 8.3 in 2003, 6.6 in 2018 and 6.1 in 2021.
- Volcano: Active volcanoes include Mount Usu, Mount Tokachi and Mount Meakan.
Also Read: Indian Islands
Hokkaido Islands FAQs
Q1: Where are the Hokkaido Islands located?
Ans: Hokkaido is the northernmost main island of Japan, located near Russia’s Sakhalin. It is separated from Honshu by the Tsugaru Strait and bordered by the Sea of Japan, Sea of Okhotsk and the Pacific Ocean.
Q2: What is the total area of the Hokkaido Islands?
Ans: Hokkaido covers 83,423.84 square kilometres, making it the second largest island of Japan and ranking 21st largest island in the world by area.
Q3: What type of climate does the Hokkaido Islands have?
Ans: Hokkaido has a sub arctic climate with an average annual temperature of 8°C and annual precipitation of about 1,150 mm. Winters are snowy and temperatures in January can fall to -9°C in central areas.
Q4: Why is the Hokkaido Islands important for biodiversity?
Ans: Hokkaido hosts three distinct lineages of Ussuri brown bears and has Asia’s largest brown bear population outside Russia. It also supports species like Steller’s sea eagle and Yezo sika deer.
Q5: What recent climate change trend has been observed in the Hokkaido Islands?
Ans: In April 2024, Sapporo recorded 26°C, its earliest summer day. Sea ice in the Sea of Okhotsk has lost about 30% thickness over the past 30 years.