Kamchatka Earthquake 2025 Latest News
- A powerful 8.8 magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula, leading to widespread tsunami warnings across the Pacific.
- The quake, centered 119 km southeast of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky at a shallow depth of 19.3 km, was initially reported as 8.0 but later upgraded. It was followed by a strong 6.9 aftershock.
- This marks the strongest global quake since Japan’s devastating 9.0 magnitude earthquake in March 2011 that triggered the Fukushima nuclear disaster.
Understanding Earthquake Magnitude and Measurement
- The 8.8 magnitude earthquake off Kamchatka is classified as a great earthquake, a rare event globally.
- According to the US Geological Survey (USGS), earthquakes of this scale release immense energy — with each whole-number increase in magnitude corresponding to roughly 31.6 times more seismic energy.
- For instance, the Kamchatka quake released over 30 times more energy than Myanmar’s 7.7 magnitude quake in March 2024.
- While “magnitude” refers to the measured energy released by an earthquake, “intensity” describes the perceived shaking at specific locations.
- Earthquake movements are recorded using a seismograph, which tracks the relative motion between the Earth’s surface and a suspended mass to determine seismic activity.
Kamchatka: A High-Risk Seismic Zone
- The Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia’s Far East is one of the world’s most earthquake-prone regions.
- This 1,250-km landmass has witnessed several powerful quakes in recent history — including those in 2020, 2006, 1959, 1952, and 1923 — many of which triggered tsunamis.
- Historical accounts also mention similar events in 1841 and 1737.
Frequent Earthquakes Fuelled by Tectonic Plate Movements
- The region’s high seismic activity is due to the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the Okhotsk microplate.
- Subduction is a geological process where a denser tectonic plate slides beneath a lighter one, causing stress at plate boundaries.
- This stress, when released, results in earthquakes.
- The Himalayas were formed by the Indian plate pushing under the Eurasian plate through subduction, making the region highly earthquake-prone.
- This tectonic interaction forms the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench, which reaches depths of nearly 10 km.
- As the Pacific Plate descends at a rate of around 86 mm per year, stress builds up along the megathrust fault line, periodically releasing as massive earthquakes and resulting tsunamis in the North Pacific.
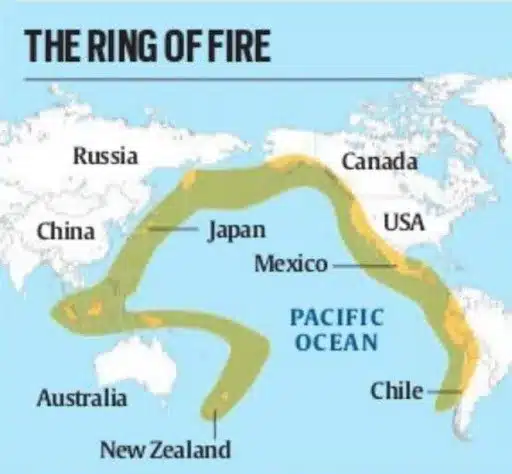
Kamchatka and the Pacific Ring of Fire
- The Kamchatka Peninsula is part of the Pacific Ocean’s Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped belt of intense seismic and volcanic activity encircling the Pacific Plate.
- Stretching over 40,000 km, this zone marks the boundaries of multiple tectonic plates — including the Eurasian, North American, Indian, Australian, and others — making it one of the most geologically active regions on Earth.
- The Ring of Fire spans more than 15 countries, including Russia, Japan, Indonesia, the US, Chile, and the Philippines, all of which frequently experience earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis due to constant tectonic movements.
Tectonic Forces Behind the Ring of Fire
- The intense seismic and volcanic activity in the Ring of Fire is driven by constant tectonic plate movement.
- Plates frequently slide past, collide, or subduct beneath one another.
- When rough plate edges get stuck while the rest of the plate continues moving, stress builds up until it suddenly releases, causing an earthquake — as seen in the recent Kamchatka quake and tsunami.
- Volcanoes in this zone also form due to subduction, where a denser plate sinks beneath a lighter one, creating deep ocean trenches and magma build-up that fuels eruptions.
Global Earthquake Zones and Their Impact
- The Circum-Pacific Belt (Ring of Fire) is Earth’s most active seismic zone, generating around 80% of major earthquakes.
- The second-most active is the Alpide Belt, stretching from Indonesia through the Himalayas to Turkey, contributing 15–17% of quakes.
- Though less active, it runs through densely populated regions, making its quakes more deadly.
- E.g., the sparsely populated Kamchatka Peninsula, despite facing a powerful 8.8 quake, saw no casualties, unlike Nepal’s 7.6 magnitude quake in 2015 that killed over 15,000.
- The third major zone, the mid-Atlantic ridge, lies deep underwater and causes moderate, less impactful quakes.
- Earthquake strength is also influenced by faultline length; a magnitude 9.5 quake is likely the upper limit, as no faultline spans the Earth to enable a stronger quake.
Last updated on January, 2026
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 Postponed for CSE & IFS which was scheduled to be released on 14 January 2026.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Kamchatka Earthquake 2025 FAQs
Q1. What caused the Kamchatka earthquake?+
Q2. What is the Ring of Fire?+
Q3. Why is Kamchatka vulnerable?+
Q4. What is earthquake magnitude vs. intensity?+
Q5. How are earthquakes measured? +
Tags: Kamchatka earthquake 2024 mains articles upsc current affairs upsc mains current affairs