The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is the world’s largest development agency within the United Nations system. It works in 177 countries to reduce poverty, strengthen democratic institutions, support crisis recovery, and promote sustainable development. UNDP plays a leading role in helping nations work toward the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), while focusing on fairness, human dignity, and long-term growth. Established in 1965, the organisation remains central to global development efforts.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) was formed on 22 November 1965 and continues to serve as a key international actor in development cooperation. It provides technical expertise, financial assistance, and policy support to developing nations. Its mandate covers poverty reduction, crisis prevention, democratic governance, environmental sustainability, and development financing. UNDP works closely with governments, civil society, international institutions, and private partners to deliver development results. Its programmes ensure that development is inclusive, resilient, and sustainable.
Also Read: United Nations Environment Programme
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Historical Background
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) emerged from the merger of the Expanded Programme of Technical Assistance (EPTA) and the UN Special Fund.
- EPTA, formed in 1949, focused on economic assistance and capacity building for developing countries.
- The Special Fund, created in 1958, aimed to prepare nations for long-term development by supporting large-scale technical projects.
- The merger was recommended by the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) to reduce duplication of tasks and make development support more systematic.
- By 1966, the merger was complete, and the UNDP began functioning as the primary global development agency of the UN.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Purpose
UNDP’s core mandate is to help countries eliminate poverty, reduce inequality, and achieve sustainable human development. It also focuses on building local capacity so that nations can eventually manage development independently. UNDP assists countries in planning economic strategies, improving governance systems, and strengthening institutions. It also supports countries during crises such as natural disasters, conflicts, and public health emergencies. UNDP’s work is closely linked with the SDGs and international development frameworks.
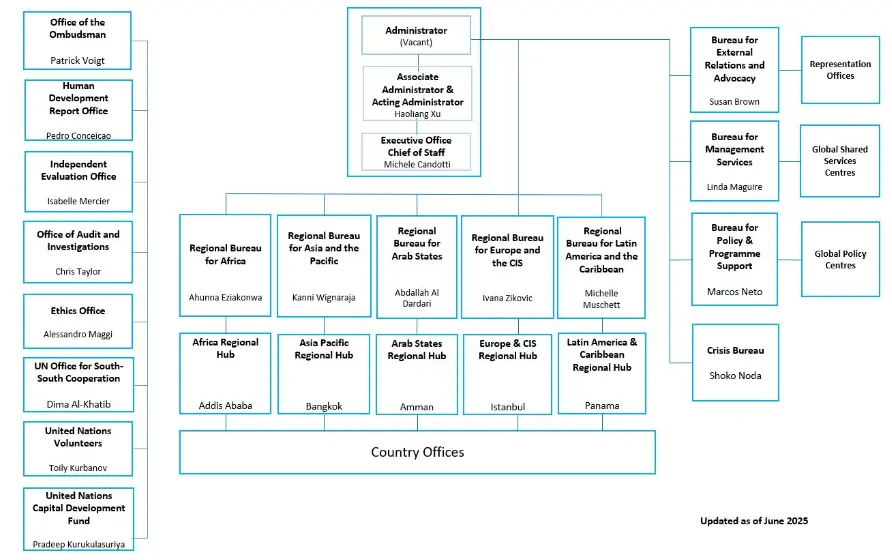
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Organizational Structure
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is headquartered in New York City and operates through a network of country offices. It is led by an Administrator who holds the rank of Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations. The Administrator oversees a global workforce and supervises regional bureaus that manage development programmes across continents. As of 2025, Haoliang Xu is serving as the Acting Administrator. UNDP employs 7,394 staff worldwide (2022).
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Global Presence
UNDP works in 177 countries and territories, making it the largest development assistance agency in the UN system. Country offices collaborate directly with national governments to design policies, prepare development frameworks, and execute long-term programmes.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Budget
UNDP is financed entirely through voluntary contributions from UN member states. It does not receive funding through compulsory UN assessments. Funding includes core contributions and earmarked resources for specific programmes. United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)’s total budget in 2022 was US$6.73 billion. UNDP has been rated highly for financial transparency and ranked first in the Aid Transparency Index (2015, 2016) with a score of 93.3%.
Also Read: International Labour Organisation
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Areas of Work
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) focuses on five main development challenges. These areas guide its country-level and global operations.
- Democratic Governance: UNDP supports democratic transitions by improving electoral systems, strengthening public institutions, and promoting citizen participation. It offers technical support for elections, public administration reforms, anti-corruption frameworks, and inclusive governance systems. Many countries rely on UNDP for training officials, improving public service delivery, and creating mechanisms for accountability.
- Poverty Reduction: Poverty reduction is central to UNDP’s mission. It helps countries design policies that widen access to economic opportunities, promote financial inclusion, and strengthen social protection systems. UNDP also assists in reforming trade, promoting debt relief, and attracting investment to boost local economies. A 2013 independent evaluation noted that UNDP effectively supported national poverty programmes but required stronger monitoring mechanisms.
- Crisis Prevention and Recovery: UNDP’s crisis-related work includes conflict prevention, disaster management, and peacebuilding. It supports countries in early recovery, demobilization of ex-combatants, reintegration of displaced communities, and restoration of essential services. During humanitarian crises, UNDP often works alongside UN agencies to stabilize governance and rebuild infrastructure. After foreign aid to Afghanistan was suspended in 2021, UNDP funded 25,000 health workers to maintain essential health services.
- Environment and Energy: UNDP addresses climate change, biodiversity loss, land degradation, renewable energy access, and pollution control. It supports countries in transitioning to clean energy, managing natural resources responsibly, and protecting ecosystems. Key environmental programmes include:
-
- BIOFIN (Biodiversity Finance Initiative)- works in 30 countries to develop biodiversity financing plans.
- Equator Prize- recognizes local communities protecting biodiversity.
- Sustainable land and water management initiatives across Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
- HIV/ AIDS Response: UNDP works on reducing HIV impact through awareness programmes, policy reforms, and strengthening health systems. The Global Commission on HIV and the Law (2012) is a major initiative supported by UNDP to improve the legal environment for people affected by HIV.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Initiatives
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) runs several global programmes to drive innovation and collaboration:
- Human Development Report (since 1991)- Introduced the Human Development Index (HDI) which measures development beyond income.
- World Alliance of Cities Against Poverty
- ART Global Initiative
- Territorial Approach to Climate Change
- Global Policy Centres in Seoul, Nairobi, Oslo, Singapore, and Istanbul
United Nations Development Programme and SDGs
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is the custodian agency for several SDG indicators and plays an integrating role within the UN system to coordinate SDG implementation. It supports countries in preparing SDG frameworks, aligning national budgets, and strengthening data systems. UNDP’s support is essential for countries that struggle with institutional capacity or financial challenges.
United Nations Development Programme and UN Coordination
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) serves as the Vice-Chair of the UN Sustainable Development Group (UNSDG). It works through the Resident Coordinator (RC) System to ensure all UN agencies collaborate effectively at the country level.
- Resident Coordinators operate in over 130 countries.
- They lead joint UN efforts, ensure unified planning, and coordinate humanitarian and development assistance.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Innovations
Launched in 2014, the Innovation Facility supports creative development solutions. It offers seed funding, digital tools, and technical expertise. In 2015, it supported 62 initiatives across 45 countries, contributing to 16 SDGs. Its innovation labs test artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data systems for development challenges.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Controversies
UNDP has faced several allegations over the years. These incidents highlighted internal weaknesses, whistleblower protection issues, and governance challenges. These include:
- NSA surveillance exposure (2013): Documents revealed UNDP emails were monitored by international intelligence agencies.
- Gaza Project Allegations (2016) involving claims of resource misuse.
- North Korea Financial Irregularities reported by former staff.
- Russia GEF Project Corruption (2010-2014) where misappropriation of funds was alleged.
- Iraq Stabilization Fund Corruption Scandal (2024) involving 136 reported corruption cases.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Challenges
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) faces numerous operational, financial, and structural challenges while working globally. The following are the major concerns and recommended solutions:
- Dependence on voluntary contributions, leading to unpredictable funding.
- Weak accountability mechanisms in crisis-hit and fragile states.
- Difficulty in monitoring outcomes in long-term development projects.
- Governance and corruption allegations affecting credibility.
- Slow bureaucratic procedures delaying implementation.
- Challenges in whistleblower protection, as observed in recent scandals.
- Climate change complexities making adaptation and mitigation expensive.
- Increasing geopolitical tensions affecting development work.
Way Forward:
- Introduce stronger financial oversight mechanisms, especially in fragile states.
- Strengthen digital monitoring systems to track project outcomes in real time.
- Enhance whistleblower protection policies to ensure transparency.
- Diversify funding sources to reduce reliance on a few donors.
- Promote climate financing partnerships with private and public actors.
- Simplify internal procedures for faster project delivery.
- Expand capacity-building programmes for national institutions.
- Improve community-level participation to ensure sustainable results.
United Nations Development Programme in India
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has operated in India since 1951, working on governance, livelihoods, energy, disaster resilience and inclusion. UNDP-India supports national priorities such as poverty alleviation, climate action, gender equality and strengthening institutions to deliver public services. Recent UNDP-India work includes support for state-level climate planning, social protection design, and data systems that underpin SDG tracking.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) UPSC
UNDP remains one of the most influential actors in global development. For more than six decades, it has supported developing nations through poverty eradication, governance reforms, crisis recovery, and environmental sustainability. While the organisation faces stiff challenges related to funding, corruption allegations, and operational limitations, its global presence and technical expertise continue to make it indispensable. Strengthening internal governance and building more transparent systems will further enhance United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)’s impact in the coming decades.
To deliver on the SDGs and respond to emerging shocks, UNDP’s priorities include: scaling climate-resilient development, deepening impact in fragile contexts, expanding data and digital systems for better policy making, and mobilizing blended finance for SDG investments. Increasing core funding and improving country-level partnerships will be crucial so UNDP can remain agile and catalytic, helping governments secure equitable, resilient development pathways.
Last updated on February, 2026
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is Out on the official website at upsc.gov.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
United Nations Development Programme FAQs
Q1. What is the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)?+
Q2. When was United Nations Development Programme established?+
Q3. What are the main focus areas of United Nations Development Programme?+
Q4. What is the Human Development Report released by United Nations Development Programme?+
Q5. How does United Nations Development Programme support countries like India?+
Tags: united nations development programme united nations development programme (undp)