Bioremediation Latest News
- India is witnessing an urgent environmental crisis triggered by decades of unchecked waste generation, industrial pollution, pesticide accumulation, oil spills, and heavy-metal contamination.
Understanding Bioremediation
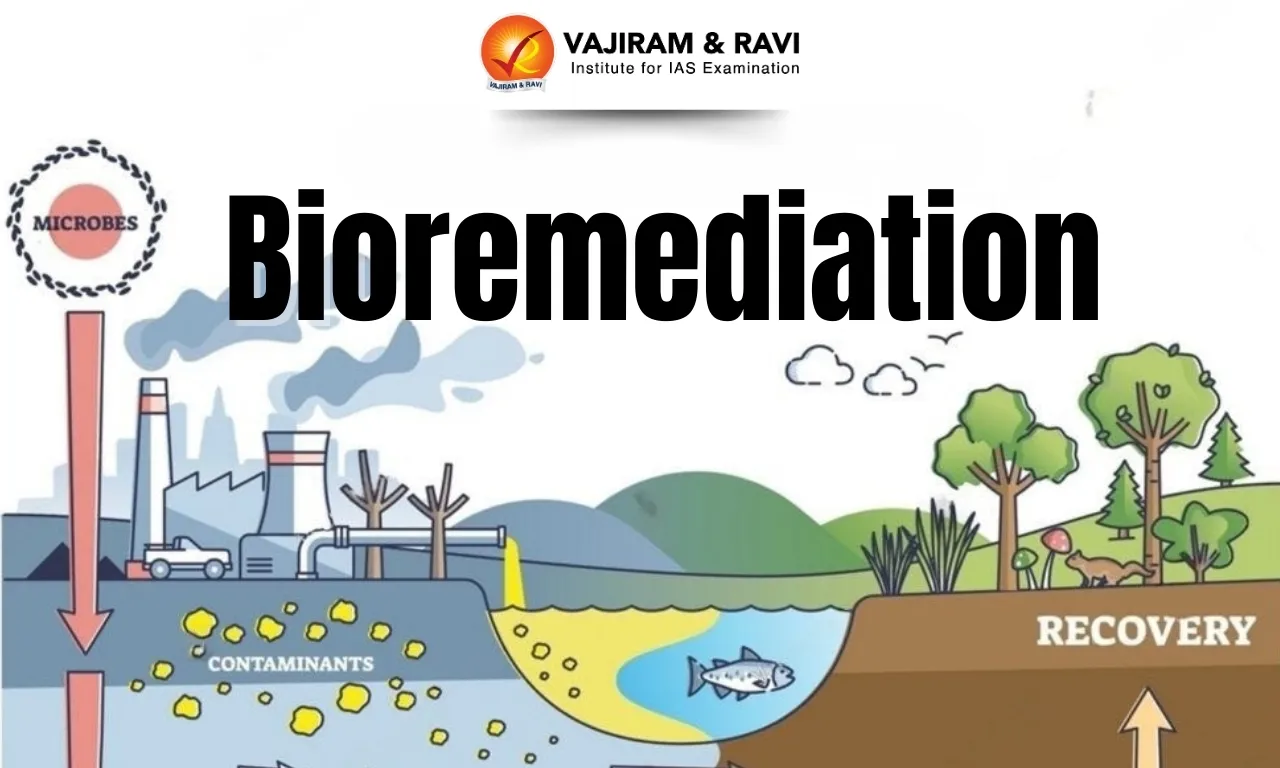
- Bioremediation literally means “restoring life through biology.” It relies on naturally occurring or engineered microorganisms, bacteria, fungi, algae, or plants to break down dangerous pollutants into harmless by-products.
- These pollutants range from oil and pesticides to plastics and toxic heavy metals.
- Microbes metabolise pollutants as food, converting them into water, carbon dioxide, or organic acids, while certain organisms transform metals into safer, non-leaching forms.
Types of Bioremediation Techniques
- In Situ Bioremediation
- Treatment occurs directly at the contaminated site.
- Examples include oil-eating bacteria deployed over ocean spills.
- Ex Situ Bioremediation
- Contaminated soil or water is removed, treated in a facility, and then returned.
- This approach allows controlled treatment for complex pollutant mixtures.
- Modern bioremediation blends traditional microbiology with advanced biotechnology, enabling precise identification of biomolecules and replication of microbes tailored for specific environments like sewage systems or agricultural fields.
- Synthetic biology has introduced:
- GM microbes for tough pollutants such as plastics and oil residues,
- Biosensing organisms that change colour or fluoresce when detecting toxins, aiding early warnings and monitoring.
Urgent Need for Bioremediation in India
- India’s rapid industrialisation and urbanisation have come with steep environmental costs.
- Heavily polluted rivers like the Ganga and Yamuna, untreated sewage, toxic effluents, oil leaks, pesticide residues, and heavy metals have created widespread ecological degradation.
- Traditional clean-up systems, thermal treatments, chemical neutralisation, and mechanical extraction are expensive, energy-intensive, and often produce secondary pollution.
- Bioremediation stands out as a cost-effective, scalable, and environmentally sustainable alternative, especially critical for a country dealing with:
- Large polluted land areas,
- Limited resources for remediation,
- Dense urban centres are overwhelmed by waste.
- India’s natural biodiversity gives it an additional advantage. Indigenous microbes adapted to extreme environments (heat, salinity, acidity) can outperform imported strains in cleaning local contamination.
India’s Current Progress in Bioremediation
- India’s bioremediation ecosystem is growing but remains mostly at the pilot-project stage. Key developments include:
- Government-Led Initiatives
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) supports bioremediation projects through its Clean Technology Programme, encouraging partnerships between universities, research institutes, and industries.
- The CSIR–NEERI has a mandate to develop and implement bioremediation programmes nationwide.
- Research Innovations
- IIT researchers created a nanocomposite material from cotton to clean oil spills.
- Scientists have identified bacteria capable of degrading soil pollutants.
- Start-up Participation
- Companies now offer microbial formulations for cleaning wastewater and soil, indicating growing commercial adoption.
Global Trends in Bioremediation
- Japan uses plant- and microbe-based systems in urban waste strategies.
- The European Union funds multinational collaborations for oil spill clean-up and mining land restoration.
- China applies engineered bacteria to restore industrial wastelands under its soil pollution control programme.
- These global examples underline how bioremediation can be mainstreamed in national environmental management.
Opportunities for India
- India has immense opportunities to integrate bioremediation into:
- River rejuvenation (e.g., Namami Gange), Sewage treatment infrastructure, Land reclamation, Industrial clean-up missions.
- Beyond environmental benefits, bioremediation can create jobs in:
- Biotechnology research, Waste management, Environmental consulting, Local start-up ecosystems.
Risks and Regulatory Challenges
- Bioremediation also carries risks, especially when using genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- Poor containment or inadequate testing can harm ecosystems. India currently faces:
- A lack of unified national standards for bioremediation, Insufficient site-specific data, Weak biosafety guidelines, and Limited trained personnel.
Way Forward
- Creating national bioremediation standards and certification systems,
- Building regional bioremediation hubs linking universities, industries, and local governments,
- Supporting start-ups under the DBT-BIRAC ecosystem,
- Engaging communities to dispel myths and build acceptance of microbial clean-up technologies.
Source: TH
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Bioremediation FAQs
Q1. What is bioremediation?+
Q2. Why is bioremediation important for India?+
Q3. Which organisations are leading bioremediation research in India?+
Q4. What are the major types of bioremediation?+
Q5. What risks does bioremediation pose?+
Tags: bioremediation mains articles upsc current affairs upsc mains current affairs