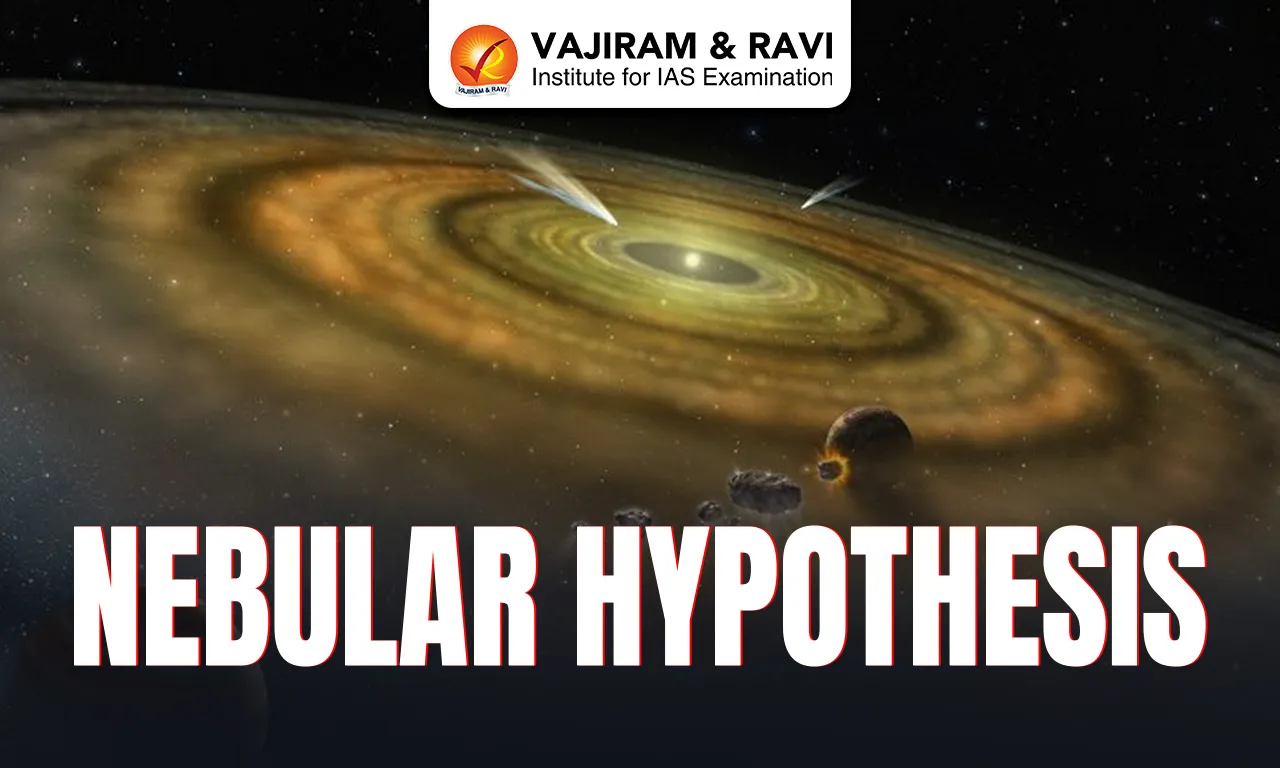
The Nebular Hypothesis is one of the earliest scientific theories that explains how the Solar System was formed. It describes how the Sun, planets, and other celestial bodies developed from a massive cloud of gas and dust called a nebula. This theory was first proposed by philosophers and scientists like Immanuel Kant and Pierre-Simon Laplace in the 18th century. Even today, it forms the base of modern theories related to planetary formation.
What is Nebula?
A nebula is a large cloud of gas, dust, and other cosmic particles found in outer space. These clouds are often considered the birthplace of stars and planetary systems.
Nebulae are mainly made of hydrogen and helium gases, along with small amounts of other elements. They are formed when stars explode or when gas and dust gather together due to gravitational forces. Some nebulae glow because of nearby stars, while others appear dark because they block light.
Also Read: Star Formation
Nebular Hypothesis of Kant
The Nebular Hypothesis of Kant was proposed by Immanuel Kant, a German philosopher, in 1755. He suggested that the Solar System was formed from a large rotating cloud of gas and dust.
- Kant believed that the universe was originally made of cold, solid, and unmoving particles.
- These particles collided due to gravitational force, which produced heat and started motion.
- The motion created angular momentum, causing the particles to rotate.
- Gradually, this rotating mass developed into a hot nebula.
- As the nebula rotated faster, it generated centrifugal force, which led to the formation of rings of matter.
- These rings cooled down and eventually formed planets and satellites.
- Kant accepted the existence of primordial matter, but he did not explain where this matter originated.
- He also failed to explain the source of energy that caused the particles to start moving.
Nebular Hypothesis of Laplace
The Nebular Hypothesis of Laplace was introduced by French mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace in 1796. He expanded Kant’s ideas and gave a more detailed explanation of planetary formation.
- Pierre-Simon Laplace expanded Kant’s theory and suggested that the nebula was made of gases instead of solid particles.
- He believed that all celestial bodies, including the Sun, planets, stars, and asteroids, were formed from a nebula cloud.
- Initially, there was a massive cloud made of hydrogen, helium, and dust particles, similar in size to the present Solar System.
- As the nebula rotated rapidly, lighter gases like hydrogen and helium moved toward the centre.
- Continuous collisions among gases led to fusion reactions, which formed the Sun.
- Heavier elements moved away from the centre, which resulted in the formation of planets.
- The Sun mainly consists of lighter elements, while planets are made of heavier materials.
- The planets later formed smaller nebulas around them.
- Continuous rotation, friction, and fusion led to the development of a disk-shaped cloud, forming planets and satellites.
Nebular Hypothesis of Laplace Criticism
- Laplace did not explain the origin of the nebula, including the source of its heat and motion.
- The theory failed to clarify why the nebula produced a specific number of rings and planets.
- It is difficult to believe that an entire ring of matter could condense into a single planet.
- According to dynamical theory, rings would likely break into several pieces, forming multiple planets.
- Due to weak cohesion among nebula particles, ring formation should have been continuous, not occasional as suggested by Laplace.
- If the Sun was the remaining centre of the nebula, it should show a bulge at the equator, but such a bulge is not observed.
- If planets formed from nebula gases, they should initially exist in liquid form, which would make stable rotation and revolution difficult.
- Only solid bodies can maintain stable orbits and shapes during rotation.
- According to the theory, all satellites should rotate in the same direction as their planets, but some satellites of Jupiter and Saturn rotate in opposite directions.
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Nebular Hypothesis FAQs
Q1. What is the Nebular Hypothesis?+
Q2. Who proposed the Nebular Hypothesis?+
Q3. What is a nebula?+
Q4. How did Kant explain the origin of the Solar System?+
Q5. How did Laplace modify Kant’s theory?+
Tags: nebular hypothesis