About is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
- CCS refers to a host of different technologies that capture CO2 emissions from large point sources like refineries or power plants and trap them beneath the Earth.
- Notably, CCS is different from carbon dioxide removal (CDR), where CO2 is removed from the atmosphere.
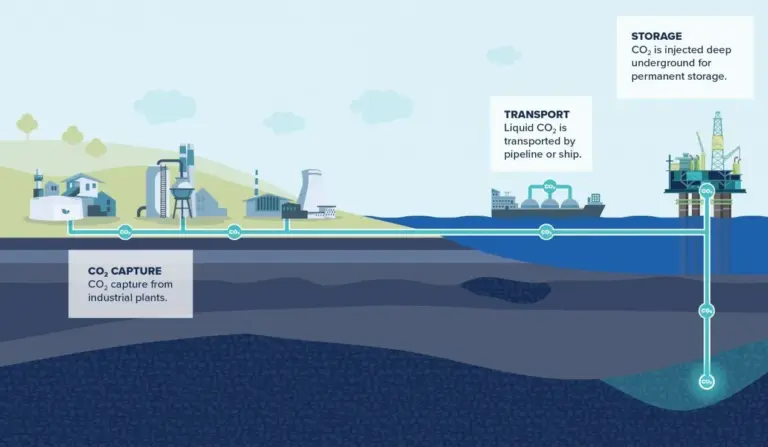
- It’s a three-step process, involving: capturing the carbon dioxide produced by power generation or industrial activity, such as steel or cement making; transporting it; and then storing it deep underground.
- CCS involves three different techniques of capturing carbon, including post-combustion, pre-combustion, and oxyfuel combustion.
- In post-combustion, CO2 is removed after the fossil fuel has been burnt. By using a chemical solvent, CO2 is separated from the exhaust or ‘flue’ gases and then captured.
- Pre-combustion involves removing CO2 before burning the fossil fuel. “First, the fossil fuel is partially burned in a ‘gasifier’ to form synthetic gas. CO2 can be captured from this relatively pure exhaust stream. The method also generates hydrogen, which is separated and can be used as fuel.
- In oxyfuel combustion, the fossil fuel is burnt with almost pure oxygen, which produces CO2 and water vapour. The water is condensed through cooling, and CO2 is separated and captured.
- Out of the three methods, oxyfuel combustion is the most efficient, but the oxygen burning process needs a lot of energy.
- After capture, CO2 is compressed into a liquid state and transported to suitable storage sites.
- Possible storage sites for carbon emissions include saline aquifers or depleted oil and gas reservoirs.
- There are also only a few operational CCS projects across the world, even though the technology has been pushed for decades.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), there were 40 operational CCS projects in 2023, which captured more than 45 metric tonnes (Mt) of CO2 annually.
Q1) What is syngas?
Syngas, also called a synthesis gas, is a mix of molecules containing hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, water vapours, as well as other hydrocarbons and condensable compounds. It is a main product of gasification and majority product of high temperature pyrolysis carried on any biomass, residues and waste. When produced in pyrolysis, it is created by the vaporisation of volatile compounds from the raw material thanks to the heat, which induces a set of complex reactions.
Source: Warming up to climate change: What is carbon capture and can it help save the planet?
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India