The China Type Climate, also known as the Warm Temperate Eastern Margin Climate, is one of the world’s major climatic types characterized by hot, humid summers and cool, dry winters. This climate type plays a vital role in shaping the geography, vegetation, and economy of eastern Asia, especially in China, Korea, and Japan.
China Type Climate
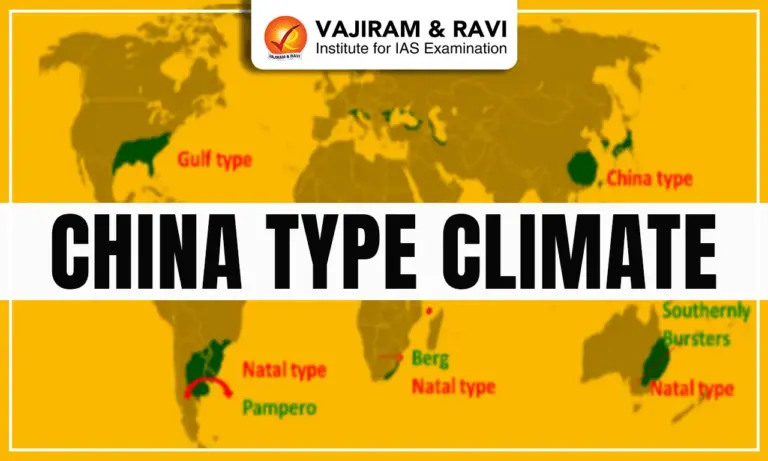
The China Type Climate lies along the eastern coasts of continents between 20° and 35° latitudes in both hemispheres. It is influenced by monsoonal winds, with the summer monsoon bringing heavy rainfall from the ocean and the winter monsoon bringing dry, cold air from inland areas. The climate is often described as subtropical monsoon climate in Asia.
China Type Climate Distribution
The China Type Climate is found mainly in eastern margins of continents in the warm temperate belt. This distribution shows that while the climate is named after China, it has global presence in both hemispheres due to similar latitude and oceanic influence.
Major regions include:
- Asia: Eastern China, Taiwan, South Korea, Southern Japan
- North America: Southeastern USA (North Carolina, Georgia, Florida)
- South America: Southeast Brazil, Uruguay
- Australia: Southeastern coastal areas (New South Wales, Queensland)
Read About: Equatorial Climate
China Type Climate Map
The China Type Climate Map highlights the regions lying between 20°N and 35°N latitudes along the eastern continental margins. It includes eastern and southern China, Korea, Japan, and parts of Taiwan. These areas show clear monsoonal influence, with dense population and agricultural dominance. The map also marks major rivers like the Yangtze and Xi Jiang, vital for farming.
China Type Climate Characteristics
The China Type Climate shows distinct seasonal variations caused by shifting monsoon winds and ocean currents.
Main features:
- Temperature: Hot, humid summers (25°C-30°C) and mild to cool to cold winters often dropping temperature below freezing points..
- Rainfall: Annual rainfall ranges between 1000-1500 mm, mostly during summer.
- Humidity: High in summer due to maritime influence.
- Seasonality: Four well-defined seasons-spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
- Typhoons: Late summer and autumn often experience tropical cyclones in coastal China and Japan.
Factors Affecting China Type Climate
Several natural and geographical factors shape the characteristics of this climate:
- Monsoonal Influence- The East Asian Monsoon dominates the region, bringing wet summers and dry winters.
- Latitude- The region lies in the warm temperate zone, influencing moderate temperature ranges.
- Ocean Currents- The Kuroshio (Japan Current) warms eastern coasts, while cold currents reduce temperatures further north.
- Topography- The Himalayas act as a massive barrier that prevents the warm, moist monsoonal winds from reaching Central Asia, contributing to the formation of the Gobi and other deserts.
- Continental and Maritime Interaction- Inland areas face greater temperature extremes compared to coastal zones.
Read About: Tropical Climate
China Type Climate Vegetation
- Natural Vegetation
The vegetation is mainly mixed forests due to moderate rainfall and warm temperatures. Dominant species:
- Evergreen trees: Camphor, laurel, and magnolia
- Deciduous trees: Oak, maple, beech, chestnut
- Conifers: Pine and cypress in cooler regions
- Shrubs and Herbs
- Shrubs: Bamboo, rhododendron, azalea
- Herbs: Ferns, mosses, and flowering grasses
- Soil
- Red and Yellow soils dominate due to heavy rainfall and leaching.
- Fertile alluvial soils are found in river basins such as the Yangtze River Valley.
- The drier and cooler north has different, often more alkaline soils (pedocals), while the wetter and hotter south has leached, more acidic soils (pedalfers).
- Fauna
- Animal species include giant panda, red fox, deer, squirrel, and pheasants.
- Coastal areas have rich marine biodiversity due to warm currents.
China Type Climate Agriculture
Agriculture is the economic backbone of regions under the China Type Climate. The warm and moist conditions are ideal for crop growth. Double cropping is common, especially in China’s Yangtze and Xi River valleys, due to the long growing season. Main crops include:
- Rice: Principal summer crop in river plains and deltas.
- Wheat and Barley: Winter crops in cooler regions.
- Tea, Silk, and Cotton: Major commercial crops.
- Sugarcane and Tobacco: Grown in southern parts with high rainfall.
- Fruits: Citrus, peach, and mulberry thrive in subtropical zones.
China Type Climate Seasons
The China Type Climate experiences four distinct seasons due to its mid-latitude position and the strong influence of monsoons.
- Spring (March-May): Moderate temperatures (15-20°C) and light rainfall help sowing of early crops.
- Summer (June-August): Hot and humid; temperatures reach 28-35°C with heavy monsoon rains exceeding 1000 mm, ideal for rice cultivation.
- Autumn (September-November): Cool, dry, and pleasant; crops sown in winters are harvested.
- Winter (December-February): Cool to Cold (5-10°C) and dry below freezing point due to continental winds; frost occurs in northern China and Korea.
China Type Climate Human Adaptations
People living in China Type Climate regions have developed ways to adjust to changing temperatures, monsoons, and seasonal variations.
- Agriculture: Farmers practice double cropping, growing rice in summer and wheat in winter to use the long growing season.
- Housing: Buildings are designed with sloped roofs and raised platforms to prevent flood damage.
- Clothing: Lightweight cotton is worn in summer, and layered wool in winter.
- Infrastructure: Drainage systems and embankments are built to manage monsoon floods.
- Technology: Urban areas use climate control systems and irrigation technologies for year-round farming efficiency.
Economic Activities in China Type Climate
The regions under the China Type Climate are economically very active and support both agriculture and industry. The warm and wet climate, fertile soil, and long growing season help people engage in multiple forms of economic activities.
- Agriculture
- Major crops include rice, tea, silk, wheat, and cotton.
- Double cropping is common due to long frost-free seasons.
- Regions like Yangtze Basin and South China Plain are top farming zones.
- Fishing and Forestry
- Fishing is highly developed in coastal areas of China, Japan, and Korea.
- Forests provide timber, bamboo, and lacquer, used for crafts and trade.
- Industry and Urbanization
- Cities such as Shanghai, Tokyo, and Seoul have become major industrial and manufacturing hubs.
- Textile, electronics, and automobile industries are highly developed.
- Trade and Ports
- Large ports like Shanghai, Yokohama, and Busan handle international trade.
- Coastal trade supports regional development and connects local industries to global markets.
China Type Climate Region Challenges
Despite its productivity, the China Type Climate region faces several environmental and economic challenges:
- Floods and Typhoons- Frequent storms cause destruction to crops and settlements.
- Droughts in Winter- Dry winters impact water supply.
- Soil Erosion- Heavy monsoon rains wash away fertile topsoil.
- Urban Pollution- Industrialization leads to severe air and water pollution.
- Climate Change Impacts- Rising temperatures and irregular monsoons affect agriculture.
Way Forward:
Addressing these issues requires sustainable practices, climate adaptation, and cooperation between governments to ensure long-term ecological and economic stability in the region.
- Adopt climate-resilient crops to reduce agricultural losses.
- Implement integrated water resource management to control floods and droughts.
- Afforestation and soil conservation programs to prevent erosion.
- Promote clean energy and pollution control in industrial cities.
- Enhance regional cooperation for climate monitoring and disaster management.
Impact of Climate Change on China Type Climate
Climate change has started to alter the natural pattern of the China Type Climate, affecting agriculture, rainfall, and living conditions.
- Rising Temperatures
- IPCC report (2022) states regional trends in Asia varied, with some areas experiencing increases between 1°C to 3°C per century.
- Longer summers and extreme heatwaves are becoming more frequent.
- Irregular Rainfall
- Shifting monsoon patterns cause floods in some areas and droughts in others, disrupting farming cycles.
- Increased Typhoons and Storms
- The frequency of severe typhoons has increased, causing coastal flooding and loss of life.
- Agricultural Impact
- Crops such as rice and wheat face reduced productivity due to heat stress and water shortages.
- Threat to Biodiversity
- Changes in rainfall and temperature threaten forest species, soil fertility, and wildlife habitats.
China Type Climate UPSC
In 2025, few regions of eastern China and South Korea reported record-breaking summer heatwaves, with average temperatures crossing 38°C, causing water shortages and energy demand spikes. Additionally, Japan and Taiwan faced strong typhoons in July 2025 and Super Typhoon Ragasa, also hit the region in September 2025, resulting in severe coastal flooding and crop damage. These events highlight the growing influence of climate change on China Type Climate regions.
| Also Check Other Posts | |
| Coastal Regulation Zone | Global Plastic Treaty |
| Nitrogen Cycle | Carbon Cycle |
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
China Type Climate FAQs
Q1. What is China Type Climate?+
Q2. Where is China Type Climate found?+
Q3. What are the main crops in China Type Climate?+
Q4. What vegetation grows in China Type Climate?+
Q5. What challenges affect China Type Climate regions?+
Tags: china type climate