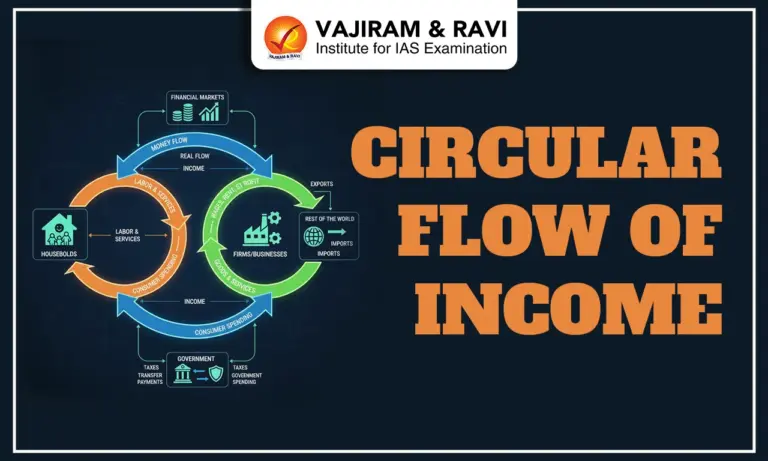
The Circular Flow of Income is an economic model that explains the continuous movement of money, goods, and services between different sectors of the economy, primarily households and firms. In this model, households provide factors of production such as labour, capital, land, and entrepreneurship to firms and, in return, earn income in the form of wages, rent, interest, and profits and Firms use these factors to produce goods and services, which households then purchase, creating a continuous cycle of spending and income generation. In this article, we are going to cover the Circular Flow of Income, its types, phases and significance.
Circular Flow of Income
Circular Flow of Income is an engine that keeps economic activity in motion. It is a fundamental concept in economics that explains how money, resources, and goods circulate between different sectors of an economy like households, firms, and the government. This constant exchange makes sure that production, consumption, and distribution take place in a balanced manner, ultimately sustaining the overall economic structure.
The Circular Flow of Income shows how households, as the owners of factors of production, provide labour, capital, and land to businesses, in return for which they receive wages, rent, interest, and profits as income. This income is then used by households to purchase goods and services produced by firms, creating a cycle of demand and supply. At the same time, businesses not only generate profits but also provide employment and contribute taxes to the government, which then spends on welfare, infrastructure, and public goods. In this way, the circular flow captures the cycle of production, income distribution, spending, and reinvestment that fuels economic growth.
Circular Flow of Income Types
The Circular Flow of Income can be understood by two different but complementary streams. These are: Real Flow and Money Flow. Both the streams show the dual nature of exchanges that take place in the economy.
- Real Flow
The Real flow means the actual movement of goods and services as well as factor services within the economy. Households provide factors of production like labour, capital, land, and entrepreneurship to firms. In exchange, firms utilize these inputs to produce goods and services, which then flow back to households for consumption. This flow represents the physical and tangible side of economic activity. - Money Flow
The Money Flow shows the monetary counterpart of the real flow. When firms hire factor services from households, they make payments in the form of wages, salaries, rent, interest, and profits. Households, in turn, use this income to purchase goods and services from firms, thereby generating revenue for businesses. This financial exchange forms the monetary cycle that mirrors and supports the real flow.
Together, the real flow and money flow show the symbiotic relationship between households and firms, showing how resources are transformed into goods and services and how income circulates back into the economy.
Circular Flow of Income Phases
The continuous movement of income within an economy can be studied in three important phases: Generation, Distribution, and Disposition.
- Generation Phase
In the starting phase, businesses combine many inputs like labour, capital, and natural resources to produce goods and services. This production process results in the creation of economic value and contributes to the total output of the economy. The generation of income essentially begins here, as businesses add value through their productive activities. - Distribution Phase
Once goods and services are produced, the income generated from this production is distributed among the factors of production. Wages are paid to workers, rent to landowners, interest to providers of capital, and profits to entrepreneurs. In this phase, households receive their due share of income, based on their role in the production process. - Disposition Phase
In the final phase, households decide how to allocate their income. A portion is spent on consumption of goods and services, another part is saved or invested, and a share is paid as taxes to the government. The government then redistributes these resources through expenditure on welfare programmes, infrastructure, and other public services. This phase highlights the crucial choices made by households that influence demand, savings, investment, and overall economic stability.
These three phases together illustrate how income is created, distributed, and utilized, forming the backbone of the economic cycle.
Circular Flow of Income Importance
The concept of the circular flow is not just theoretical but holds practical importance in understanding and managing economies. The significance of Circular Flow of Income includes:
- Interdependence: Shows the close linkages between households, businesses, and the government, showing the need for balance and coordination in policies.
- Economic Stability: Helps identify gaps or imbalances in production, income, and spending, thereby helping in policymakers in stabilizing the economy.
- Income Distribution: Shows patterns of income distribution and enables the government to design measures for reducing inequality and ensuring inclusive growth.
- Economic Growth: Shows the drivers of growth, including investment, consumption, and government expenditure, and provides insights for sustainable economic planning.
- Policy Formulation: Serves as a guide for checking the impact of fiscal and monetary policies on different sectors, ensuring informed economic decision-making.
| Also Check Other Posts | |
| Care Economy | Mutual Funds |
| Alternative Investment Funds | GDP Deflator |
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ UPSC will release the UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2025 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Circular Flow of Income FAQs
Q1. What is the circular flow of income?+
Q2. What is the 4 sector circular flow of income?+
Q3. What is the 5 circular flow of income model?+
Q4. What are the four main points of the circular flow model?+
Q5. What are the five sectors of the economy?+
Tags: circular flow of income