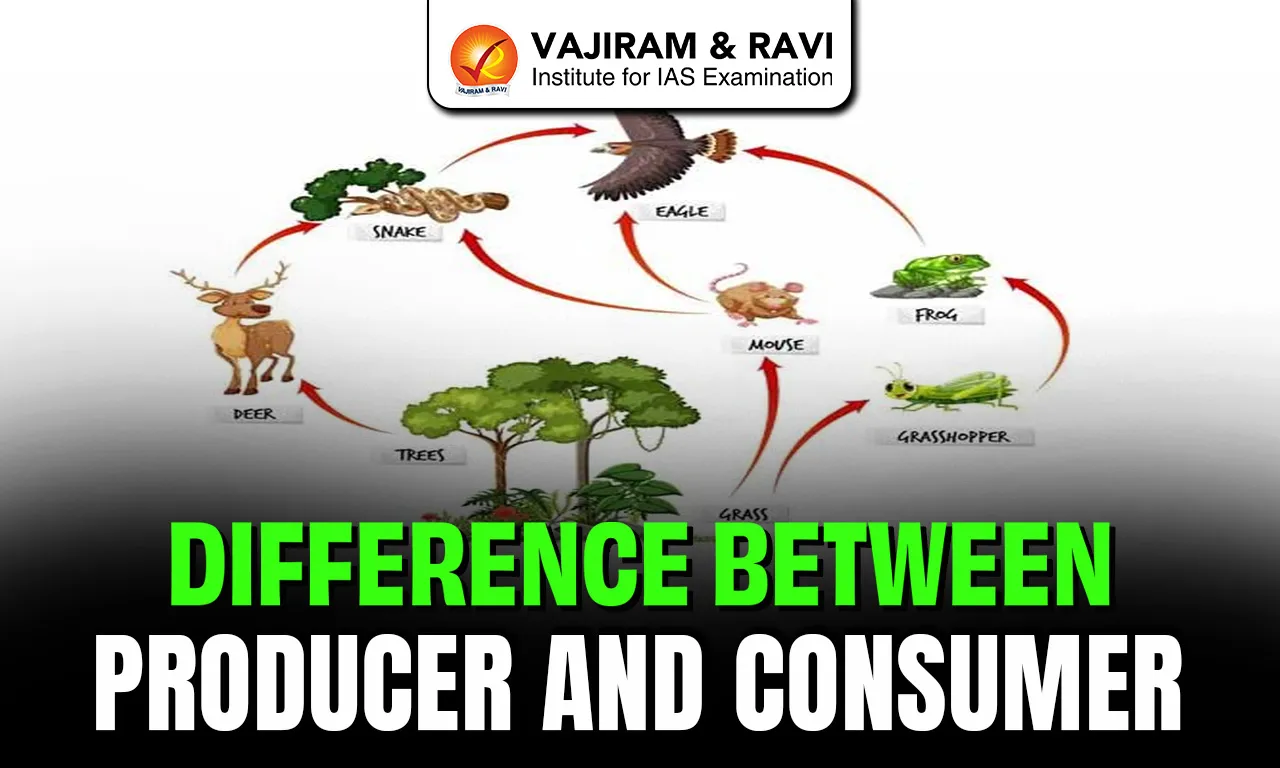
Understanding the Difference Between Producer and Consumer is fundamental in environmental studies and ecology. These two components form the base of every ecosystem, drive the food chain, and maintain ecological balance.
What is a Producer in Ecology?
A producer in ecology is an organism that prepares its own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Producers are also called autotrophs because they do not depend on other organisms for nutrition. They form the first trophic level and act as the primary source of energy in every ecosystem.
-
- Self-Food Production: Producers manufacture their own food through photosynthesis or chemical processes.
- Base of Food Chain: They occupy the first trophic level and support all higher trophic levels.
- Energy Conversion: Convert solar energy into chemical energy stored in food (glucose).
- Oxygen Production: Release oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis, essential for life.
- Types of Producers:
-
- Photoautotrophs – Use sunlight (e.g., green plants, algae).
- Chemoautotrophs – Use chemical energy (e.g., certain bacteria).
- Examples: Grass, trees, phytoplankton, algae, cyanobacteria.
- Ecological Importance: Maintain atmospheric balance and regulate carbon dioxide levels.
- Foundation of Ecosystems: Without producers, consumers and other life forms cannot survive.
Also Read: Difference between Sympathy and Empathy
What is a Consumer in Ecology?
A consumer in ecology is an organism that cannot make its own food and depends on other organisms for nutrition. Consumers are known as heterotrophs because they rely directly or indirectly on producers for energy. They occupy the second and higher trophic levels in a food chain and help in the transfer of energy within an ecosystem.
-
- Dependence on Other Organisms: Consumers obtain food by eating plants (producers) or other animals.
- Cannot Perform Photosynthesis: Unlike producers, they lack the ability to prepare their own food.
- Higher Trophic Levels: They occupy the second, third, or higher trophic levels in ecological pyramids.
- Energy Transfer Role: Help in transferring energy from one trophic level to another.
- Population Control: Maintain balance by regulating plant and animal populations.
- Types of Consumers:
-
- Primary Consumers (Herbivores): Eat plants (e.g., deer, goat).
- Secondary Consumers: Eat herbivores (e.g., frog, small fish).
- Tertiary Consumers: Eat secondary consumers (e.g., snake).
- Quaternary Consumers (Top Predators): Highest-level carnivores (e.g., lion, eagle).
- Omnivores: Eat both plants and animals (e.g., humans).
- Examples: Humans, tiger, cow, fish, birds, lion.
Difference Between Producer and Consumer
The difference between producer and consumer is based on how they obtain energy and their position in the ecosystem. Producers prepare their own food and form the base of the food chain, while consumers depend on producers or other organisms for survival.
| Difference Between Producer and Consumer | ||
|
Basis of Comparison |
Producer |
Consumer |
|
Meaning |
Organisms that make their own food |
Organisms that obtain food from other organisms |
|
Also Called |
Autotrophs |
Heterotrophs |
|
Mode of Nutrition |
Autotrophic mode of nutrition |
Heterotrophic mode of nutrition |
|
Ability to Prepare Food |
Can prepare their own food |
Cannot prepare their own food |
|
Process Involved |
Photosynthesis or chemosynthesis |
Ingestion and digestion |
|
Energy Source |
Sunlight or chemical energy |
Producers or other consumers |
|
Position in Food Chain |
Base of the food chain |
Above producers in food chain |
|
Trophic Level |
First trophic level |
Second, third, or higher trophic levels |
|
Dependency |
Independent for food |
Dependent on producers directly or indirectly |
|
Chlorophyll Presence |
Usually present (in green plants) |
Absent |
|
Oxygen Production |
Release oxygen (most producers) |
Do not produce oxygen |
|
Role in Ecosystem |
Convert solar energy into chemical energy |
Transfer energy between trophic levels |
|
Impact on Population |
Support life of all organisms |
Regulate population of plants and animals |
|
Biomass Pyramid |
Largest biomass at base |
Biomass decreases at higher levels |
|
Examples |
Grass, trees, algae, phytoplankton |
Humans, lion, deer, tiger, fish |
|
Ecological Importance |
Foundation of ecosystem stability |
Maintain ecological balance and biodiversity |
Also Read: Difference between Natural Farming and Organic Farming
Role of Producers and Consumers in the Ecosystem
Producers and consumers play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the smooth flow of energy in an ecosystem.
- Energy Production and Transfer – Producers convert solar energy into chemical energy, and consumers transfer this energy across trophic levels.
- Foundation of Food Chain – Producers form the base of the food chain, while consumers occupy higher trophic levels.
- Maintenance of Ecological Balance – Consumers control plant and animal populations, preventing overgrowth or extinction.
- Oxygen and Carbon Cycle Regulation – Producers release oxygen and absorb carbon dioxide, maintaining atmospheric balance.
- Support Biodiversity – The interaction between producers and consumers sustains diverse life forms in an ecosystem.
- Stability of Ecosystem – Together, they ensure proper energy flow, nutrient cycling, and long-term sustainability of the environment.
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the second week of April 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Difference Between Producer and Consumer FAQs
Q1. What is the main difference between producer and consumer?+
Q2. What are producers also called?+
Q3. What are consumers also called?+
Q4. Which trophic level do producers occupy?+
Q5. Which trophic levels do consumers occupy?+
Tags: business studies difference between producer and consumer economics