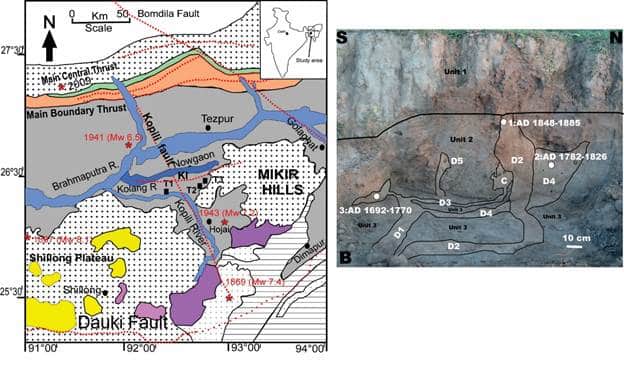
About Kopili fault zone
- It is a 300 km long and 50 km wide lineament situated in the northeastern region (NER).
- It extends from the western part of Manipur to the tri-junction of Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh, and Assam.
- It is closer to Himalayan Frontal Thrust.
- This is a seismically active area falling in the highest Seismic Hazard Zone V.
- It is associated with collisional tectonics because of the Indian Plate subducting beneath the Eurasian Plate.
- The fault itself is a transpressional fracture that generates lower crustal dextral strike-slip earthquakes.
- A tectonic depression filled up by the alluvium of the Kopilli river and its tributaries, the Kopili fault zone has witnessed many seismic activities in the past including the 1869 earthquake (7.8 magnitude) and the 1943 earthquake (7.3 magnitude).
Key points about the research
- Seismogenic liquefaction features, including multiple sand dykes and sand sills, were pinpointed in the Kopili Fault zone.
- To mitigate future earthquake occurrences in the Kopili Fault zone, scientists conducted investigations at three trench sites in the floodplain deposits of the Kolong River, near KF.
- The identified liquefaction features, including sand dykes and sand sills, directly respond to the liquefaction of saturated sediment induced during past seismic activity.
- The study utilized a technique called optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating on seven samples from marker horizons to constrain the chronology of liquefaction features.
- The OSL age constraints revealed evidence of two earthquake-induced liquefaction events near the Kopili Fault approximately 480 years ago.
- This crucial information aids in the interpretation of the long-term rupture history of faults and intraplate seismicity in the region.
Q1) What is Dyke?
In geology, a tabular or sheetlike igneous body that is often oriented vertically or steeply inclined to the bedding of preexisting intruded rocks is known as Dyke.
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India