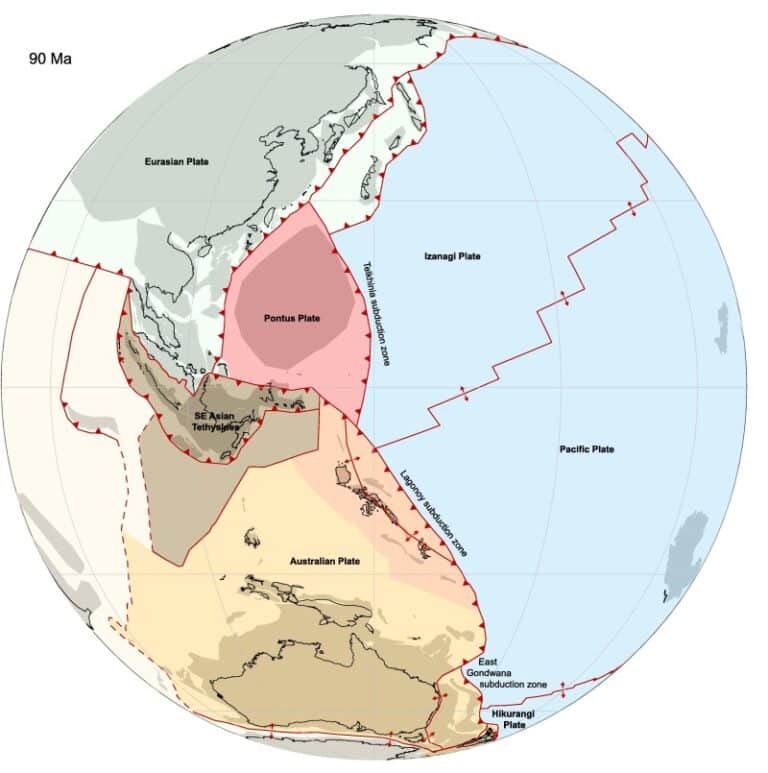
About Pontus Tectonic Plate
- It is a long-lost tectonic plate recently discovered in the west Pacific Ocean.
- It is believed that the massive tectonic plate was once about 15 million square miles in size, which equates to approximately one quarter of the Pacific Ocean.
- It can be traced back as far as 160 million years, and even more recently to around 20 million years back.
- It was slowly subducted and lost over millions of years, pulled down under a neighbouring plate by gravity.
- How the discovery was made?
- The subducting plate is actually denser than the surrounding mantle, so gravity basically pulls the plate down into the mantle.
- A subducted plate leaves behind traces when it ‘sinks’ into Earth’s mantle – namely, fragments of rock hidden in mountain belts.
- During the process of subduction, however, the upper parts of the subducting plate are sometimes scraped off.
- The researchers used geological data to reconstruct the movements of the current plateswith computer modelling, which hinted at a wide area potentially vacated by a subducted plate.
- Using magnetic techniques, researchers determined the basalt from Borneo were relics of Pontus that were left behind when this part of the plate subducted, some 85 million years ago.
What is a Tectonic Plate?
- A tectonic plate (also called lithospheric plate) is a massive, irregularly shaped slab of solid rock, generally composed of both continental and oceanic lithosphere.
- Plate size can vary greatly, from a few hundred to thousands of kilometers across; the Pacific and Antarctic Plates are among the largest.
- Plate thickness also varies greatly, ranging from less than 15 km for young oceanic lithosphere to about 200 km or more for ancient continental lithosphere (for example, the interior parts of North and South America).
- Theory of Plate Tectonics:
- Plate tectonics is the theory that Earth’s outer shell is divided into large slabs of solid rock, called “plates,” that glide over Earth’s mantle, the rocky inner layer above Earth’s core.
- Earth’s solid outer layer, which includes the crust and the uppermost mantle, is called the lithosphere. Below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere — a viscous layer kept malleable by heat deep within the Earth.
- It lubricates the undersides of Earth’s tectonic plates, allowing the lithosphere to move around.
Q1: What is mantle?
The mantle is the largest layer of the earth, lying between the crust and the outer core. It is 2,900 kilometres thick and makes up around 60% of the planet’s mass.
Source: Scientists discover ghost of ancient mega-plate that disappeared 20 million years ago
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the first week of March 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India