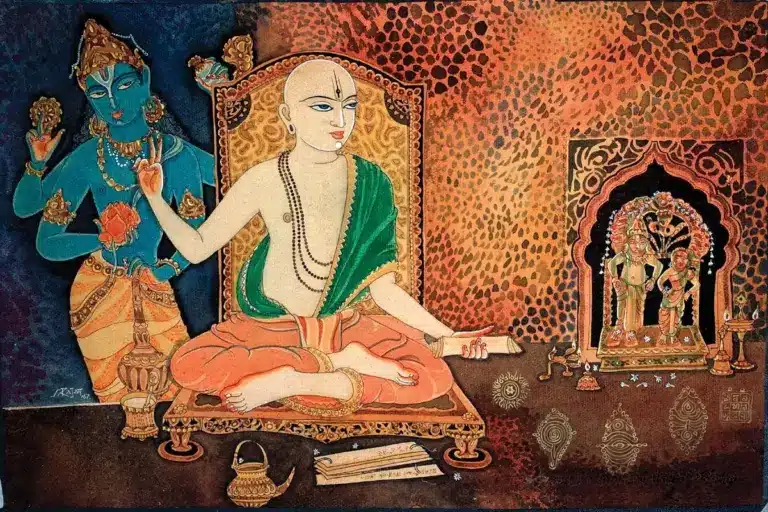
About Saint Narahari Tirtha:
- Narahari Tirtha (c. 13th century) was a prominent Dvaita Vedanta philosopher, scholar, and saint in the Madhva tradition.
- He was a disciple of Madhvacharya, the founder of Dvaita philosophy, and played a key role in spreading the doctrine in eastern India, particularly in the Kalinga region (modern Odisha and Andhra Pradesh).
- Believed to have hailed from Chikakolu town (present Srikakulam), Tirtha’s ancestors were aristocrats in the Gajapati empire in what is now the Odisha state.
- Available epigraphical evidence suggests that kings of Eastern Ganga dynasty were assisted by the saint for three decades.
- He ensured that the king followed Sanatana Dharma and took care of its adherents by formulating a proper executive system to oversee the temple administration.
- His contributions on this front are well documented in inscriptions available in the Simhachalam and Srikurmam (Srikakulam) temples.
- Some honorific prefixes being used along with the name of this saint are: ‘Loka Suraksḥaṇa Ati Nipuṇaḥ’, ‘Yo Avati Kalinga Bhu Sambhavān’.
- As saint Ramanuja had introduced Vaiṣṇavism in the region, it was Narahari Tīrtha’sprolonged presence that resulted in Acharya’s Vaiṣhṇavism getting a firm following in this region, but in a completely non-interfering and secular manner.
- Shri Narahari wrote fifteen books, but only two of his works,Gita Bhasya and Bhavaprakasika are existing today.
- He is the first one to have composed Devaranamas in Kannada.
- He was instrumental in propagating two more art forms:Yakṣagana Bayalaṭa which is a form of dance-drama famous in and around coastal Karnataka; and the classical dance form that evolved in Andhra Pradesh as the famous Kuchipudi.
- The saint, upon his passing away, was consecrated near the rock adjacent to Chakratirtha at Hampi on the banks of river Tungabhadra.
- His contributions are linked to the temple traditions of Puri Jagannath, strengthening the Madhva influence in Odisha.
Q1: What is Indian Philosophy?
Indian Philosophy refers to several traditions of philosophical thought that originated in the Indian subcontinent, including Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain philosophy. Indian philosophy has been designated as‘darsana’, generally translated as philosophy, but it meansintuitive vision.
Source: Saint Narahari Tirtha statue discovered in Simhachalam Temple
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the first week of March 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India