About Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030:
- It was the first major agreement of the post-2015 development agenda and provides member states with concrete actions to protect development gains from the risk of disaster.
- It was adopted by the UN member states at the Third UN World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction in Sendai, Japan, on March 18, 2015.
- It is the successor instrument to the Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) 2005-2015.
- The Sendai Framework advocates for:
- The substantial reduction of disaster risk and losses in lives, livelihoods, and health and in the economic, physical, social, cultural, and environmental assets of persons, businesses, communities, and countries.
- It recognizes that the State has the primary role to reduce disaster risk, but that responsibility should be shared with other stakeholders, including local government, the private sector, and other stakeholders.
- Four Priorities:
- Understanding disaster risk
- Strengthening disaster risk governance to manage disaster risk
- Investing in disaster risk reduction for resilience
- Enhancing disaster preparedness for effective response and “Building Back Better” in recovery, rehabilitation, and reconstruction.
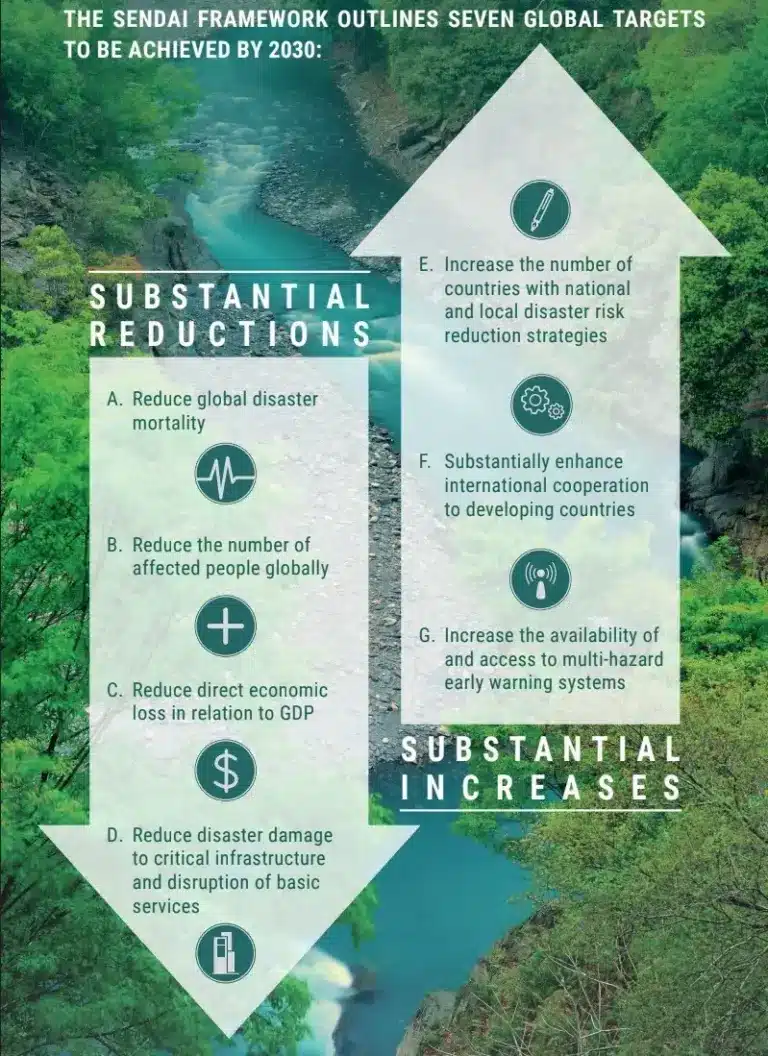
- Targets:
- Substantially reduce global disaster mortality.
- Substantially reduce the number of affected people globally.
- Reduce direct disaster economic loss in relation to global GDP.
- Substantially reduce disaster damage to critical infrastructure and disruption of basic services.
- Substantially increase the number of countrieswith national and local disaster risk reduction strategies.
- Substantially enhance international cooperation to developing countries.
- Substantially increase the availability of and access to multi-hazard early warning systems and disaster risk information and assessments to people.
- The Sendai Framework covers technological hazards in addition to natural hazards, which represent an evolution compared to its predecessor, the Hyogo Framework for Action.
- These technological hazards include chemical/industrial hazards further to radiological, nuclear, biological, and others.
- It works hand in hand with the other 2030 Agenda agreements, including the Paris Agreement on Climate Change, the Addis Ababa Action Agenda on Financing for Development, the New Urban Agenda, and ultimately the Sustainable Development Goals.
- The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR)is tasked tosupport the implementation, follow-up and review of the Sendai Framework.
Q1: What are the stages of a disaster risk management cycle?
The disaster risk management cycle consists of four phases: Prevention/Mitigation and Preparedness in the pre-disaster stage, and Response and Rehabilitation/Reconstruction in the post-disaster stage.
Source: India committed to Sendai Framework for disaster risk reduction: PM’s aide P.K. Mishra
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the first week of March 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India