Turbidity Currents in Submarine Canyons Latest News
A recent study published in ACS Environmental Science & Technology has provided the first direct evidence of turbidity currents transporting microplastics into the deep sea through submarine canyons, even in areas not fed by rivers (e.g., Whittard Canyon off Ireland).
What are Turbidity Currents?
- Turbidity currents are rapid, downslope flows of water heavily laden with sediments, increasing the water’s density.
- They function similarly to underwater avalanches, triggered by:
- Earthquakes
- Submarine landslides
- Slope failures and other geological disturbances
- Key Features of Turbidity Currents
- As turbidity increases, water becomes denser and less transparent.
- These flows erode the seafloor, forming and enlarging submarine canyons.
- They deposit sediment in graded layers, with coarser particles settling first and finer ones later.
- Aid in deep-sea sedimentation and shaping oceanic topography.
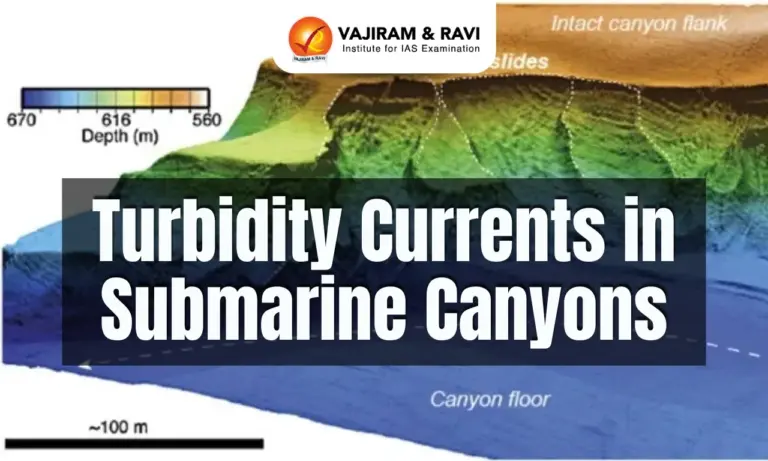
Submarine Canyons
- Submarine canyons are narrow, steep-sided underwater valleys found on continental slopes and rises, often extending from the continental shelf into the deep ocean.
- They are carved out mainly by erosional forces like turbidity currents, similar to how river canyons are formed on land.
- Globally, there are about 9,477 known submarine canyons, covering nearly 11% of continental slope areas.
- Canyons on active margins (tectonically active zones) tend to be steeper and shorter, while those on passive margins are more gradual.
- Their walls can be nearly vertical and are prone to collapse, adding sediment to turbidity flows.
Types of Submarine Canyons
- Bank: A flat-topped elevation on continental margins, formed by erosional and depositional processes, e.g., Dogger Bank in the North Sea.
- Shoal: A shallow area of sediment accumulation, often hazardous to navigation, and generally found at depths <10 meters at low tide.
- Reef: Built from calcareous skeletons of corals and algae; coral reefs are biodiversity hotspots and prominent in the Pacific Ocean, associated with guyots and seamounts.
Source: PHY
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Turbidity Currents in Submarine Canyons FAQs
Q1. What are turbidity currents?+
Q2. How do turbidity currents form submarine canyons?+
Q3. Where are major submarine canyons located?+
Tags: prelims pointers turbidity currents in submarine canyons upsc prelims current affairs