Falkland Islands Latest News
Beneath that stern exterior of the Falkland Islands, researchers have just uncovered a buried forest that flourished long before humans or sheep ever set foot on the archipelago.
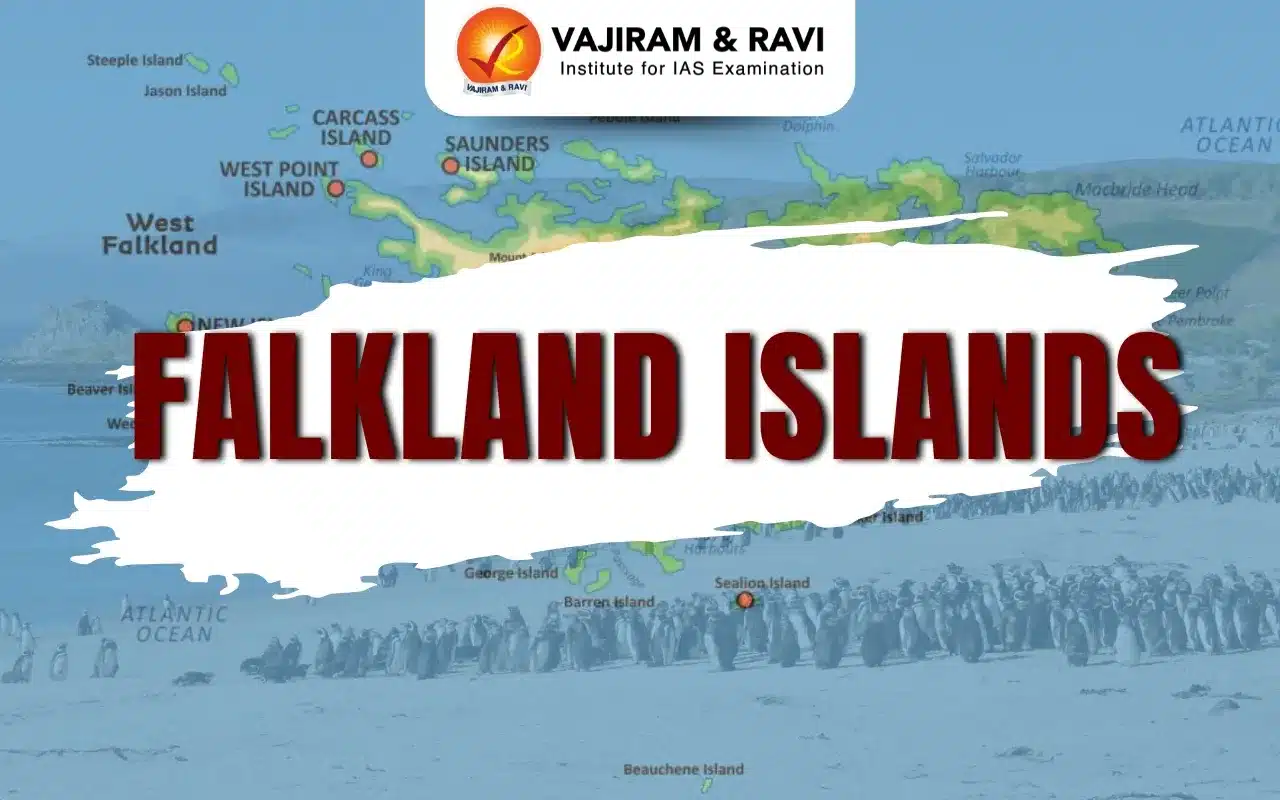
About Falkland Islands
- Also known as the Malvinas Islands, the Falkland Islands is an internally self-governing overseas territory of the United Kingdom in the South Atlantic Ocean.
- It lies about 480 km northeast of the southern tip of South America and a similar distance east of the Strait of Magellan.
- It consists of two main islands, East Falkland and West Falkland, together with 776 smaller islands.
- The two large islands are separated by the Falkland strait.
- The islands are positioned both in the southern and western hemispheres of the Earth.
- It covers a total area of 12,173 sq.km.
- Capital: The capital and major town is Stanley, on East Falkland.
- Climate: A cool temperate oceanic climate that is characterised by its lack of extremes.
- Demographics: The population is English-speaking and consists primarily of Falklanders of African-Irish descent (88% of population).
- Economy: The economy was formerly based on agriculture, mainly sheep farming, but fishing and tourism currently comprise the bulk of economic activity.
- Currency: The official currency is the Falkland pound, which is on par with the British pound.
- History:
- At various times, the islands have had French, British, Spanish, and Argentine settlements.
- Britain reasserted its rule in 1833, although Argentina maintains its claim to the islands.
- In April 1982, Argentine forces temporarily occupied the islands.
- British administration was restored two months later at the end of the Falklands War.
- Most Falklanders favour the archipelago remaining a UK overseas territory, but its sovereignty status is part of an ongoing dispute between Argentina and the United Kingdom.
- Government:
- Executive authority is vested in the British crown, and the islands’ government is headed by a governor appointed by the crown.
- The islands are self-governing, although foreign affairs and defence matters are handled by the British government.
- The government of the Falkland Islands also administers the British overseas territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, including the Shag and Clerke rocks, lying from 700 to 2,000 miles (1,100 to 3,200 km) to the east and southeast of the Falklands.
- Wildlife:
- Rich in seabird and marine life.
- Home to five species of penguins, sea lions, elephant seals, and albatrosses.
Source: EARTH
Falkland Islands FAQs
Q1: The Falkland Islands are located in which ocean?
Ans: South Atlantic Ocean
Q2: What is the capital of the Falkland Islands?
Ans: Stanley
Q3: What is the status of the Falkland Islands in relation to the UK?
Ans: It is an internally self-governing overseas territory of the United Kingdom.
Q4: Which country also claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands?
Ans: Argentina
Q5: What is the official currency of the Falkland Islands?
Ans: The official currency is the Falkland pound, which is on par with the British pound.