False Smut Disease Latest News
According to reports, the paddy crop, which is at the maturing and harvest stage, has been infested with false smut disease, causing widespread damage across Punjab.
About False Smut Disease
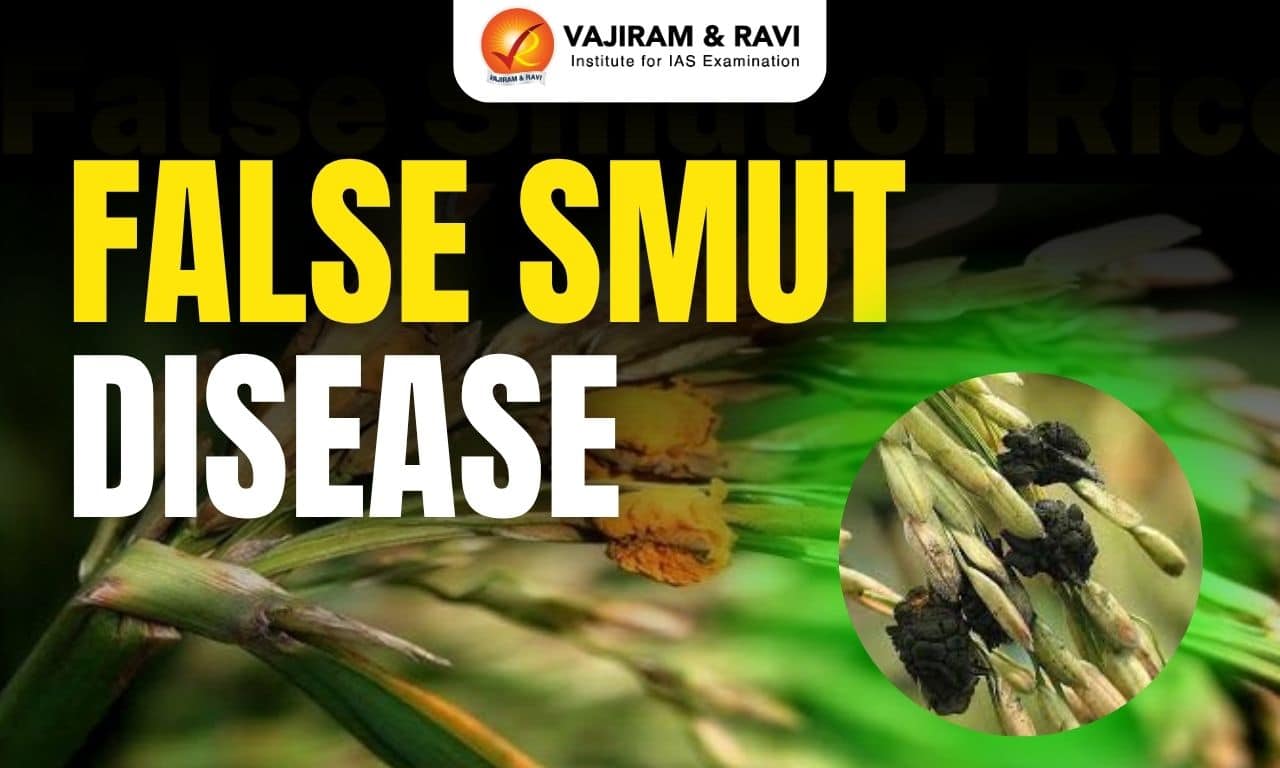
- False smut (haldi rog) is an important fungal disease of rice (paddy).
- It is caused by the fungus Ustilaginoidea virens.
- It is also known as Lakshmi disease or Oothupathi disease of rice.
- The disease is hard to stop, because fungus infects the crop during the flowering stage, and symptoms of the disease are evident after emergence of rice panicles.
- The typical symptom of the disease is black fungal mycelium growth in paddy grains, which become covered with yellow fungal growth in the field.
- Mature spores are orange and turn yellowish green or greenish black in colour.
- Only a few grains in a panicle are usually infected, and the rest are normal.
- It doesn't directly impact other plant parts.
- It causes chalkiness of grains, which leads to reduction in grain weight. It also reduces seed germination.
- The percentage of infected panicles and the extent of infection within each panicle significantly impact yield loss.
- Favorable Factors for False Smut in Paddy Crops?
- Warm and humid weather: Temperatures between 25-30°C and high humidity (>80%) promote fungal growth.
- Presence of infected plant debris: Spores can survive on leftover stubble and straw from previous harvests.
- High nitrogen content in soil: Excessive nitrogen application can increase susceptibility.
- Control of false smut of rice through fungicide application is feasible; however, high usage of fungicides has led to the resistance development in causal agents besides environmental pollution.
Source: HT
False Smut Disease FAQs
Q1: What is the causal organism of False Smut disease in rice?
Ans: It is caused by the fungus Ustilaginoidea virens.
Q2: By which other names is False Smut disease of rice known?
Ans: False Smut disease of rice is also known as Haldi Rog, Lakshmi Disease, and Oothupathi Disease.
Q3: At which stage of crop growth does False Smut infect rice plants?
Ans: It infects the crop during the flowering stage.
Q4: What is the most typical symptom of False Smut disease in paddy grains?
Ans: The typical symptom of the disease is black fungal mycelium growth in paddy grains, which become covered with yellow fungal growth in the field.