Uruguay Latest News
Recently, Uruguay's senate has passed a law decriminalising euthanasia.
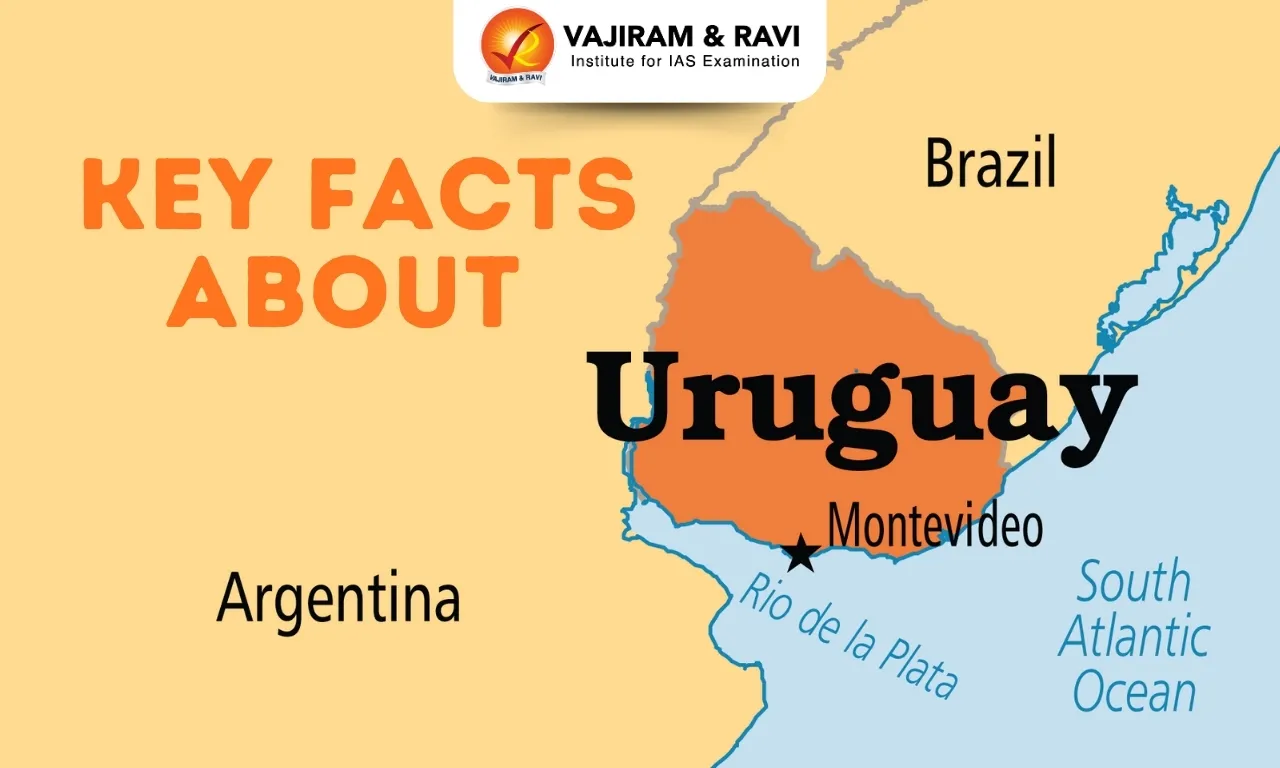
About Uruguay
- It is a country located on the southeastern coast of South America.
- It is the only South American nation to be situated entirely south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Bordered by: Argentina (west and southwest), Brazil (north and east); and by the South Atlantic Ocean to the southeast.
Geographical Features of Uruguay
- Climate: It is characterized as a humid subtropical climate.
- Terrain: It is influenced by the Pampas, these grasslands traditionally used for extensive livestock farming. It also consists of rolling plains, low plateaus, and hills.
- It also consists of Haedo Ridge (Cuchilla de Haedo) in the north and Grande Ridge (Cuchilla Grande) in the southeast.
- Major Rivers: Rio de la Plata/Parana River, Uruguay river (It forms the border between Uruguay and Argentina).
- Uruguay's coast is influenced by the Brazil Current (warm, northward) and Malvinas (Falkland) Current.
- Highest Point: Mount Catedral
- Capital city: Montevideo
Source: TH
Uruguay FAQs
Q1: What is the capital of Uruguay?
Ans: Montevideo
Q2: Which countries share a border with Uruguay?
Ans: Argentina and Brazil