In an era of rapid industrialization and shrinking arable land, the conventional agricultural paradigm is facing unprecedented pressure. With nearly 80% of the global population expected to reside in urban centers by 2050, the demand for food security has led to the rise of Vertical Farming. This innovative approach, which involves “protected cultivation,” moves beyond traditional horizontal land use. By utilizing vertically stacked layers and controlled environments, this method optimizes scarce resources like land and water. In India, where only 4% of the world’s water resources are available, vertical farming serves as a vital strategic tool to achieve carbon neutrality and sustainable food systems.
Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is the practice of cultivating crops indoors under artificial conditions of light and temperature to maximize productivity in minimal space. The term was first coined by Gilbert Ellis Bailey in 1915, while the modern conceptual framework was proposed in 1999 by Professor Dickson Despommier. The core philosophy is to produce food in proximity to consumers, thereby shortening supply chains and reducing the carbon footprint of transportation. By regulating variables such as humidity, soil-less nutrients and temperature, vertical farming systems can operate year round, independent of seasonal variations and the vagaries of the monsoon.
Vertical Farming Method
The methodology of Vertical Farming has been discussed below:
- Layered Cultivation: Crops are grown in a tower like structure of stacked layers, allowing for significantly higher yield per unit area than the traditional methods.
- Artificial Lighting: A combination of natural and programmable LED lights maintains optimal light levels, enhancing the efficiency of photosynthesis through technologies like rotating beds.
- Controlled Environment: Precision systems regulate temperature and humidity, ensuring that crops are entirely resistant to extreme or unexpected weather disruptions.
- Soil-less Growing Mediums: Instead of traditional soil, non-soil mediums such as peat moss, coconut husks, perlite, or rock wool are utilized for plant support.
- Micro-mist Technology: In certain systems, internal micro-jets spray a soilless mist directly onto roots, ensuring they remain uncovered and exposed to high oxygen levels for faster growth.
Vertical Farming Types
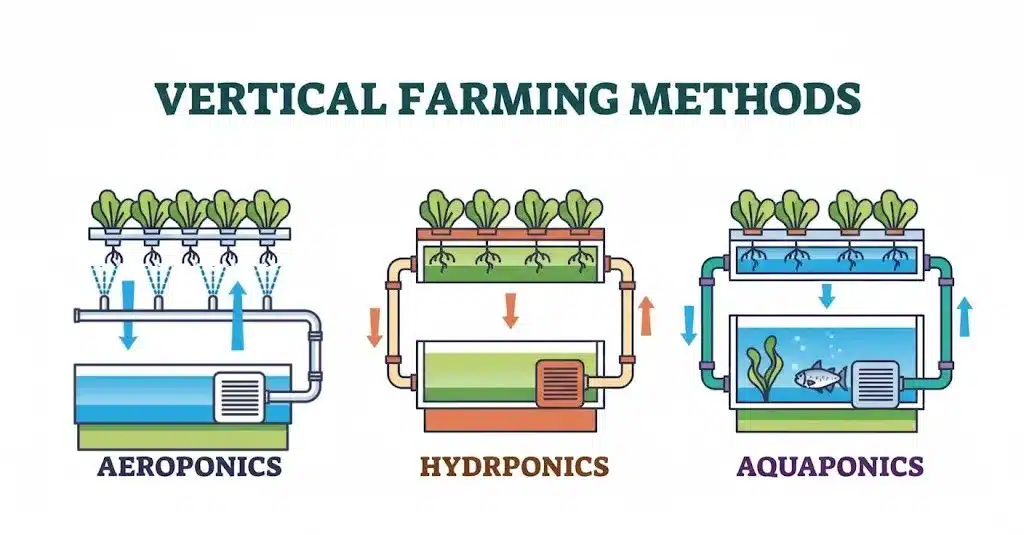
Vertical farming is broadly classified into three major soilless methods, each varying by the nutrient delivery system and the medium used.
- Aeroponics: A highly technical method where plant roots are suspended in a humid air environment and regularly sprayed with nutrient rich mist.
- Hydroponics: This is the most widely adopted method where plants are grown in a water based, nutrient charged aqueous solution.
- Aquaponics: An integrated, symbiotic system that combines traditional fish farming (aquaculture) with soilless plant cultivation.
Hydroponics Method of Vertical Farming
Pioneered in the 1930s by William Frederick Gerick, hydroponics is a method that provides minerals and hydration directly to the plant’s root zone.
- Aqueous Nutrient Solution: Plants receive a balanced mineral solution through either active systems (using pumps to circulate water) or passive systems (using gravity or capillary action).
- Inert Support Medium: The root system is physically supported by mediums like clay pellets, vermiculite, or perlite, which do not provide nutrients but facilitate oxygen access.
- Pest Control: By eliminating soil, the system significantly reduces soil borne insect infestations and diseases, leading to a “zero pesticide” produce.
- Higher Density: The lack of root competition for soil nutrients allows for much higher plant density and an extended growing season.
- System Vulnerability: Despite its efficiency, the method is vulnerable to power outages and waterborne diseases, requiring constant monitoring of pH and nutrient levels.
Aeroponics Method of Vertical Farming
Motivated by NASA’s research into space based agriculture in the 1990s, aeroponics is the most technical and water efficient variation of vertical farming.
- Suspended Root System: Roots grow in a humid environment without any soil or flowing water, suspended in the air within a support structure.
- Nutrient Misting: High pressure pumps and mist nozzles spray the roots with a nutrient solution, allowing for maximum absorption and healthy growth.
- Oxygenation: Because roots are exposed to oxygen 24/7, aeroponic plants typically grow faster and absorb more nutrients than those in other systems.
- Water Efficiency: This technique uses considerably fewer nutrients and water on average than any other farming method due to the targeted misting.
- Root Health: The absence of a growing medium allows for easy disinfection of the root chamber, preventing debris related pathogens from residing in the system.
Aquaponics Method of Vertical Farming
Aquaponics is a revolutionary system representing a symbiotic relationship between fishes, plants and nitrogen fixing bacteria within a closed loop system.
- Symbiosis: Fish waste provides organic fertilizer for the plants, while the plants act as biological filters, cleaning the water for the fish.
- Biological Components: Nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia from fish feces into nitrates, which are essential nutrients for plant growth.
- Water Efficiency: It is an extremely water efficient system, as water is continuously recycled between the fish tanks and the hydroponic beds.
- Nutritional Diversity: Unlike other methods, aquaponics provides a balanced output of both plant based vegetables and animal based protein.
- Biosecurity: The system offers high levels of biosecurity and lower risks from external contaminants, making it suitable for non-arable lands like deserts or sandy islands.
Vertical Farming Significance
The adoption of vertical farming holds massive potential for national food security and economic optimization.
- Water Conservation: Vertical farming methods are over 95% more water efficient compared to traditional agriculture, a vital factor for India’s water stressed regions.
- Enhanced Yield: These systems can produce over ten times of the crop yield per acre than traditional methods, helping to feed a growing population.
- Public Health: Most crops are grown without chemical pesticides, leading to healthier produce and long term positive contributions to public health.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Indoor production reduces the need for heavy farm machinery, protecting soil and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Employment Opportunities: Protected cultivation creates new economic opportunities and skill sets for agriculture students and technical professionals.
Vertical Farming Challenges
While the benefits are substantial, several structural and economic hurdles must be addressed for wide scale implementation.
- Economic Viability: The initial capital cost for computerized monitoring, automated racking and climate control systems remains a major barrier.
- Pollination Constraints: In the absence of insects within a controlled environment, pollination must be done manually, which is labor intensive and expensive.
- Energy Intensity: Vertical farms depend heavily on electricity for lighting and pumps; any disruption in power can lead to immediate crop collapse.
- Rural Sector Disruption: If not managed properly, the rise of urban vertical farms could render traditional rural farming jobs obsolete, impacting agricultural dependent communities.
Way Forward
- Incentivizing Soilless Techniques: Governments should consider providing financial assistance and subsidies to make these techniques affordable for a larger number of farmers.
- Infrastructure for Food Security: Strengthening distribution systems and recognizing vertical farming as a viable alternative can tackle the burden of malnutrition.
- Knowledge and Skill Development: Transitioning to these systems requires specific technical knowledge; therefore, agricultural universities must focus on safe and sustainable implementation.
- Sustainable Land Management: By shifting the focus from land constraints to sustainable technology, India can protect its natural biomes from agricultural encroachment.
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the first week of March 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Vertical Farming FAQs
Q1. What is Vertical Farming?+
Q2. How do plants grow without soil in Vertical Farming?+
Q3. Does Vertical Farming save water?+
Q4. What are the major types of Vertical Farming Methods?+
Q5. What kind of plants are grown in Vertical Farming?+
Tags: vertical farming