What’s in today’s article?
- Why in news?
- What is Lithium-ion battery?
Why in news?
- John B Goodenough, whose contribution to lithium-ion battery technology in 1980 helped him win the 2019 Nobel Prize in chemistry, died on June 25 at the age of 100.
- He became the oldest person to receive the Nobel Prize.
- He had shared his Nobel with two other researchers:
- Michael Stanley Whittingham, a British-American chemist, and
- Akira Yoshino, a Japanese chemist – Yoshino invented the first commercially viable lithium-ion battery, which began to be sold in 1991.
- His work transformed the tech world, sparking the wireless revolution that made portable electronics ubiquitous.
What is Lithium-ion battery?
- About
- A lithium-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses lithium ions as the primary component in its electrochemical system.
- It is widely used in portable electronic devices, electric vehicles, and various energy storage applications.
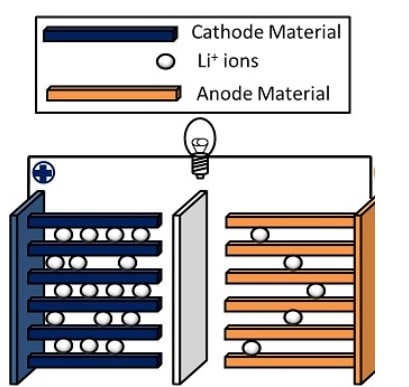
Image Caption: Schematic of a lithium ion battery
- Basic structure of a lithium-ion battery
- A battery is made up of an anode (a negative electrode), cathode (a positive electrode), separator, electrolyte, and two current collectors (positive and negative).
- The electrodes are typically made of materials that can intercalate lithium ions during charging and discharging cycles.
- Common cathode materials include lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4), and lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4).
- Graphite is commonly used as the anode material.
- Functioning
- During a discharge cycle, lithium atoms in the anode are ionized and separated from their electrons.
- The lithium ions move from the anode and pass through the electrolyte until they reach the cathode, where they recombine with their electrons and electrically neutralize.
- The lithium ions are small enough to be able to move through a micro-permeable separator between the anode and cathode.
- In part because of lithium’s small size (third only to hydrogen and helium), Li-ion batteries are capable of having a very high voltage and charge storage per unit mass and unit volume.
- Application
- Li-ion batteries are the market leader in portable electronic devices (such as smartphones and laptops).
- Li-ion batteries are also used to power electrical systems for some aerospace applications, notable in the new and more environmentally friendly Boeing 787, where weight is a significant cost factor.
- From a clean energy perspective, much of the promise of Li-ion technology comes from their potential applications in battery-powered cars.
- Advantages of Li-ion batteries
- They have one of the highest energy densities of any battery technology today.
- This means they can store a significant amount of energy for their size and weight.
- They also exhibit a relatively low self-discharge rate when compared to other rechargeable batteries, allowing them to hold their charge for extended periods.
- In addition, Li-ion battery cells can deliver up to 3.6 Volts, 3 times higher than other technologies.
- This means that they can deliver large amounts of current for high-power applications.
- Li-ion batteries have no memory effect, a detrimental process where repeated partial discharge/charge cycles can cause a battery to ‘remember’ a lower capacity.
- These batteries do not contain toxic cadmium, which makes them easier to dispose of than Ni-Cd batteries.
- They have one of the highest energy densities of any battery technology today.
- Disadvantages
- Li-ion batteries have a tendency to overheat, and can be damaged at high voltages.
- In some cases, this can lead to thermal runaway and combustion.
- This has caused significant problems, notably the grounding of the Boeing 787 fleet after onboard battery fires were reported.
- Li-ion batteries require safety mechanisms to limit voltage and internal pressures, which can increase weight and limit performance in some cases.
- Li-ion batteries are also subject to aging, meaning that they can lose capacity and frequently fail after a number of years.
- Another factor limiting their widespread adoption is their cost, which is around 40% higher than Ni-Cd.
Q1) What are Ni-Cd batteries?
Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd) batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that uses nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes. They belong to the class of electrochemical cells known as secondary batteries, which means they can be recharged and reused multiple times.
Q2) What is thermal runaway?
Thermal runaway refers to a self-accelerating and uncontrollable increase in temperature within a system or device. In the context of batteries, thermal runaway can occur when a battery undergoes an uncontrolled chain reaction of exothermic chemical reactions, leading to a rapid increase in temperature. This temperature increase can result in a destructive and potentially hazardous situation.
Source: Scientist John B Goodenough dies: How his creation of lithium-ion battery sparked the wireless revolution | Clean Energy Institute | Energy.Gov
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India