About Marburg Virus Disease (MVD):
- Definition: MVD is a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever caused by the Marburg virus, with no approved vaccines or treatments currently available.
- History and Origin: First identified in 1967 in the German city of Marburg. Named after an outbreak linked to laboratory workers exposed to infected green monkeys imported from Uganda.
- Geographical spread: Most outbreaks have occurred in sub-Saharan Africa, including countries like Tanzania, Uganda, Angola, Ghana, Kenya, and Zimbabwe.
- Transmission: Initially transmitted from fruit bats (Rousettus aegyptiacus) to humans. Spread occurs through direct contact with bodily fluids of infected individuals or contaminated surfaces.
- Symptoms:
- Early signs: High fever, severe headache, and malaise.
- Advanced stage: Severe bleeding, liver failure, multi-organ dysfunction, shock, and death within 8-9 days of symptom onset.
- Fatality rate: The average case fatality rate is approximately 50%, varying from 24% to 88% depending on the virus strain and case management.
- Diagnosis: Confirmed through RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction) tests and virus isolation procedures that require maximum biohazard containment.
- Treatment: No specific treatment exists. Supportive care includes rehydration, electrolyte replacement, and symptom management, improving survival chances.
- Vaccine development: Promising vaccines, such as the Sabin Vaccine Institute’s single-dose vaccine, are under Phase 2 trials in Uganda and Kenya. Rwanda also received investigational vaccines to support outbreak control.
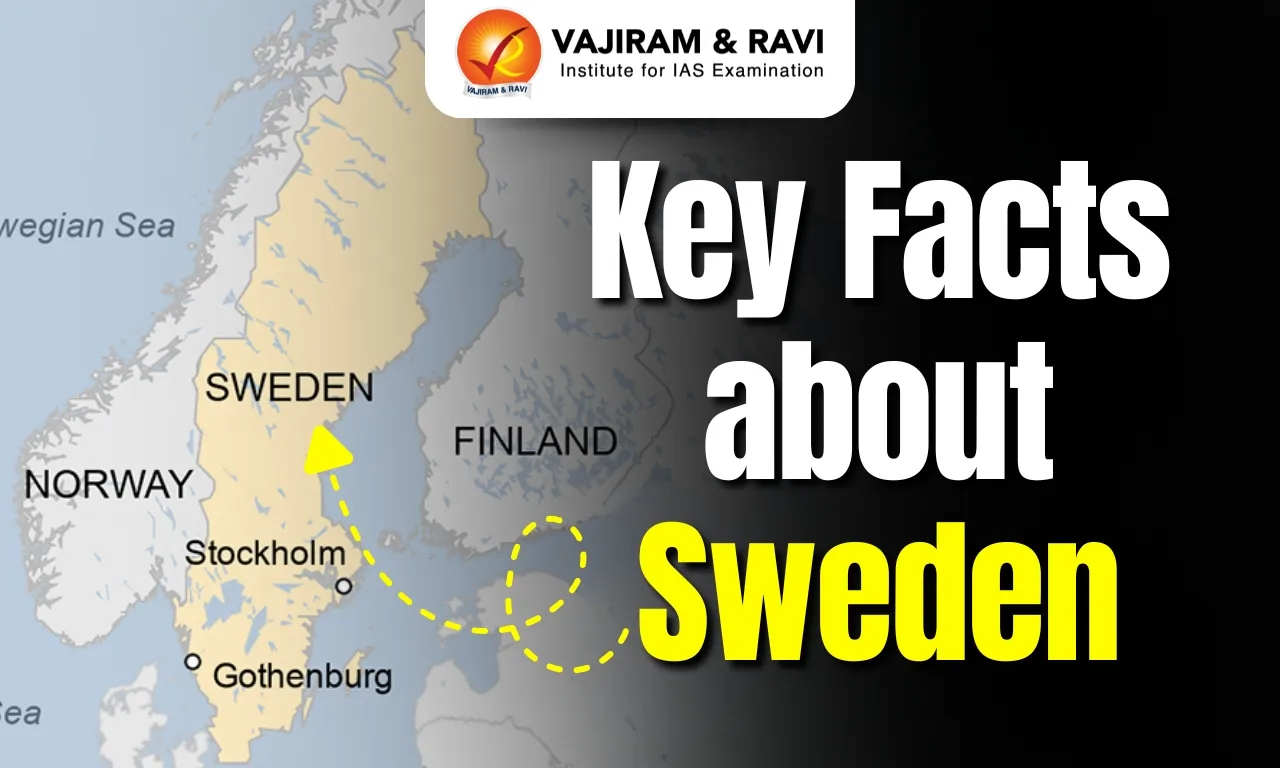
Key Facts About Rwanda:
- Geography: A landlocked country in East-Central Africa, referred to as the “Land of a Thousand Hills”.
- Borders: Burundi, Tanzania, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Rivers: The Nile and Congo rivers flow through Rwanda.
- Capital City: Kigali.
Q1). What are the components of a virus?
A virus contains genetic material (DNA or RNA) inside a protein coat called the capsid. Some viruses have an outer envelope made of lipids and proteins.
Q2). How are viruses classified based on structure?
Based on structure, viruses are classified as helical, icosahedral, enveloped, and complex. Helical viruses have spiral capsids, and icosahedral has polygonal capsids.
Source: DTE
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the first week of March 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India