Wind energy is a renewable energy source that uses wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind turbines convert the wind's kinetic energy into mechanical power, which can be used to generate electricity or perform other tasks. Wind Energy is a clean source of energy which is sustainable and cost-effective. Wind Energy has high potential in countries like India with a long coastline and high energy imports.
Wind energy use has steadily increased since the 2000s, owing to advances in research and development. However, there are some drawbacks to wind energy, such as high initial setup costs, wildlife threats, weather dependence, and so on. These challenges must be overcome to become self-reliant in energy.
Wind Energy Overview
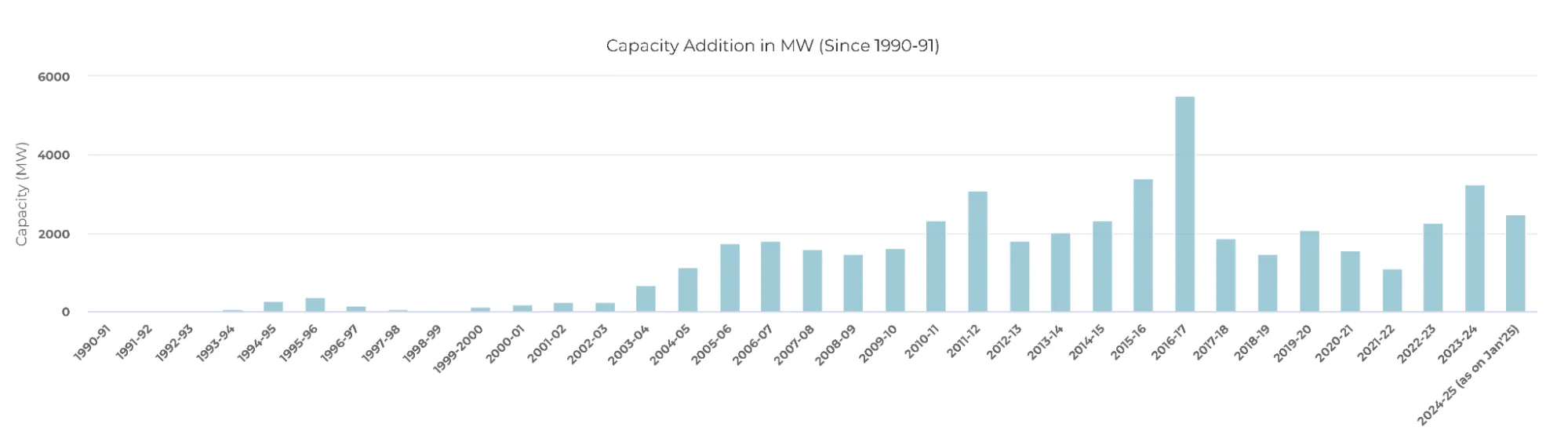
Wind energy is a renewable energy source that uses the wind's kinetic energy to generate electricity. Wind turbines capture the wind's power and use it to spin a generator, which creates electricity. Wind Energy has grown rapidly since 2000 due to R&D, supportive policies, and falling costs. Global installed wind generation capacity has increased from 7.5 GW in 1997 to 733 GW by 2018, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) data.
Wind Energy Sources
Wind energy is a byproduct of the sun. The sun's uneven heating of the atmosphere, the earth's irregular surfaces (mountains and valleys), and the planet's revolution around the sun all work together to generate wind. This wind is converted into wind energy using wind turbines.
Wind Energy Working Principle
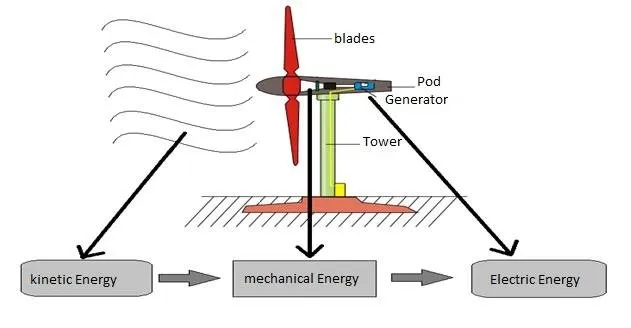
Wind Energy is generated using Wind turbines, which operate on a simple principle: rather than using electricity to create wind, as a fan does, wind turbines generate electricity from wind. Wind, which has kinetic energy, is used to rotate a turbine's propeller, which in turn spins a generator to produce electricity. The further details are mentioned below:
- Role of Wind Turbine: A wind turbine converts wind energy into electricity using the aerodynamic force of its rotor blades, which function similarly to an airplane wing or helicopter rotor blade.
- Role of air pressure: When wind blows across the blade, the air pressure on one side of the blade drops. The difference in air pressure between the two sides of the blade generates both lift and drag. The lift force exceeds the drag force, causing the rotor to spin.
- Electricity production: The rotor is connected to the generator, either directly or via a shaft and a series of gears, which speeds up the rotation and allows for a physically smaller generator. The translation of aerodynamic force into the rotation of a generator produces electricity.
Wind Energy Types
Wind Energy systems are of various types depending on their environment and geographical location. They each have certain unique characteristics and features. Wind Energy types include onshore, offshore, and hybrid systems. They are discussed in detail below:
- Onshore System: It refers to a wind power generation system where wind turbines are installed on land, harnessing the wind's energy to produce electricity. The Muppandal Wind Farm in Tamil Nadu is one such system.
- Offshore System: This refers to a wind power generation system where wind turbines are situated offshore, utilizing the force of the wind to generate electricity and supply it to the onshore electricity network. India is taking steps to build an offshore wind farm near the Gujarat Coast.
- Hybrid System: Hybrid systems combine wind with other renewable energy sources, such as solar energy systems, to improve energy reliability and grid stability. These systems exemplify the innovative approach to hybrid energy solutions, which maximise energy production from multiple sources.
Current Status of Wind Energy in India
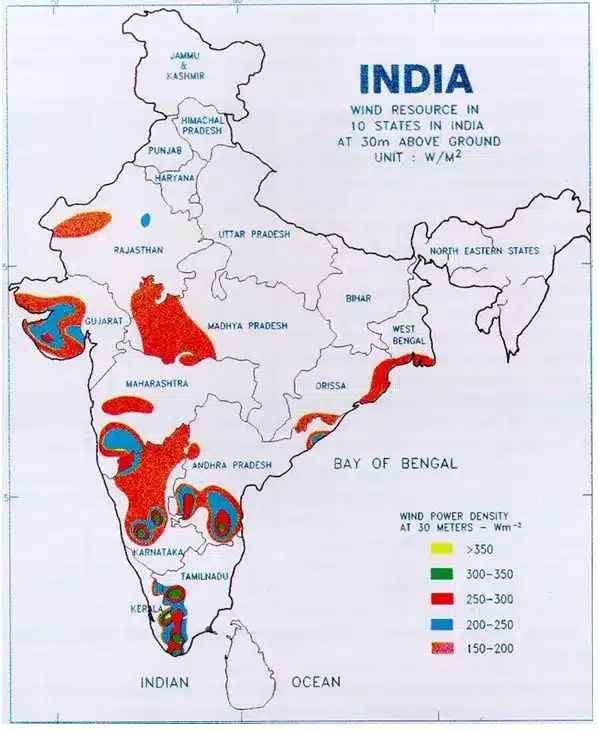
India has the fourth-highest wind installed capacity in the world, with a cumulative installed wind power capacity of 46.4 GW by May 2024. It also has a total of 695.50 GW wind potential at 120m (above ground level) and 1163.9 GW wind potential at 150m. Wind is an intermittent and site-specific resource of energy, and therefore, an extensive Wind Resource Assessment is essential for the selection of potential sites.
- The National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE) has installed over 900 wind-monitoring stations all over the country.
- Out of the total estimated potential, seven states account for more than 95 percent of commercially exploitable resources: Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu.
Wind Energy Plants in India
Wind Energy Plants in India are mainly situated in the coastal states. The Major Wind Energy Plants include Muppandal Wind Farm, Jaisalmer Wind Park, Brahmanvel Wind Farm, etc. The details are mentioned below:
- Muppandal Wind Farm: The Muppandal Wind Farm, located in the Kanyakumari district of India, is the country's largest operational wind farm. It is operated by the Tamil Nadu Energy Development Agency and has a total installed capacity of 1,500 MW.
- Jaisalmer Wind Park: The Jaisalmer wind park, which is the country's second-largest onshore wind project with a capacity of 1,064 MW, is located in Rajasthan's Jaisalmer district and includes sites such as Amarsagar, Badabaug, Baramsar, Tejuva, Soda, Mada, etc.
- Brahmanvel Wind Farm: It was developed by Parakh Agro Industries with a capacity of 528 MW in Maharashtra's Dhule district.
- Dhalgaon Wind Farm: It was developed by Gadre Marine Exports with a capacity of 278 MW in Sangli, Maharashtra.
- Vankusawade Wind Park: It is situated on a mountain plateau 1,150m above the Koyana Reservoir, near Satara, with a capacity of 259 MW.
Wind Energy Top States in India
Wind Energy States in India include Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Telangana, Madhya Pradesh, etc. The details for some top wind energy potential states are mentioned below:
- Gujarat: It has the highest wind potential in India with 142.56 GW at 120m and 180.8 GW at 150m. It was also felicitated for achieving the highest wind capacity addition through open access in financial year 2022-23.
- Rajasthan: It has the second-highest wind potential in India with 127.75 GW at 120m and 284.2 GW at 150m. It was felicitated for achieving the highest wind capacity addition in the financial year 2022-23.
- Tamil Nadu: Tamil Nadu has the highest repowering potential of any wind energy-generating state, with over 7,000 MW of installed capacity that can be replaced or refurbished. It was felicitated for initiating the repowering of wind turbines in the financial year 2022-23.
Wind Energy Advantages
Wind Energy, being a renewable source of energy, has several advantages, which include being a clean source of energy, cost-effectiveness, generating extra revenue, and supporting economic growth. The details are discussed below:
- Unlimited Supply: Wind Energy is unlimited in supply; this makes wind power a sustainable energy source for the future, ensuring a consistent supply of energy while not depleting the Earth's resources.
- Clean Source: Wind energy is an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels, as it generates electricity without releasing harmful gases or pollutants into the air, making it a clean energy source that helps protect our planet.
- Cost-Effective: The Land-based, utility-scale wind turbines are one of the least expensive energy sources available today. Furthermore, as wind energy science and technology advances, its cost competitiveness improves.
- Provides Economic Stability: Wind power can decrease a country's reliance on imported fossil fuels, generating electricity locally. It also mitigates the impact of fluctuating oil and gas prices, ensuring a consistent energy supply.
- Easy Integration: Wind energy generation works well in agricultural and multi-use work environments. Wind energy is easily integrated into rural or remote areas, such as farms and ranches, as well as coastal and island communities, which frequently have high-quality wind resources.
- Promotes technological growth: The advancement of wind power drives technological innovation, enhancing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of wind turbines. This progress can benefit other areas of renewable energy and technology.
Wind Energy Disadvantages
Wind Energy is a sustainable source of energy, but it possesses some disadvantages which reduce its adoption. The disadvantages include threats to wildlife, high initial setup costs, noise of windmills, etc. The details are discussed below:
- High Initial costs: The initial cost of building a wind farm can be high due to the cost of land, manufacturing, installation, and infrastructure.
- Weather Dependent: Wind turbines' electricity generation is influenced by weather conditions, making it challenging to predict their output over time. Low wind speeds can prevent the turbine's rotor from spinning, making wind energy unavailable during peak demand periods.
- Noise Pollution: Wind turbines produce both aerodynamic noise from the blades cutting through the air and mechanical noise from the power generation machinery inside them. The noise can disturb wildlife and may affect their habitation, reproduction cycle, and migration habits.
- Location Dependent: Wind power is not suitable for all areas, as it requires strong and steady winds. Even in ideal locations like coastal areas, hills, and open fields, energy generation slows or stops when the wind stops, a concept known as "intermittency".
- Danger to Wildlife: Wind turbines can be deadly to wildlife. The interference with bat sonar navigation leads to their collision with turbines. Similarly, birds collide with turbines while migrating, leading to their death.
Wind Energy Government Initiatives
Government Initiatives for India's indigenous wind energy sector have demonstrated consistent progress. The result was a robust ecosystem for the expansion of the wind industry and the creation of a manufacturing base of approximately 18,000 MW annually. The various support mechanisms are discussed in detail below:
- National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy (2018): The policy seeks to promote hybrid projects that combine wind and solar power, thereby improving grid stability and reducing reliance on a single energy source.
- Financial Incentives: The government is promoting wind power projects across the country through private sector investment, offering fiscal and financial incentives like Accelerated Depreciation benefits and concessional custom duty exemption on wind generator components, and the Generation-Based Incentive Scheme for projects commissioned before March 31, 2017.
- Increasing Wind Capacity: The government has declared a trajectory for the Wind Renewable Purchase Obligation until 2030, as well as a waiver of Interstate Transmission System (ISTS) charges for interstate sales of solar and wind power for projects that will be commissioned by June 30th, 2025.
- Transparent Bidding Process: Government Guidelines for Tariff-Based Competitive Bidding Process for Power Procurement from Grid-Connected Wind Power Projects seek to provide a transparent, standardised wind power procurement process.
National Offshore Wind Energy Policy
National Offshore Wind Energy Policy was notified by the Ministry of New & Renewable Energy in 2015 under the power conferred to it by Article 297 of the Constitution. The National Offshore Wind Energy Policy aims to increase the utilization of the offshore wind energy potential of India. The National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE) will be the country's nodal agency for offshore wind energy development.
- The policy aims to use the country's coastline to generate renewable energy
Wind Energy Way Forward
India's approximately 7500 km long coastline offers significant potential for self-sufficiency in energy needs if wind energy is effectively utilised. The various steps for effectively utilizing wind energy include the following:
- Research & Development: Investing in advanced turbine technology for greater efficiency and developing offshore wind farms.
- Integration of renewable sources: Wind power can be integrated with other renewable sources like solar energy through hybrid systems and improved grid infrastructure for better transmission.
- Government Support: Promoting supportive government policies and fostering research and development to address environmental concerns and cost reduction.
Wind energy is a key renewable resource that will help India significantly reduce carbon emissions and meet climate change targets under the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 13. It plays a crucial role in India's commitment to achieving 50% of its electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy sources by 2030 and reaching net zero by 2070.
Wind Energy UPSC PYQs
Q.1 Examine the potential of wind energy in India and explain the reasons for their limited spatial spread. (UPSC Mains 2022)
Q.2 Do you think India will meet 50 percent of its energy needs from renewable energy by 2030? Justify your answer. How will the shift of subsidies from fossil fuels to renewables help achieve the above objective? Explain. (UPSC Mains 2022)
Q.3 “Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)”. Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (UPSC Mains 2018)
Q.4 The “Miyawaki method’ is well known for the: (UPSC Prelims 2022)
(a) Promotion of commercial farming in arid and semi-arid areas
(b) Development of gardens using genetically modified flora
(c) Creation of mini forests in urban areas
(d) Harvesting wind energy on coastal areas and on sea surfaces.
Ans. (c)
Last updated on January, 2026
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 Postponed for CSE & IFS which was scheduled to be released on 14 January 2026.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Wind Energy FAQs
Q1. What do you mean by wind energy?+
Q2. What are 5 advantages of wind power?+
Q3. What are the sources of wind energy?+
Q4. What is the principle of wind energy?+
Q5. What are the main applications of wind energy?+