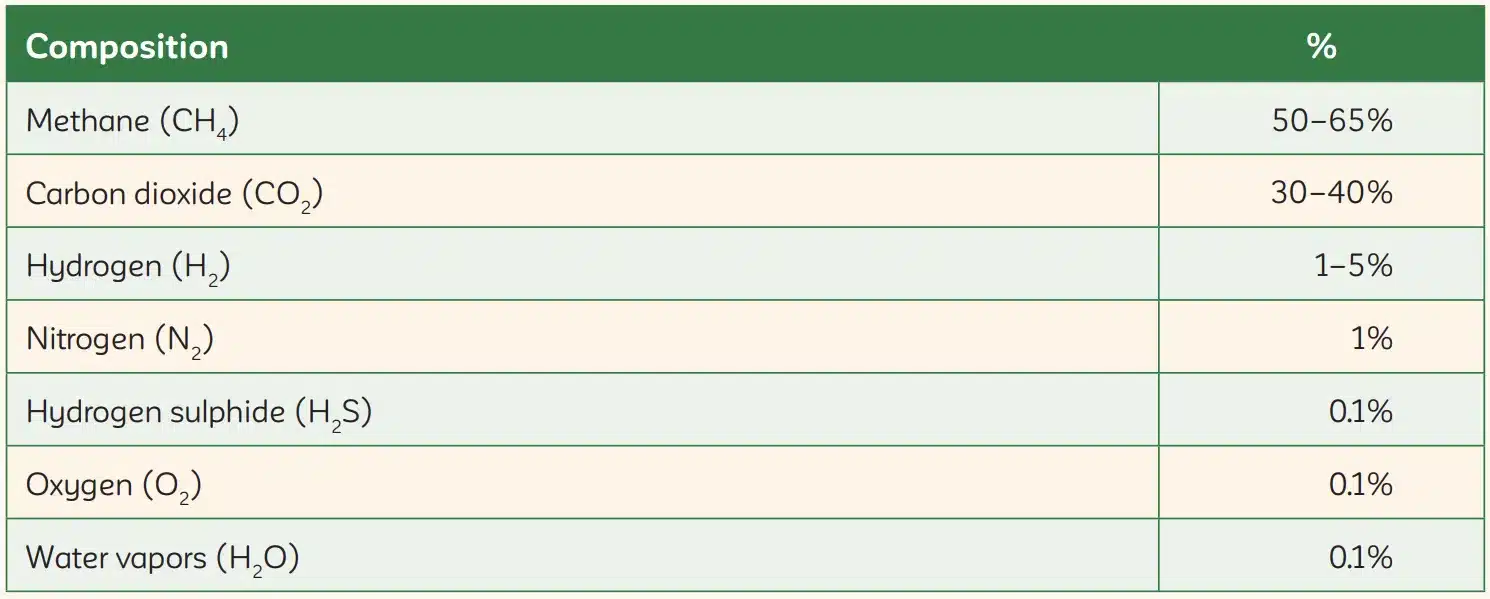
Biogas is an environmentally friendly renewable energy source formed by the breakdown of organic matter, such as food scraps and human/animal waste. Biogas is produced through anaerobic digestion, a sustainable and cyclical process that uses agricultural waste. Biogas is composed primarily of methane and carbon dioxide. It may also contain small amounts of hydrogen sulfide, siloxanes, and moisture.
Biogas production can help reduce natural gas and crude oil imports, manage waste, and generate rural employment. However, it faces issues such as a lack of funds, inconsistent quality, and supporting infrastructure. Therefore, the government needs to renew its focus on biogas to make it a sustainable fuel for the future.
About Biogas
Biogas is an energy-rich gas produced during the anaerobic digestion of biomass. Biogas, primarily composed of methane, natural gas, carbon dioxide, water vapor, and hydrogen sulfide, is mainly utilized in wastewater treatment plants for electricity generation or natural gas production.
Biogas Types
Biogas produced using organic matter mainly consists of two types, which are Liquid Biogas and Compressed Biogas. The biogas types are discussed in detail below:
- Liquid biogas (LBG): It is a clean vehicle fuel and an eco-friendly substitute for heating and electricity generation. It is derived from biogas through a liquefaction process and helps in reducing emissions and making it easier to store and transport.
- Compressed biogas (CBG): It is a high-density fuel that contains more than 90% methane and is formed by compressing biogas. It replaces conventional fossil fuels and is increasingly used in transportation as an environmentally conscious alternative.
Biogas Production
Biogas production happens in a biogas plant, which provides an oxygen-free environment for its production. The different stages in biogas production include the following:
- Pre-treatment and digestion: A variety of organic substrates enter the digester for processing. The fermentation tanks can accommodate a wide variety of substrates, but some may require pre-treatment in specialized containers before entry.
- Fermentation: The substrates are heated to a particular temperature while the microorganisms present in the digester start degrading organic matter in the absence of light and oxygen. Layer formation within the tank is avoided through careful mixing.
- Biogas production: Fermentation produces biogas, which is primarily composed of methane. Along with methane and carbon dioxide, the gas contains water and hydrogen sulfide, emphasizing the need for strong steel tanks to withstand gas exposure.
- Digestate extraction: Following fermentation, the digester is purged of any residual digestate. This nutrient-rich biogas compost acts as an environmentally friendly fertilizer, helping to reduce waste and improve agricultural practices.
- Biogas purification: Rigorous biogas-upgrading processes remove water, impurities, and hydrogen sulfide from biogas. This meticulous purification yields biomethane, which is suitable for energy and heat generation. Quality control ensures the suitability of the final product.
Biogas Applications
Biogas has numerous applications in the energy sector, improving efficiency while reducing environmental impact. The various applications include use as alternative fuels, electricity generation, waste management, and so on. The applications are discussed in detail below:
- Alternative Fuel: Biogas, a valuable alternative to fossil fuel, can be used to replace traditional gasoline or diesel. Biogas combustion emits significantly fewer greenhouse gases and pollutants, helping to clean the air and reduce carbon emissions.
- Electricity Generation: Biogas presents a renewable way to generate electricity which can be then fed into the grid or used on-site.
- Waste Management: Biogas is produced by the digestion of crop residues and manure in wet or dry processes. This helps in the processing of waste materials that would otherwise pollute landfills.
- Use in gas pipeline: Biogas can be upgraded into biomethane, also called renewable natural gas (RNG), and injected into natural gas pipelines. This can help boost natural gas supply.
Biogas Production in India
Biogas Production in India, since the 1980s, has expanded through decentralized models that use cattle manure in rural areas, as well as programs for energy recovery from municipal, industrial, and agricultural waste. The status of biogas production in India is discussed in detail below:
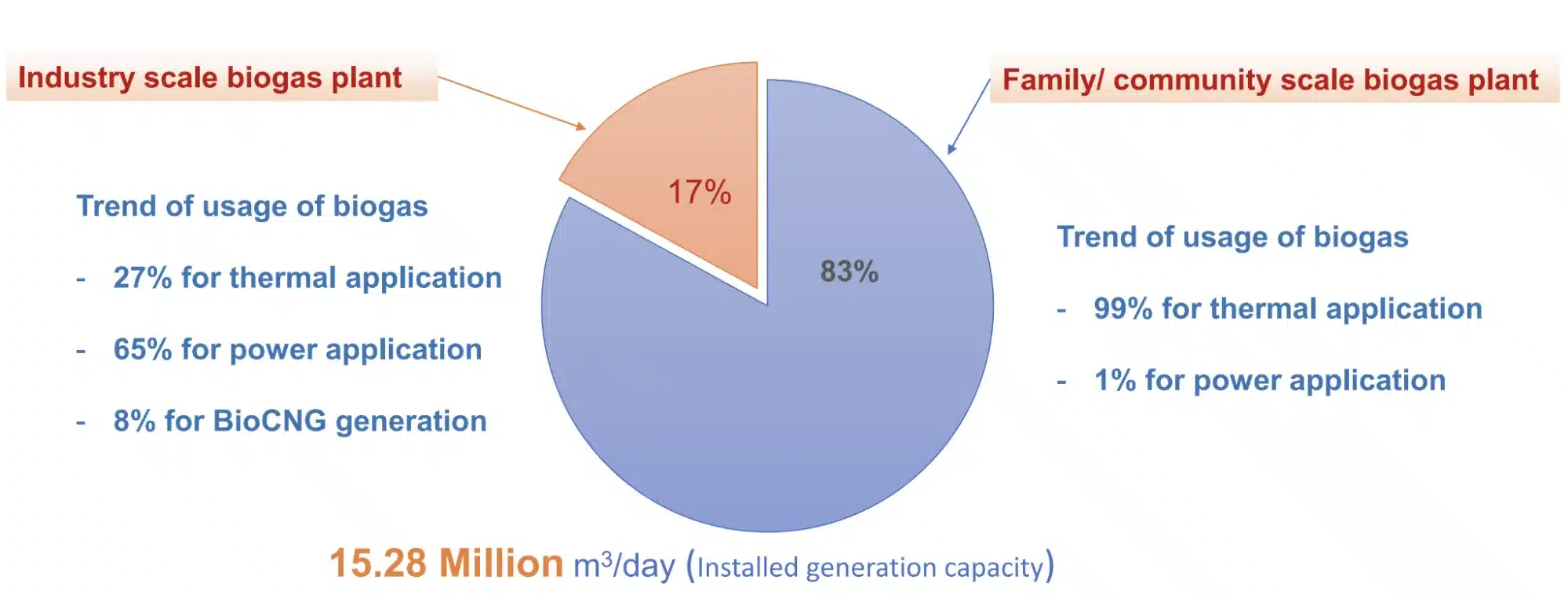
- Biogas Plants: There are more than 5.1 million biogas plants installed in India.
- Nature: The majority of these plants are household/community type, producing 1-25 m3 biogas per day to meet cooking fuel needs.
- Capacity: These plants have a biogas generation capacity of approximately 4.43 million cubic meters per day (MCD), which is equivalent to around 47 gigawatts or 3.2 billion cubic meters per year.
Biogas Advantages
Biogas has several advantages, including being environmentally friendly, reducing pollution, producing organic fertilizer, promoting the circular economy, and so on. The advantages are discussed in detail below:
- Environmentally Friendly: Biogas is a renewable and clean energy source generated through biodigestion, a natural process that reduces greenhouse emissions without combustion.
- Pollution Reduction: Biogas generation improves water quality by deactivating pathogens and parasites, reducing waterborne diseases. Biogas plants improve waste collection and management, leading to improvements in the environment, sanitation, and hygiene.
- Organic fertilizer: Biogas generation produces enriched organic digestate, a suitable alternative to chemical fertilizers. This fertilizer enhances plant growth and disease resistance.
- Boosts Circular Economy: Biogas production is a cost-effective and easy-to-set-up technology that uses kitchen waste and animal manure. The gas produced is used for domestic consumption and farms.
- Healthy Alternative: Biogas generators save women and children from firewood collection, allowing more time for cooking and cleaning. Cooking on a gas stove prevents smoke exposure, preventing deadly respiratory diseases.
Biogas Disadvantages
Biogas is a promising bioenergy alternative, but it has several disadvantages as well. The disadvantages include inefficient production, weather dependence, lack of suitability for dense urban areas, foul odor, etc. The disadvantages are discussed in detail below:
- Dependence on Weather: Biogas generation is influenced by weather, with optimal bacteria digestion temperature around 37°C, and in cold climates, digesters require heat energy to maintain a constant biogas supply.
- Lack of Technological Developments: Biogas production is currently inefficient due to a lack of new technologies, making large-scale production unattainable for large populations.
- Despite some energy needs being met by biogas plants, many governments are hesitant to invest in the sector, limiting its potential for large-scale production.
- Unsuitable for Metropolitan: Biogas generation is more suitable for rural and suburban areas due to its limited use in industrial plants, where abundant raw materials like food waste and manure are available.
- Foul Odour: Biogas plants emit foul odours from their waste, indicating that power plants should be located away from residential and industrial areas.
National Policy on Biofuels
National Policy on Biofuels was made in 2009 by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy. It was amended in 2018 and 2022, with the new indicative target set to 20% blending of ethanol in petrol and 5% blending of biodiesel in diesel by 2030. The salient features are discussed in detail below:
- Biofuel Classification: The policy distinguishes between Basic Biofuels (1G) and Advanced Biofuels (2G and 3G) to facilitate financial incentives.
- Raw Material Expansion: It permits diverse materials for ethanol production, including surplus food grains and damaged crops like Sugarcane Juice, Sweet Sorghum, broken rice, Rotten Potatoes, etc.
- Role of Coordination Committee: Farmers face potential price inconsistencies during surplus production, so the policy permits the use of surplus food grains for ethanol production and petrol blending, with approval from the National Biofuel Coordination Committee.
- Viability Gap Funding: The policy proposes a Rs.5000 crore funding scheme for 2G ethanol biorefineries over 6 years, focusing on advanced biofuels, with additional tax incentives and higher purchase prices compared to 1G biofuels.
- Supply Chain Setup: The Policy promotes the establishment of supply chain mechanisms for biodiesel production using non-edible oilseeds, used cooking oil, and short gestation crops.
Biogas Government Initiatives
The Government of India has launched several initiatives to promote biogas in India. The various initiatives include the National Biogas Programme, the SATAT Initiative, and the Gobar Dhan Scheme, among others. The initiatives are discussed in detail below:
- National Biogas Programme (NBP): The Biogas Programme aims to develop biogas plants for clean cooking fuel and decentralized power generation.
- It also aims to improve sanitation, management of biogas plant slurry, and creating rural employment, ultimately reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- SATAT Initiative: The Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) scheme for Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) encourages entrepreneurs to establish CBG plants and supply it to Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) for use as automotive and industrial fuels.
- Gobar Dhan Scheme: The Galvanising Organic Bio-Resources Dhan (GOBARdhan) scheme is an initiative to convert organic waste like cow dung & agricultural residue into energy and wealth.
- It is part of the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) and aims to improve village cleanliness and environmental sanitation.
- RUCO Initiative: The Food and Safety Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) initiated the Repurpose Used Cooking Oil (RUCO) initiative to combat the reintroduction of UCO back into the food supply, aiming to create a legal framework to shift UCO towards other waste-to-wealth industries like Biogas production.
Biogas Way Forward
Biogas has huge potential in India, it can support India's energy transition by improving energy security & affordability, promoting entrepreneurship, and boosting local economies. The further need is to improve infrastructure, strengthen the regulatory framework, and generate awareness about the potential of Biogas.
- Developing the biogas industry is crucial for India's energy security and meeting ambitious climate goals, including Sustainable Development Goal 7 of Affordable & Clean Energy.
Biogas UPSC PYQs
Q.1 Do you think India will meet 50 percent of its energy needs from renewable energy by 2030? Justify your answer. How will the shift of subsidies from fossil fuels to renewables help achieve the above objective? Explain. (UPSC Mains 2022)
Q.2 Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (UPSC Mains 2018)
Q.3 Write a note on India’s green energy corridor to alleviate the problems of conventional energy. (UPSC Mains 2013)
Q.4 Which one of the following statements best describes the term ‘Social Cost of Carbon’?
It is a measure, in monetary value, of the (UPSC Prelims 2020)
- long-term damage done by a tonne of CO2, emissions in a given year
- requirement of fossil fuels for a country to provide goods and services to its citizens, based on the burning of those fuels
- efforts put in by a climate refugee to adapt to live in a new place
- contribution of an individual person to the carbon footprint on the planet Earth
Ans: (a)
Q.5 Consider the following: (UPSC Prelims 2019)
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into the atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the second week of April 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Biogas FAQs
Q1. What is the composition of biogas?+
Q2. What are the main uses of biogas?+
Q3. What are the properties of biogas?+
Q4. What is the working principle of biogas plant?+
Q5. Where is Asia's largest biogas plant?+
Tags: biogas quest upsc economy notes