Hydro Energy is a renewable source of energy generated from flowing water. Hydro Energy is one of the world’s oldest and largest renewable energy sources. Hydro energy, also known as hydroelectric power, is generated by using the kinetic energy of flowing water to turn a turbine, which then spins a generator to produce electricity. Hydropower currently generates more electricity than all other renewable technologies combined and is expected to remain the world’s largest source of renewable electricity generation into the 2030s.
The hydro energy capacity of India is 42 GW (2024), and it plans to increase it to 67 GW by 2031-32. Thus, there is a need to capitalize on the potential of Hydro Energy to create a sustainable future.
Hydro Energy Overview
Hydro Energy is the energy generated by harnessing the flow of water through a turbine, which generates electricity as it spins. Hydro energy is a clean source of energy that relies on the water cycle. Hydro energy projects range from small-scale systems for homes to large-scale systems for entire regions or countries. Hydro Energy accounts for approximately 71% of total renewable electricity generation on Earth.
Hydro Energy Plants
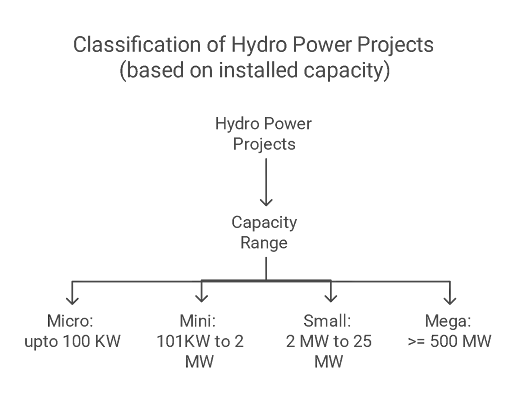
Hydro Energy Plants are classified into different types based on factors such as water availability, power generation scale, and geographical conditions. The various types of Hydro Energy Plants based on net volume and flow of water include run-of-river, storage-based, pumped storage, and offshore hydro energy plants.
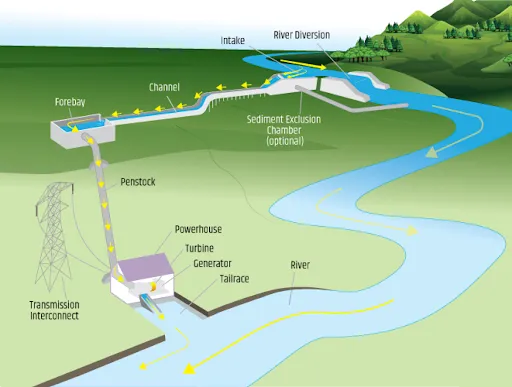
- Run-of-River: A diversion, also known as a "run-of-river" facility, is a project where a portion of a river is channeled through a canal or penstock to harness the natural decline of the river bed elevation for energy production. It may not require a dam for working.
- Examples include the Coo-Trois-Ponts plant in Belgium, the Khimti I project in Nepal, the Kishanganga project in India.
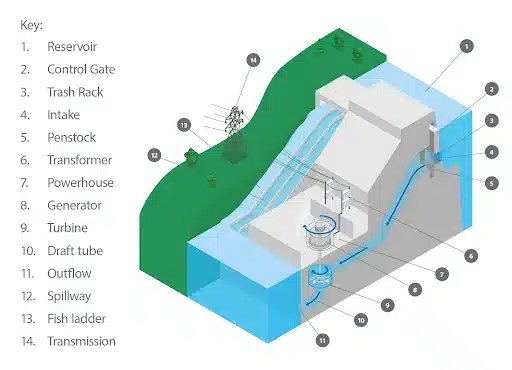
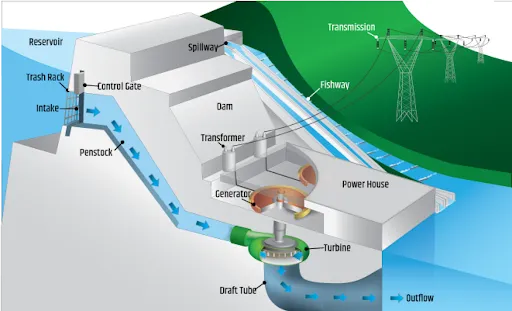
- Storage-based: An impoundment facility, also known as “storage-based hydropower”, is a large hydroelectric power plant that uses a dam to store river water in a reservoir. The water is then released through a turbine, spinning and generating electricity to meet various needs like flood control, recreation, fish passage, and environmental and water quality.
- Example includes the Koyna Hydroelectric Project(India), the Three Gorges Dam (China), and the Grand Coulee Dam (USA)
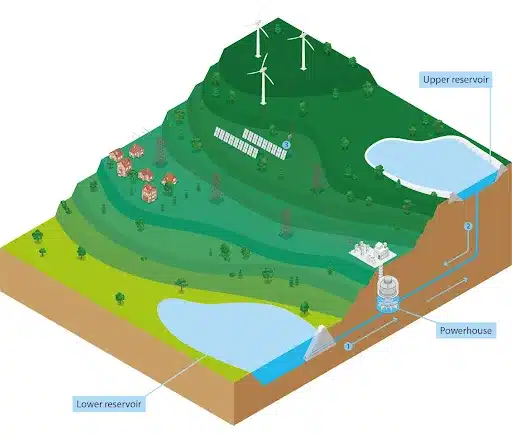
- Pumped Storage: Pumped storage hydropower (PSH), also known as ‘the Water Battery’, is a type of hydropower that stores electricity from other sources like solar, wind, and nuclear.
- It works like a giant battery, pumping water from a lower reservoir to an upper one. When demand is low, water is stored, and during high demand, it is released back to the lower reservoir, generating electricity.
- Example includes the Nagarjuna Sagar project (India) and the Fengning Pumped Storage Power Station (China).
- Offshore hydropower: It is a less established but growing group of technologies that generate electricity from seawater by harnessing tidal currents or wave energy.
Hydro Energy Working Model
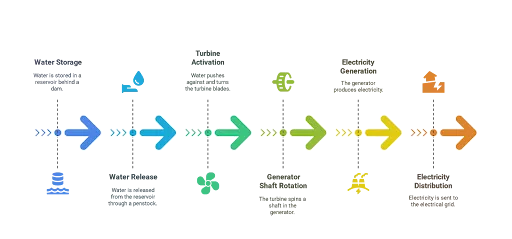
Hydro Energy Power Plants work on the principle of converting the kinetic energy of flowing water into electricity. The plants are generally located near the water sources. The water is elevated to a height and allowed to flow through a pipe called penstock. The water pushes against the blades of the turbine and spins them. The turbines then power a generator which produces electricity. This is sent to the electricity grid for consumption.
Hydro Energy Advantages
Hydro Energy has several advantages such as cost-effective nature, clean source of energy, tourism potential, flexibility, etc. The following are advantages of hydro energy:
- Renewable Source: Hydropower generates energy from the water cycle, which is powered by the sun, making it renewable.
- Cost-Effective: Hydro Energy has minimal recurring costs and low long-term expenditure, making it cheaper than coal and gas-fired electricity.
- Disaster management: Hydropower offers numerous benefits beyond electricity generation, including flood control, irrigation support, and clean drinking water.
- Flexible Supply: Hydropower plants are crucial for providing backup power during electricity outages as they can swiftly adjust their output to meet demand.
- Tourism potential: Storage-based hydropower creates reservoirs for recreational activities such as fishing, swimming, and boating.
Hydro Energy Disadvantages
Hydro Energy has several disadvantages, such as impact on marine life, high upfront cost, drought, safety issues, etc. The disadvantages are discussed in detail below:
- Impact on Environment: Building dams leads to the disruption of marine life and may affect the natural flow of the river, leading to floods.
- High Initial Costs: Hydropower plants have high upfront costs, which, when compared to the falling prices of solar installations, becomes a disadvantage.
- Impact of Drought: A drought can significantly decrease the capacity to generate electricity by limiting the flow of water into the plant.
- Globally, hydropower output experienced a significant drop of 8.5% during the first half of 2023, primarily attributed to widespread droughts.
- Safety issues: Hydropower plants can result in huge damage and loss of life in case of failure.
- Tiware Dam in Maharashtra's Ratnagiri district was breached, flooding seven villages and sweeping away 20 people on July 2, 2019.
- Cultural issues: Large Hydropower Plant construction leads to the displacement of Indigenous people (tribes are most affected) who have a cultural and spiritual connection with the land, leading to conflict.
Hydro Energy Way Forward
Hydro Energy is an efficient way to produce energy for a sustainable future. The solution lies in improved efficiency, energy decentralization, and continued investment in developing new plants along with technological developments. Hydro Energy, along with other sources such as solar and wind energy, has the potential to meet global energy demand and reduce the global carbon footprint.
Hydro Energy UPSC PYQs
Q.1 Suggest measures to improve water storage and irrigation system to make its judicious use under the depleting scenario. (UPSC Mains 2020)
Q.2 What do you understand by run of the river hydroelectricity project? How is it different from any other hydroelectricity project? (UPSC Mains 2013)
Q.3 Recently, the term “pumped-storage hydropower” is actually and appropriately discussed in the context of which one of the following? (UPSC Prelims 2024)
(a) Irrigation of terraced crop fields
(b) Lift irrigation of cereal crops
(c) Long duration energy storage
(d) Rainwater harvesting system
Ans. (c)
Q.4 With reference to ‘Water Credit’, consider the following statements: (UPSC Prelims 2021)
- It puts microfinance tools to work in the water and sanitation sector.
- It is a global initiative launched under the aegis of the World Health Organization and the World Bank.
- It aims to enable the poor people to meet their water needs without depending on subsidies.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Hydro Energy FAQs
Q1. What is meant by hydro energy?+
Q2. What is benefit of hydro energy?+
Q3. What is the principle of hydroelectricity?+
Q4. What are the disadvantages of hydropower?+
Q5. Who is the top producer of hydropower?+