Hydroelectric power plants play a crucial part in India's energy sector. Due to the presence of 197 Hydroelectric power plants, India ranks fifth in hydropower capacity. In 1947, hydropower accounted for approximately 37% of the total power generating capacity and more than 53% of power generation. In the late 1960s, coal-fired power generation began to supplant hydropower in India, and hydropower's share of capacity and generation fell dramatically.
With India’s ambitious renewable energy target of achieving 500 GW from non-fossil sources by 2030. The hydro capacity of India is likely to increase from 42 GW to 67 GW by 2031-32, marking an increase of more than half of the present capacity.
Hydroelectric Power Plants in India Overview
Hydroelectric power plants in India provide huge potential to transition towards clean and sustainable electricity generation. India has the world’s 5th largest hydropower capacity due to the presence of numerous rivers, lakes, etc., along with the monsoon climate. Hydroelectric power plants in India have a potential of 1,45,320 MW, but as of 2023, only 29% is being utilized.
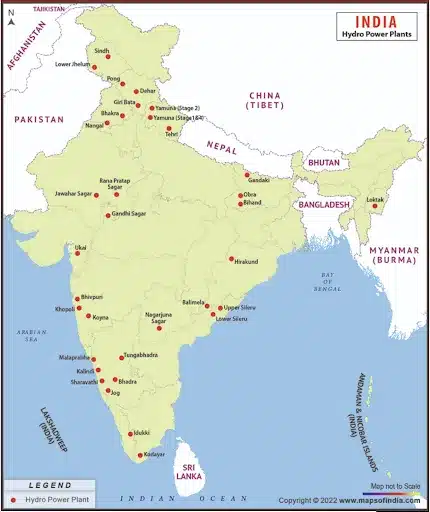
Hydroelectric Power Plants in India Map
Hydroelectric power plants in India map shows the location of the most important Hydroelectric power plants, including Koyna, Nagarjuna Sagar, Hirakund, Bhakra, Pong, and Idukki, among others. The map of Hydroelectric power plants in India is shown below:
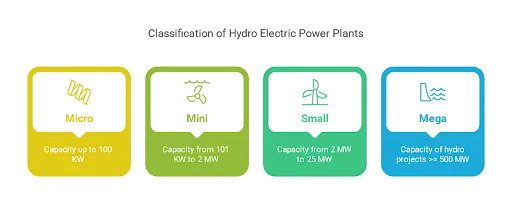
Hydroelectric Power Plants in India Classification
Hydroelectric power plants in India are categorized into small and large hydro plants, based on their size. In India, projects up to 25 MW are classified as Small Hydro Power (SHP). The categories include micro (up to 100 KW), mini (101KW to 2 MW), small (2 MW to 25 MW), and mega (500 MW).
While the Ministry of Power, Government of India, is responsible for large hydro projects, the mandate for the subject of small hydro power (up to 25 MW) is given to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
List of Hydroelectric Power Plants in India
List of Hydroelectric power plants in India shown below contains some of the major Hydroelectric power plants in India such as Koyna Hydroelectric Project, Tehri Hydroelectric Project, Sardar Sarovar Dam, Nathpa Jhakri Hydroelectric Station, etc. The List of Hydroelectric power plants in India is as mentioned below:
Hydroelectric Power Plant in India |
State |
River |
|
Koyna Hydroelectric Project |
Maharashtra |
Koyna |
|
Tehri Hydroelectric Project |
Uttarakhand |
Bhagirathi |
|
Sardar Sarovar Dam |
Gujarat |
Narmada |
|
Nathpa Jhakri Hydroelectric Station |
Himachal Pradesh |
Sutlej |
|
Bhakra Nangal Hydroelectric Project |
Himachal Pradesh/Punjab |
Sutlej |
|
Indira Sagar Hydroelectric Project |
Madhya Pradesh |
Narmada |
|
Subansiri Lower Hydroelectric Project |
Arunachal Pradesh/Assam |
Subansiri |
|
Ramagundam Hydroelectric Project |
Telangana |
Godavari |
|
Chamera Hydroelectric Project |
Himachal Pradesh |
Ravi |
|
Dulhasti Hydroelectric Project |
Jammu & Kashmir |
Chenab |
Hydroelectric Power Plants in India Facts
Hydroelectric power plants in India have several important statistics and facts, such as a hydroelectric potential of 1,45,320 MW, a hydropower capacity of 42104.6 MW, and 90% of plants operated by the public sector etc. The facts are discussed in detail below:
- Hydropower Potential: India's hydropower potential is approximately 1,45,320 MW, which can meet the demand of approximately 84,000 MW at a 60% load factor.
- Hydropower Capacity: As of 2023, out of 145320 MW, 42104.6 MW (29%) has been developed, while 15023.5 MW (10.3%) is under construction.
- Number of Plants: The country has 197 hydropower plants, nine pumped storage stations, and a 4,786MW capacity, according to the International Hydropower Association.
- Public Sector Dominance: India's public sector, including companies like NHPC, SJVNL, NTPC-Hydro, and NEEPCO, operates over 90% of the country's hydroelectricity.
- River Basin Contribution: The majority potential is concentrated in the key basins of the Brahmaputra Basin (66 GW), Indus Basin (34 GW), Ganga Basin (21 GW), and the rivers of South India (24 GW).
- Major Contributing states: The top five hydroelectric power plants in India are located in Uttarakhand, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, and Gujarat.
- Oldest Hydropower Plant: The oldest hydropower plant, called Sidrapong Hydroelectric Power Station, is located in West Bengal's Darjeeling district. It was commissioned in 1897.
- Largest Hydropower Producer: NHPC (formerly National Hydroelectric Power Corporation Ltd) is the largest hydropower development organization in India.
- It will commission hydro projects with a total capacity of 2,170 megawatts (MW) by the end of 2025-26.
Hydroelectric Power Plants in India Advantages
Hydroelectric power plants in India have several advantages, such as cost-effective nature, clean source of energy, tourism potential, flexibility, etc. The advantages are discussed in detail below:
- Low Cost: Hydro energy has low recurring costs and long-term expenditures, making it less expensive than coal and gas-fired electricity. This helps India to reduce its import bill.
- Clean Source: Hydroelectric power plants generate electricity from hydropower, a clean and renewable source of energy. It helps in reducing India’s carbon footprint.
- Flexible Supply: Hydroelectric power plants help to meet India’s seasonal energy demand by swiftly adjusting their output to meet demand and provide backup power during electricity outages.
- Disaster Management: Hydroelectric power plants provide numerous benefits in addition to electricity generation, such as flood control, irrigation support, and safe drinking water.
- Recreation: Storage-based hydropower creates reservoirs for recreational activities such as fishing, swimming, and boating.
- Pong Reservoir is a Ramsar Site and a popular tourist destination due to its unique biodiversity, which includes birds such as the Bar-Headed Goose.
Hydroelectric Power Plants in India Disadvantages
Hydroelectric power plants in India have several disadvantages, such as impact on marine life, high upfront cost, drought, safety issues, etc. The disadvantages are discussed in detail below:
- Environmental Impact: Hydroelectric power plants may disrupt marine life and alter the natural flow of a river, resulting in floods.
- Experts warned that the Subansiri Lower Hydroelectric Project may endanger marine life because of its large size and potential to significantly impede fish migration.
- High Initial Costs: Hydroelectric power plants have high upfront costs, which, when compared to the falling prices of solar installations, becomes a disadvantage.
- Impact of Drought: A drought can significantly decrease the capacity to generate electricity by limiting the flow of water into the plant.
- Due to Drought, Tehri hydroelectric dam, India’s tallest, had no usable water stored in its reservoir in 2016.
- Safety issues: Hydropower plants can result in huge damage and loss of life in case of failure.
- Teesta Urja (run-of-the-river hydro power project) suffered massive damage in 2023 due to a flood caused by the breach in Lhonak Lake in north-west Sikkim.
- Cultural issues: Large Hydroelectric power plant construction causes displacement of Indigenous people who have a cultural and spiritual connection to the land, resulting in conflict.
Hydroelectric Power Plants in India Way Forward
Hydroelectric power plants in India have huge potential. However, Hydroelectric power projects have faced challenges like natural disasters, geological surprises, and contractual disputes, leading to slower capacity addition in recent years.
Thus, there is a need to improve private sector investment, solve inter-state disputes, clearly define eco-sensitive zones, and generate awareness about the benefits of hydropower. These steps will improve the contribution to Hydro Energy in India and help meet the growing energy demand for a Vikshit Bharat by 2047.
Hydroelectric Power Plants in India UPSC PYQs
Q.1 Dam failures are always catastrophic, especially on the downstream side, resulting in a colossal loss of life and property. Analyze the various causes of dam failures. Give two examples of large dam failures. (UPSC Mains 2023)
Q.2 Suggest measures to improve water storage and irrigation systems to make its judicious use under the depleting scenario. (UPSC Mains 2020)
Q.3 What do you understand by run-of-the-river hydroelectricity project? How is it different from any other hydroelectricity project? (UPSC Mains 2013)
Q.4 Recently, the term “pumped-storage hydropower” is actually and appropriately discussed in the context of which one of the following? (UPSC Prelims 2024)
(a) Irrigation of terraced crop fields
(b) Lift irrigation of cereal crops
(c) Long duration energy storage
(d) Rainwater harvesting system
Ans. (c)
Q.5 With reference to ‘Water Credit’, consider the following statements: (UPSC Prelims 2021)
- It puts microfinance tools to work in the water and sanitation sector.
- It is a global initiative launched under the aegis of the World Health Organization and the World Bank.
- It aims to enable the poor people to meet their water needs without depending on subsidies.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Hydroelectric Power Plants in India FAQs
Q1. How many hydroelectric power plants are there in India?+
Q2. What is the rank of India in hydropower?+
Q3. Which state produces the largest electricity?+
Q4. What is the full form of Nhpc?+
Q5. Who is the top producer of hydropower?+
Tags: hydroelectric power plants in india quest upsc economy notes