In the digital age, cybersecurity has emerged as a critical concern for governments, organisations, and individuals. India, being one of the largest digital ecosystems globally, faces significant cyber threats that necessitate a robust and comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy (NCSS).
This strategy aims to protect India's digital infrastructure and ensure the safety of its citizens in cyberspace. The Data Security Council of India (DSCI), as an industry body, has consolidated its perspective on the 2020 national cybersecurity strategy. It seeks to give India access to a reliable, secure, resilient, and dynamic cyberspace.
What is the National Cyber Security Strategy?
The National Cyber Security Strategy is a comprehensive framework designed to safeguard India’s digital ecosystem by protecting critical information infrastructure, promoting data security, enhancing cyber resilience, fostering collaboration among stakeholders, and addressing emerging cyber threats to ensure national security and economic stability.
National Cyber Security Strategy Objectives
The National Cyber Security Strategy was developed in 2020 by the Data Security Council of India (DSCI) under the leadership of Lt General Rajesh Pant. The strategy highlighted 21 key focus areas aimed at creating a secure, reliable, resilient, and growth-and-trust-fostering cyberspace for India. The objectives of the National Cyber Security Strategy include:
- Strengthen Cyber Defences: Develop robust mechanisms to safeguard critical information infrastructure (CII) against cyber threats.
- Promote Data Protection: Establish frameworks for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
- Enhance Collaboration: Foster cooperation among government agencies, private sector players, and international entities to address cybersecurity issues.
- Capacity Building: Train professionals, develop technical expertise, and enhance institutional frameworks for dealing with cyber threats.
Need for a National Cyber Security Strategy
India's rapid digital adoption and increasing cyber threats necessitate a National Cyber Security Strategy. With over 13 lakh cyber incidents in 2022, safeguarding critical infrastructure, digital transactions, and emerging technologies has become imperative amid rising geopolitical risks.
- Rising Cyber Threats: With the rapid digitisation of the economy and India being one of the fastest digital adapters, digital technology presents challenges and risks.
- According to CERT-In (Indian Computer Emergency Response Team), India witnessed over 13 lakh cyber security incidents in 2022, including phishing, ransomware, and data breaches.
- Cyberattacks in India are projected to surge to 1 trillion annually by 2033 and 17 trillion by 2047, according to a PRAHAR study.
- Rise in Digital Transactions: Since the launch of the Unified Payment Interface in 2016, digital transactions have soared. To secure these transactions, a national cyber security strategy was necessary.
- Protection of Critical Infrastructure: Sophisticated cyber threats frequently target essential sectors like energy, banking, healthcare, and defence, necessitating a robust strategy to safeguard national security and operational continuity.
- Geopolitical Risks: State-sponsored and non-state actors are leveraging cyber warfare to target Indian assets, emphasising the need for a unified strategy to strengthen resilience and response mechanisms.
- Cost of Data Breach: India is one of the most affected countries due to targeted attacks and the average cost of a data breach in India.
- A 2023 IBM report found that the average cost of a data breach in India was ₹17.6 crore.
- Emerging Technologies: The proliferation of technologies like 5G, the Internet of Things, and Artificial Intelligence creates new cybersecurity challenges that need to be addressed proactively.
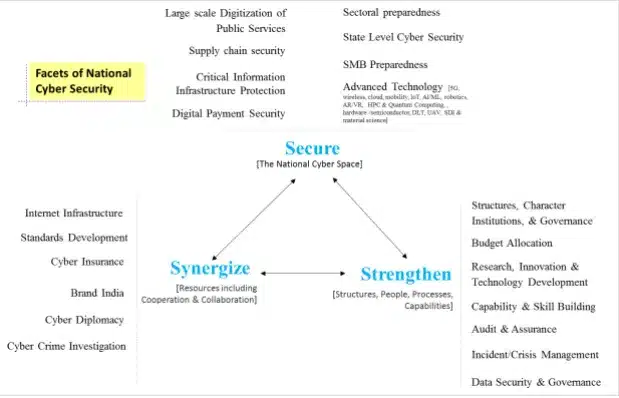
National Cyber Security Strategy Components
The National Cyber Security Strategy outlines key components to safeguard India's digital ecosystem. It focuses on robust security, strengthening institutional frameworks, and fostering synergy through innovative measures, ensuring resilience against evolving cyber threats.
Security Strategies
Security strategies aim to safeguard critical assets and infrastructure by addressing challenges like digitisation, supply chain security, critical information infrastructure protection, and emerging technologies. They ensure resilience, economic growth, and citizen safety amid evolving cybersecurity threats.
- Large-Scale Digitization of Public Services: The strategy calls for cybersecurity operations requiring advanced cybersecurity operations, such as digitisation, empowered security roles, and developing institutional capability for device assessment.
- Supply Chain Security: Under the rapid digitisation of the industry, the strategy demands a two-pronged approach to supply chain security.
- Strategy for products manufactured in the complex global supply chain.
- Strategy for products developed or value-added in India.
- Critical Information Infrastructure (CII) Protection: The strategy emphasises securing CIIs, ensuring the delivery of essential services even in the event of an attack, ensuring economic growth, and promising the safety of citizens. It can be done by integrating supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) with enterprise security.
- Advanced Technology: Disruptive technology transformations such as 5G, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, robotics, the metaverse, etc., bring entirely new paradigms for cybersecurity. The strategy accords investing in the study of technology's potential influence on business, industry, society, and the economy.
Strengthening Strategies
Strengthening strategies in cybersecurity are crucial for safeguarding India's growing digital economy. Key measures include enhancing institutional frameworks, increasing budgetary provisions, fostering skill development, improving audit frameworks, and establishing robust crisis management systems to mitigate emerging cyber risks.
- Institutional Frameworks: Structure, institutions, and governance in India are factoring in cyber security models from around the world.
- Given the complexity and cyber risks of a nation the size of India, it becomes essential to evolve the national cybersecurity and governance institutions.
- Budgetary Provisions: It is advised that cyber security receive at least 0.25% of the Government of India's annual budget. As the country gets closer to becoming a USD 5 trillion economy, with 20% of that amount going towards the digital economy, this percentage can be increased to 1%.
- Capability and Skill Development: India stands as a global leader in cybersecurity expertise. Developing a comprehensive skill-building strategy will not only reinforce this leadership but also unlock the nation’s full potential in this field.
- Additionally, such a strategy will address the growing demands of India’s $1 trillion digital economy, ensuring a skilled workforce to support its expansion.
- Audit and Assurance: As cybersecurity threats become increasingly sophisticated, targeted, and persistent, the expanding digital footprint driven by rapid digitisation heightens exposure to such risks.
- The audit and assurance framework must be restructured to effectively manage the growing scale, speed, and complexity of these challenges.
- Crisis Management: Even the most well-funded security programs cannot eliminate the risk of incidents that may escalate into major crises. Advances in science, process innovation, and technology play a crucial role in identifying and managing such incidents, enabling a more predictable and effective response to the resulting challenges.
Synergising Strategies
Synergising Strategies for India's cybersecurity involve enhancing internet infrastructure, developing technical standards, expanding cyber insurance, promoting "Brand India" in cybersecurity, advancing cyber diplomacy, and bolstering cybercrime investigation through innovation and strategic investments.
- Internet Infrastructure: India’s approach to the Internet infrastructure should be based on the economic reality of its growth in Information & Communication Technologies (ICT) and IT-enabled services.
- For example, India’s IT industry is poised to be a 350 billion dollar industry by 2025. Therefore, India should carefully plan its strategy to advance its interests in light of the geopolitical dynamics surrounding cyberspace technology.
- Standards Development: The rapid pace of technology innovation, particularly in IoT, is causing unprecedented scale and complexity in managing security, necessitating significant investment in technical standard development.
- The development of technology standards can be achieved by raising awareness, attracting top talent, promoting skill development in core technology, and incentivising individuals, institutions, and companies.
- Cyber Insurance: Cyber insurance is becoming an important instrument of cyber risk management. A coordinated national effort is required to evolve the country's cyber insurance market.
- It can be done by raising awareness of cyber insurance among various sectors, developing actuarial science to address complex cybersecurity risks, consulting stakeholders like insurers and risk managers and developing skills in risk management.
- Brand India: India's value proposition needs to be positioned and branded specifically for both domestic and international platforms to serve strategic and commercial interests.
- This can be done by promoting research, innovation, product entrepreneurship, and investment in cybersecurity to attract and develop talent in the niche field.
- India can also be promoted as a destination for cybersecurity products and research and carry out a deliberate branding campaign in cybersecurity.
- Cyber Diplomacy: It is essential to make consistent and significant efforts to support India's leadership in the global governance of cyberspace. It should be done keeping in mind that India,
- Has the world’s second-largest internet user base,
- Is the third-largest start-up ecosystem,
- Leading in successful initiatives in digitisation and
- a global and rising market for digital products and services.
- Cybercrime Investigation: Due to the pervasive role that technology plays in both the commission and detection of crimes, the investigation of cybercrimes and traditional crimes using cutting-edge technological tools and solutions, digital forensics technologies and methods, and legal procedures will be an essential area of national cybersecurity strategy.
National Cyber Security Strategy Challenges
India's National Cyber Security Strategy faces key challenges, including a shortage of skilled professionals, fragmented frameworks, evolving cyber threats, budget constraints, and limited public awareness. All of these require urgent attention for robust cyber resilience.
- Lack of Skilled Workforce: India needs more trained cybersecurity professionals, leaving critical infrastructure vulnerable to sophisticated attacks. Bridging this gap requires focused efforts on capacity building and specialised training programs.
- Fragmented Cybersecurity Framework: The absence of a unified and integrated cybersecurity framework in India complicates threat detection and response. Coordination between government agencies, private sectors, and stakeholders is essential for an effective defence mechanism.
- Evolving Nature of Threats: Emerging technologies like quantum computing, artificial intelligence, and IoT introduce complex cybersecurity risks. These rapidly advancing technologies demand constant updates in security frameworks and proactive measures to address vulnerabilities.
- Budget Constraints: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures requires substantial financial resources. Limited budgets often hinder the adoption of advanced technologies, establishment of infrastructure, and recruitment of skilled personnel for cybersecurity initiatives.
- Limited Public Awareness: Despite efforts like digital literacy campaigns, many citizens lack awareness of basic cyber hygiene practices. This gap increases the risk of phishing, fraud, and data breaches, necessitating widespread awareness programs.
National Cyber Security Strategy UPSC PYQs
Question 1: What are the different elements of cyber security? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (UPSC Mains 2022)
Question 2: Discuss the potential threats of cyber attacks and the security framework to prevent them. (UPSC Mains 2017)
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ UPSC will release the UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2025 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
National Cyber Security Strategy FAQs
Q1. What is the national cyber security strategy?+
Q2. What is a cyber security strategy?+
Q3. What are the 7 elements of national security?+
Q4. What are the three cyber security strategies?+
Q5. What is the lifecycle of a national cybersecurity strategy?+
Tags: national cyber security strategy quest UPSC Internal Security Notes