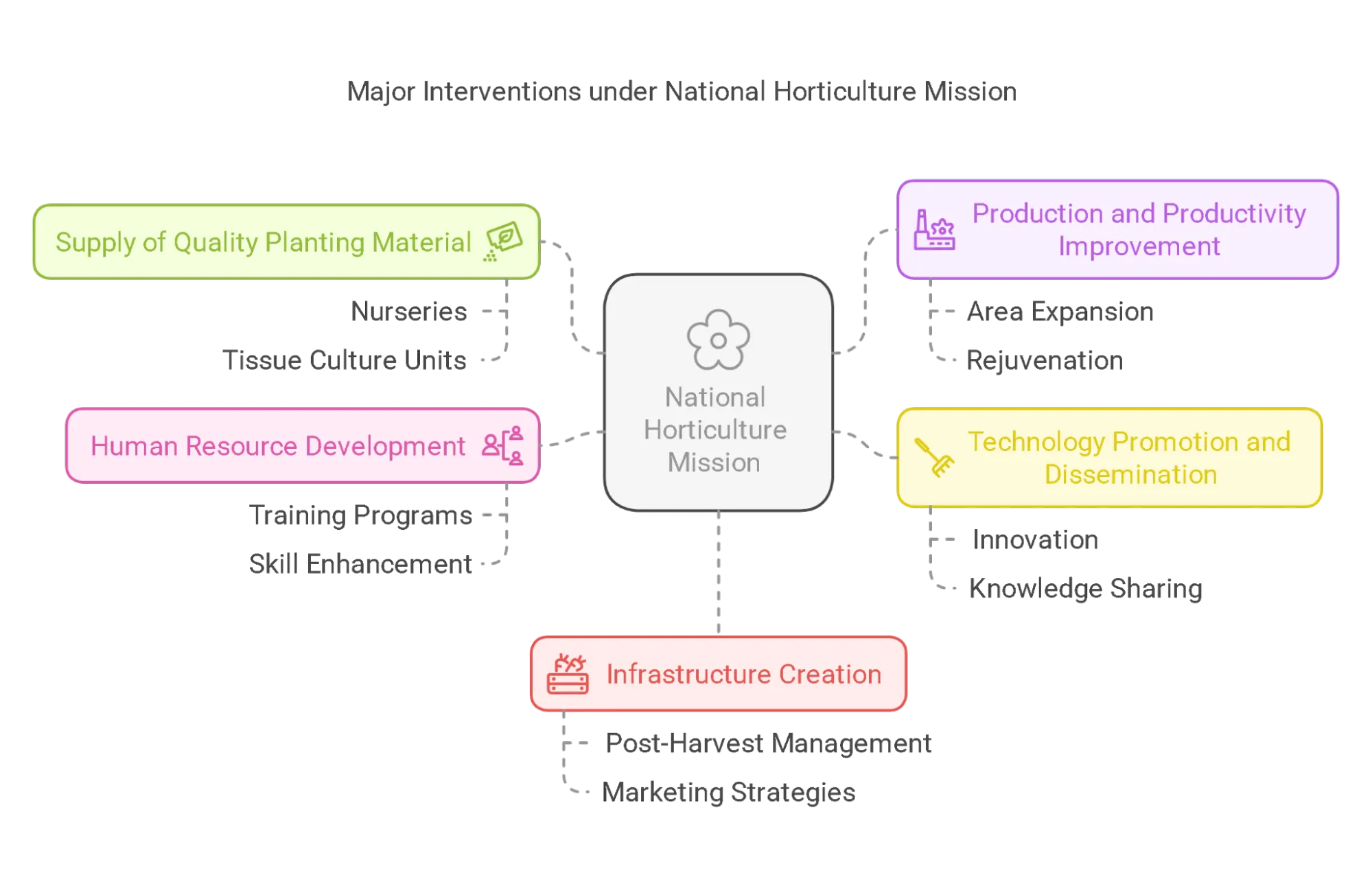
National Horticulture Mission (NHM) is a program that aims to promote holistic growth of the horticulture sector through area-based, regionally differentiated strategies. The NHM was launched in 2005-06 by the Government of India and is a centrally sponsored scheme under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH). This program seeks to ensure forward and backwards linkage through a cluster approach with the active participation of all stakeholders to promote the holistic development of the horticulture sector.
Over the years, the National Horticulture Mission has helped to increase horticulture output, which has contributed significantly to India’s agricultural GDP. However, climate change poses uncertainties and risks to the horticulture sector, imposing constraints on production systems that are required to be resolved for continued growth.
National Horticulture Mission (NHM) About
National Horticulture Mission (NHM) is a centrally sponsored horticulture scheme to promote the output of the horticulture sector. NHM was launched in 2005-06, leading to significant area expansion of horticulture and higher production in the country. NHM was subsumed under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH, 2014-15).
- MIDH, established in 2014-15, integrated various central schemes to promote holistic growth in the horticulture sector, covering fruits, vegetables, root and tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, and coconut.
National Horticulture Mission Objectives
National Horticulture Mission has a primary objective of maximizing the state's horticultural potential and increasing the state's output of all horticultural products. Its objective also includes increasing farmer’s income, improving farm output and skill development. The objectives are discussed in detail below:
- Promote Horticulture: The mission aims to promote the holistic growth of the horticulture sector, including bamboo and coconut, through regionally differentiated strategies, including research, technology promotion, extension, post-harvest management, processing, and marketing.
- Encourage Farmer Associations: To bring about economies of scale and encourage farmers to join farmer groups such as Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Enhance Income: Increase the output of horticulture, increase farmers' incomes, and improve nutritional security.
- Boost Farm Output: Increase output through the use of high-quality seed, planting material, and water-saving microirrigation techniques.
- Skill Development: Encourage young people in rural areas to develop their skills and find work in horticulture and post-harvest management, particularly in the cold chain industry.
Role of National Horticulture Mission
The Role of the National Horticulture Mission is to boost the production, productivity, and income of horticulture farms. Further, it plays a crucial role in increasing the income of farmers. Over the period, it has helped in the expansion of cultivated areas under horticulture, improved plant quality, and worked on capacity building of farmers. The details are discussed below:
- Expansion of Cultivated Area: NHM has provided financial support for the cultivation of various plants, with a focus on high-density planting and rejuvenation of old orchards to boost productivity.
- Improved Plant Quality: Established model nurseries to offer disease-free, high-yielding planting material and promoted hybrid and high-yielding varieties to enhance productivity per hectare.
- Modern Techniques: Promoted use of greenhouse farming, use of drip irrigation for enhanced water-use efficiency, and reduced dependency on chemical fertilisers.
- Capacity Building: Conducted Training programs for farmers and entrepreneurs in collaboration with the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Krishi Vigyan Kendras for research and adoption of modern horticultural practices.
- Post-Harvest Management: NHM aimed to reduce post-harvest losses by constructing cold storage, pack houses, and ripening chambers, and to enhance price realization through aggregation centres and rural markets.
- Promoted High-Value Crops: Farmers are encouraged to diversify their crops from traditional ones to high-value horticultural crops like fruits, vegetables, flowers, spices, and medicinal plants, as they offer higher returns per unit area.
- Enhanced Market Access: Promoted FPOs and directed marketing initiatives to eliminate middlemen, developed rural markets, collection centres, and contract farming linkages for improved farmer price realization.
- Encouraged Value Addition: Financial support is being provided to establish food processing units, agro-industries, and primary processing centres, enabling farmers to sell processed products at higher prices.
Status of Horticulture in India
The status of horticulture in India has improved over time due to the impact of the National Horticulture Mission and continued Government support. The status can be summarised as mentioned below:
- Contribution GDP: The horticulture sector constituting 18% of the area, contributes about 33% of the gross value to the agricultural GDP significantly boosting the Indian economy.
- The sector is being considered as a driver of economic growth and is gradually turning into an organized industry linked to seed trading, value addition, and exports.
- Employment: Horticulture provides rural employment, diversifies farm activities, and enhances farmers' income.
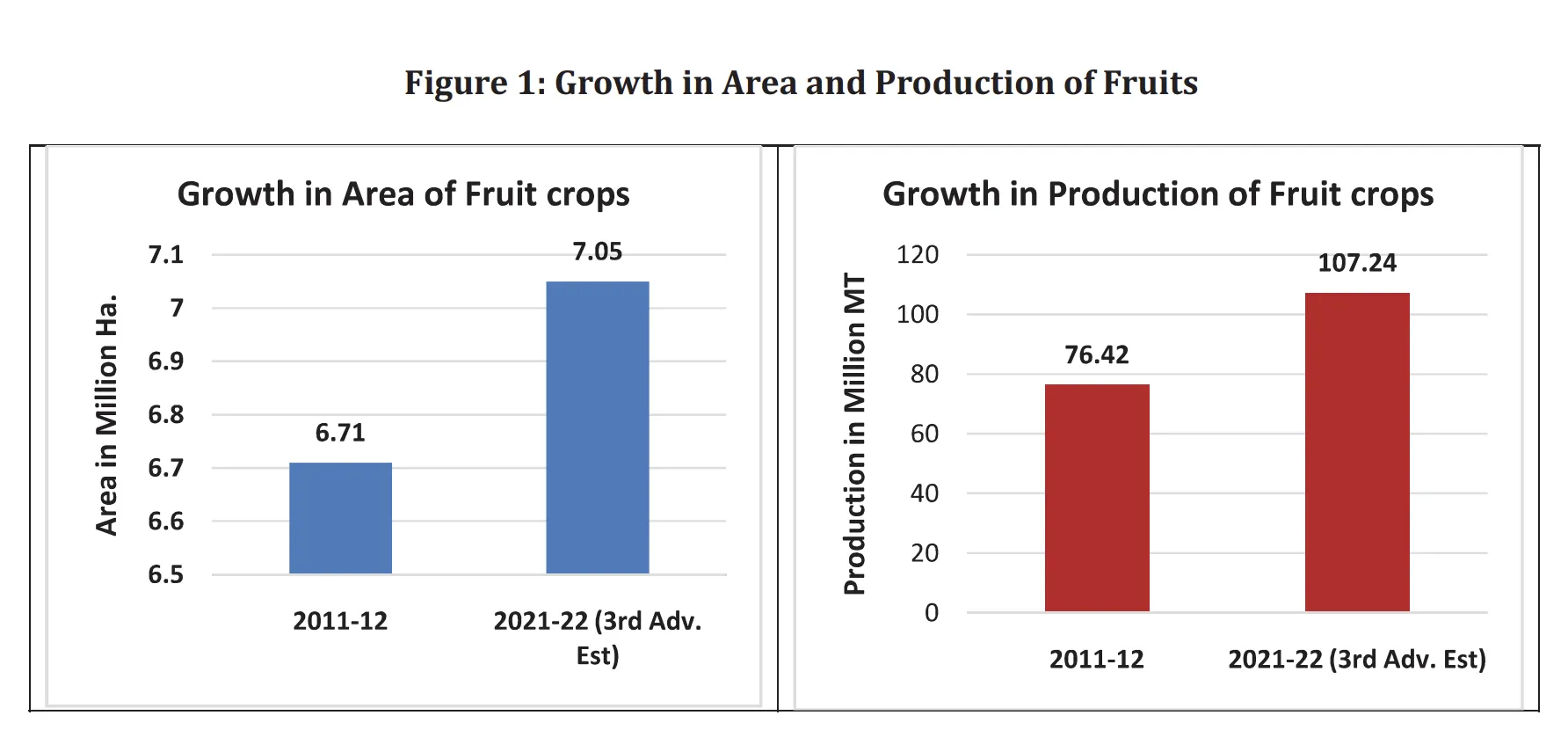
- High Production: India is currently producing about 320.48 million tones of horticulture produce which has surpassed the food grain production, that too from a much less area (25.66 million Ha. for horticulture against 127.6 M. ha. for food grains)
- High productivity: Horticulture crops have high productivity compared to food grains of Kharif and Rabi Crops (12.49 tones/ha against 2.23 tones/ha.)
- Improved India’s Position: India became the world leader in producing various fruits like mango, banana, guava, papaya etc, vegetables, spices, coconut, and cashew nuts.
National Horticulture Mission Significance
National Horticulture Mission (NHM), launched in 2005-06, significantly transformed India's horticulture sector by increasing production, improving quality, and boosting farmers' income, contributing to agricultural growth and rural development. The details are discussed as mentioned below:
- Boosted Production: The initiative boosted agricultural production by encouraging area expansion, promoting high-yielding varieties, and enhancing yield per hectare through high-density planting, protected cultivation, and organic farming.
- Enhanced Farmers Income: The shift from traditional crops to high-value horticultural ones has increased income by 2-3 times and provided employment opportunities, particularly for women and rural youth.
- Strengthened Post-Harvest Infrastructure: The establishment of cold storage, pack houses, ripening chambers, and food processing units has significantly reduced post-harvest losses.
- Contributed to Agricultural GDP: Horticulture now accounts for over 33% of India's agricultural GDP, despite covering only 18% of the total cropped area.
- Food Security: India has become the second-largest global producer of fruits and vegetables, ensuring food and nutritional security.
- Export Growth: India's horticulture exports, including mangoes, grapes, pomegranates, and spices, have significantly grown, boosting the rural economy through strengthened agri-processing industries.
National Horticulture Mission Limitations
National Horticulture Mission faces several limitations and challenges which hinder the realization of its full potential. The limitations like climate change, less technology adoption, high price volatility, and lack of credit supply, etc. have resulted in reducing its positive impact. The details are discussed below:
- Price Volatility: High price volatility in fruits and vegetables affects farmers' income stability.
- Insufficient Cold Storage: Post-harvest losses are high due to inadequate cold chains, pack houses, and processing units, resulting in spoilage and wastage of horticultural crops, reducing profitability.
- Lack of Credit: Small and marginal farmers often face a credit crunch due to delays in the disbursement of subsidies and credit because of red tapism.
- Less Technology Adoption: Low awareness and lack of training results in farmers still focusing on traditional methods of agriculture resulting in lower productivity.
- Climate Change: The issue of climate change and the vagaries of monsoon have led to decreased output for the highly sensitive horticulture crops.
National Horticulture Mission Way Forward
National Horticulture Mission in India needs reforms and interventions to enhance productivity, income, and sustainability, focusing on a more inclusive, technology-driven, and market-oriented approach. The solution lies in improving market linkages, expanding storage facilities, providing credit support, etc. The details are discussed below:
- Improve Market Linkages: Promotion of FPOs to improve collective bargaining potential and expand e-NAM (National Agriculture Market) to include more horticulture produce.
- Better Storage Facilities: Improved Warehousing facilities could be developed using PPP, and support could be provided from the Mega Food Parks scheme.
- Credit support: Focus on enhancing credit supply through interest-free loans and securing the produce through insurance schemes like PM Fasal Bima Yojana
- Technology adoption: Awareness generation among farmers to increasing technology adoption, like Artificial Intelligence-based pest control, drone spraying, etc.
- Climate Resilience: Encourage techniques like organic farming and agroforestry to maintain soil health and biodiversity. Also, methods like rainwater harvesting can help in reducing dependence on monsoons.
- Improve Coordination: Better collaboration between Government, Civil Society Organisations, and Agri-Startups can lead to improved outcomes. Farmer cooperatives for horticulture on the model of AMUL could also be formed to achieve better results.
Thus, to realize the full potential of the National Horticulture Mission a farmer-centric approach is required. As India moves ahead to become the food basket of the world, the role of horticulture becomes very crucial and the National Horticulture Mission can help us further improve our agriculture production.
National Horticulture Mission UPSC PYQs
Q.1 What are the present challenges before crop diversification? How do emerging technologies provide an opportunity for crop diversification? (UPSC Mains 2021)
Q.2 Assess the role of the National Horticulture Mission (NHM) in boosting the production, productivity, and income of horticulture farms. How far has it succeeded in increasing the income of farmers? (UPSC Mains 2018)
Q.3 Explain various types of revolutions, took place in Agriculture after Independence in India. How have these revolutions helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India? (UPSC Mains 2017)
Q.4 In the context of food and nutritional security of India, enhancing the ‘Seed Replacement Rates’ of various crops helps in achieving the food production targets of the future. But what is/are the constraint/constraints in its wider / greater implementation? (UPSC Prelims 2014).
- There is no National Seeds Policy in place.
- There is no participation of private sector seed companies in the supply of quality seeds of vegetables and planting materials of horticultural crops.
- There is a demand-supply gap regarding quality seeds in the case of low-value and high-volume crops.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
a) 1 and 2
b) 3 only
c) 2 and 3
d) None
Ans. (b)
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the second week of April 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
National Horticulture Mission FAQs
Q1. When was the National Horticulture Mission launched?+
Q2. What are the main objectives of the National Horticulture Mission?+
Q3. What is the mission of the National Horticulture Board?+
Q4. What is the new name for the National Horticulture Mission?+
Q5. Who started horticulture in India?+
Tags: national horticulture mission quest UPSC Agriculture Notes