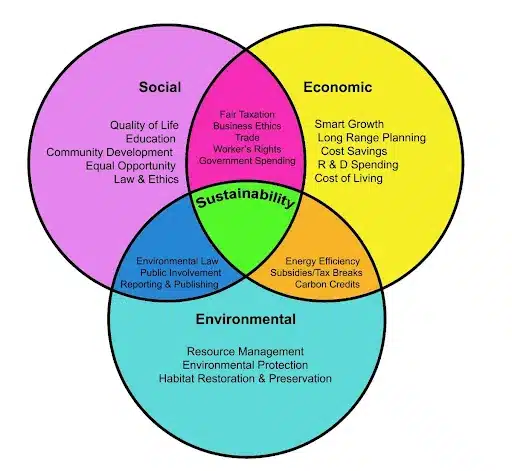
Sustainable development has become crucial as the world faces environmental, social, and economic challenges. Defined by the Brundtland Report (1987), it ensures present needs are met without compromising future generations' ability to meet theirs. It is based on three pillars: economic sustainability (equitable growth), environmental sustainability (resource preservation), and social sustainability (justice and inclusivity).
Milestones like the Stockholm Conference (1972) and the Rio Earth Summit (1992) shaped global sustainability efforts, including the SDGs. Challenges include war, poverty, and environmental degradation. India's initiatives, such as Swachh Bharat and Jal Jeevan Mission, support these global efforts for inclusive, sustainable growth.
Sustainable Development Meaning
Sustainable development, according to the Brundtland Report (1987), is "development that meets present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." The three pillars of sustainability—economic growth, environmental conservation, and social equity—are highlighted in this formulation in a balanced manner.
- Economic sustainability is the process of ensuring that growth in the economy is equitable, helps all facets of society, and doesn't deplete natural resources or harm the environment.
- Environmental sustainability is the preservation of the environment through the wise use of natural resources, lowering pollution levels, and lessening the effects of climate change.
- Social sustainability is the advancement of social justice, equity, and inclusivity while guaranteeing that everyone has access to opportunity, fundamental necessities, and an education.
Sustainable Development History
Sustainable development’s history has evolved from early environmental concerns into a global framework uniting economic growth, social equity, and environmental protection, reflecting our awareness of their interconnectedness.
- Stockholm Conference(1972): The Stockholm Conference was the first global meeting to address environmental issues, leading to the creation of UNEP and recognizing the need to integrate environmental protection with economic development.
- The Brundtland Commission (1987): The Brundtland Report, "Our Common Future," formally introduced sustainable development as a concept that balances present needs with future generations' ability to meet theirs, calling for integrated policies.
- The Rio Earth Summit(1992): The Rio Earth Summit produced Agenda 21 and other key agreements, marking a major global effort to draft strategies for sustainable development and address issues like climate change and biodiversity.
- Continuing the Journey Toward Sustainability(2015): The adoption of the 2030 Agenda and the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set a global framework to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all by 2030.
Sustainable Development Features
Sustainable development features focus on balancing economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity. These principles guide policies to ensure long-term well-being without compromising resources for future generations.
- Intergenerational Equity: Ensures that current development activities do not compromise the ability of future generations to meet their needs, promoting fairness across time.
- Integration of Environmental and Economic Goals: Emphasises the harmonious advancement of economic growth alongside environmental preservation, recognising that long-term prosperity depends on a healthy ecosystem.
- Social Inclusion and Equity: Advocates for equal access to resources and opportunities, aiming to reduce disparities and foster inclusive societies where all individuals can thrive.
- Precautionary Principle: Encourages proactive measures to prevent environmental degradation, even in the face of scientific uncertainty, to safeguard ecological integrity.
- Polluter Pays Principle: Holds that those responsible for pollution should bear the costs of managing it, incentivising environmentally responsible practices.
Sustainable Development Objectives
Sustainable Development Objectives aim to harmonise economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection to ensure a balanced and equitable future. They serve as a blueprint for global progress, addressing challenges like poverty, inequality, and climate change. By fostering partnerships and encouraging responsible resource use, these objectives strive to create resilient societies and a healthier planet for current and future generations.
Sustainable Development Principles
Sustainable development principles combine social, economic, and environmental goals to promote global well-being. They aim to provide quality education, healthcare, and employment while preserving ecosystems and protecting all forms of life.
- Protecting the natural environment and ecosystems
- Safeguarding global biodiversity and species variety
- Promoting inclusive and long-term societal progress
- Enhancing and preserving human capital through health and education
- Regulating population growth for resource balance
Sustainable Development Importance
Sustainable development is vital for balancing economic growth with environmental protection and social equity, as it fosters resource efficiency, climate change mitigation, social inclusion, and global cooperation to address pressing challenges.
- Environmental Protection: Reduces the negative effects of pollution, deforestation, and climate change to preserve ecosystems for future generations.
- Resource Efficiency: Promotes the wise use of finite resources such as water, minerals, and energy.
- Economic sustainability: Encourages long-term strategies for strong and resilient economic systems.
- Social inclusion: It ensures equitable access to basic necessities, which helps to reduce poverty and social disparities.
- Climate Change Mitigation: The goal is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote renewable energy adoption to address climate challenges.
- Global Responsibility: Encourages international cooperation to combat global issues such as environmental degradation and poverty.
Sustainable Development Challenges
Sustainable development faces numerous challenges, including war and instability, implementation barriers in developing countries, governmental resistance to change, persistent poverty and inequality, economic fluctuations, rapid population growth, environmental degradation, and technological and financial gaps.
- War and Instability: Conflicts disrupt sustainable development efforts, as seen in the global food security impact of the Ukraine war.
- Implementation Barriers: Developing countries struggle to adopt sustainable practices without financial and technological support.
- Governmental Resistance: Political priorities and reliance on industries like fossil fuels often hinder sustainable development.
- Poverty and Inequality: Addressing poverty and inequality is complex, with issues like unemployment and energy poverty exacerbated by global crises like COVID-19.
- Economic Fluctuations: Global economic downturns negatively affect sustainability, particularly in poorer nations reliant on trade.
- Population Growth: Rapid growth increases demand for resources, making it harder to achieve sustainability goals.
- Environmental Degradation: Ongoing issues like deforestation and pollution challenge efforts to balance development with environmental protection.
- Technological and Financial Gaps: Limited access to modern technologies and funding hampers sustainable development, especially in developing nations.
Sustainable Development Initiatives
Global sustainable development initiatives, like the Stockholm Conference, Earth Summit, and Paris Agreement, have integrated environmental concerns into economic policies, encouraging nations to adopt sustainable practices. In India, national initiatives such as the Swachh Bharat Mission, Jal Jeevan Mission, and Namami Gange align with these global efforts, focusing on inclusive growth, environmental sustainability, and improving rural and urban living standards.
Sustainable Development Global Initiatives
Global initiatives like the Stockholm Conference, Earth Summit, and Paris Agreement have integrated environmental concerns into economic policies, promoting sustainable practices. Key agreements, including the Kyoto Protocol and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), have played an important role in incorporating environmental concerns into economic policies, encouraging countries to adopt sustainable practices.
- The Stockholm Conference (1972): The first major global effort to address environmental issues, resulting in the Stockholm Declaration and the establishment of the UNEP to coordinate global environmental actions.
- Earth Summit (1992): Held in Rio de Janeiro, this summit resulted in key agreements such as the UNFCCC and Agenda 21, which laid the groundwork for incorporating environmental sustainability into global economic development.
- Kyoto Protocol (1997): Establishes legally binding targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and introduces economic incentives such as carbon trading to encourage cleaner technologies.
- Rio+10 (2002): Following the Earth Summit, the World Summit on Sustainable Development reviewed progress and emphasized the importance of global cooperation in sustainable development.
- The Paris Agreement (2015): It strengthened global commitments to reducing carbon emissions, encouraging investments in renewable energy, and promoting sustainable economic practices.
- Global Conventions: Agreements like the Ramsar Convention (1971), Montreal Protocol (1987), and Convention on Biological Diversity (1992) have integrated sustainability into global policies, promoting economic growth while preserving natural resources.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): These 17 global goals, which were launched in 2015, aim to achieve long-term economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection by 2030, with a focus on poverty eradication and equality.
Sustainable Development National Initiatives
India's national sustainable development initiatives are consistent with the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These programs prioritise health, sanitation, water management, rural development, and infrastructure etc to achieve inclusive and long-term growth throughout the country.
- The Swachh Bharat Mission (Clean India Mission): It was launched in 2014 to eliminate open defecation and improve solid waste management, transforming hygiene practices across the country.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: It was launched in 2019 to provide piped water to every rural household by 2024, with a focus on water source development and community participation.
- National Rural Drinking Water Program (NRDWP): It ensures safe drinking water in rural areas by promoting sustainability and community-based management.
- Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY): ABHY was launched in 2018 to manage groundwater resources sustainably through community involvement and demand management.
- National Urban Sanitation Policy (NUSP): It aims to improve urban sanitation through effective waste management and toilet construction.
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP): It was established in 2019 to combat air pollution through prevention, control, and abatement measures, as well as increased monitoring.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS): It offers guaranteed employment through public works projects, improving rural livelihood security.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G): It aims to provide affordable housing in rural areas.
- Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana - National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY NRLM): It helps rural communities improve their livelihoods through skill development and self-help groups.
- POSHAN Abhiyan: It uses targeted strategies to reduce stunting, undernutrition, anaemia, and low birth weight.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana: The world's largest health assurance program offers annual health coverage of ₹5 lakh per family for poor and vulnerable households.
- Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan: It enhances school effectiveness and educational outcomes while promoting equitable access to quality education.
Sustainable Development Way Forward
India is at a watershed moment in its journey towards sustainable development, attempting to strike a balance between rapid economic growth and environmental stewardship. To create a more sustainable future, the country is taking a multifaceted approach that focuses on energy, agriculture, and urban planning.
- Expand Wind Power: More wind turbines should be installed in high-wind regions to generate clean energy and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Invest in Solar Energy: Invest in solar photovoltaic cells to capture abundant sunlight and support the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to encourage global solar energy adoption.
- Subsidise LPG: Subsidise LPG to replace traditional biomass fuels like wood and dung cakes, thereby reducing indoor air pollution and deforestation.
- Encourage Biogas Plants: Promote biogas plants that use cow dung as a clean energy source and organic fertiliser, improving energy access and soil quality in rural communities.
- Increase CNG Use: Increase the use of compressed natural gas (CNG) in public transportation systems to reduce urban air pollution and improve air quality.
- Mini-Hydel Plants: Install small-scale hydropower solutions, particularly in mountainous areas, to generate local electricity with minimal environmental impact.
- Restore Traditional Healthcare: Promote traditional healthcare systems like Ayurveda, which provide eco-friendly treatments with few side effects.
- Adopt Sustainable Agriculture: Encourage the use of compost, natural fertilisers, and biopesticides in agriculture to improve soil health and reduce chemical inputs.
- Promote Electric Vehicles: Encourage the use of electric vehicles (EVs) and build the necessary charging infrastructure to reduce emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Strengthen Climate Resilience: Implement disaster preparedness and climate adaptation strategies to better address the effects of climate change.
Sustainable Development UPSC PYQs
Question 1: Define the concept of the carrying capacity of an ecosystem as relevant to an environment. Explain how understanding this concept is vital while planning for the sustainable development of a region. (UPSC Mains 2019)
Question 2: “R2 Code of Practices” constitute a tool available for promoting the adoption of (UPSC Prelims 2021)
(a) Environmentally responsible practices in the electronics recycling industry
(b) Ecological management of ‘’Wetlands of International Importance” under the Ramsar Convention
(c) Sustainable practices in the cultivation of agricultural crops in degraded lands
(d) ‘’Environmental Impact Assessment’’ in the exploitation of natural resources
Answer: (a)
Question 3: In rural road construction, the use of which of the following is preferred for ensuring environmental sustainability or to reduce carbon footprint? (UPSC Prelims 2020)
- Copper slag
- Cold mix asphalt technology
- Geotextiles
- Hot mix asphalt technology
- Portland cement
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 4 and 5 only
(d) 1 and 5 only
Answer: (a)
Question 4: The Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE) a UN mechanism to assist countries transition towards greener and more inclusive economies, emerged at (UPSC Prelims 2018)
(a) The Earth Summit on Sustainable Development 2002, Johannesburg
(b) The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development 2012, Rio de Janeiro
(c) The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change 2015, Paris
(d) The World Sustainable Development Summit 2016, New Delhi
Answer: (b)
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Sustainable Development FAQs
Q1. What are the 4 concepts of Sustainable development?+
Q2. What are the 5 Sustainable development?+
Q3. What is the main aim of Sustainable development?+
Q4. Why Sustainable development class 10?+
Q5. What are the 5 C's of sustainable development?+