Thermal Power Plants in India are the cornerstone of India’s energy sector, contributing approximately 78% of the country’s total electricity supply. Thermal Power Plants in India provide critical base-load power, which promotes industrial growth and infrastructure development. While providing energy security and affordability, they also help to balance intermittent renewable energy sources.
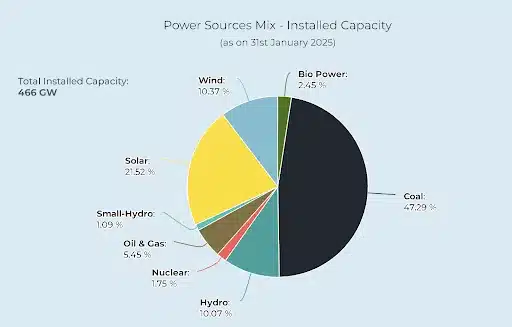
Thermal Power Plants in India in 2024 had a capacity of 243.21 GW, with coal-based plants dominating at 210.96 GW. The nation aims to diversify its energy mix by 2030, aiming for 500 gigawatts (GW) of non-fossil electricity. However, their reliance on fossil fuels raises environmental concerns, necessitating the development of cleaner technologies and a shift to a more sustainable energy mix.
Thermal Power Plants in India Overview
Thermal power plants in India are critical to meeting the increasing energy demand. As of 2023, the number of thermal power plants in India stands at 271. The coal-based Thermal power plants in India have a present installed capacity of 217.5 Gigawatt (GW), additionally, the Government plans to expand by a minimum of 80GW by 2031-32.
- Currently, India has 27,180 MW of Thermal Capacity under construction, and the total anticipated Thermal capacity addition by 2031-2032 is likely to be 87,910 MW.
- Since Renewable energy has an intermittent nature, Thermal Power Plants in India remain crucial for an uninterrupted supply of energy.
- Major Thermal Power Plants in India include Vindhyachal Thermal Power Plant(TPP), Mundra TPP, Sasan TPP, Tiroda TPP, etc.
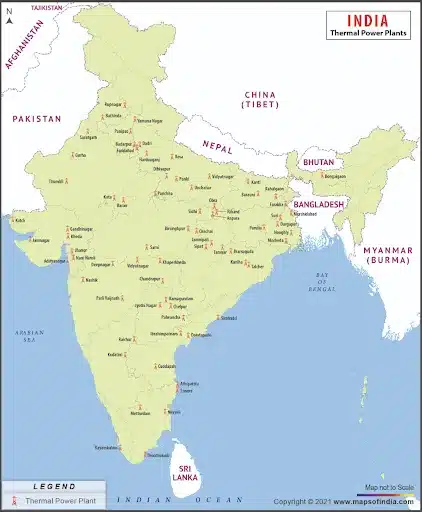
Thermal Power Plants in India Map
Thermal Power Plants in India Map shows the major thermal power plants in India. Thermal power plants are spread across India, with a sparse presence in hilly regions. The Map is shown below with major thermal power plants:
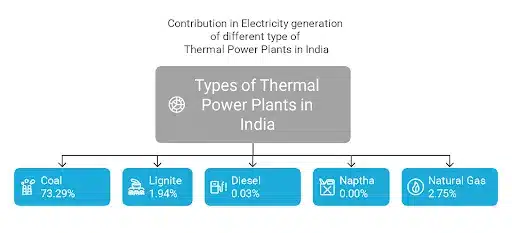
Thermal Power Plants in India Types
Thermal power plants convert the heat energy of primary fuels like coal into electric power. In most thermal power plants, the combustion of primary fuels heats water and converts it to steam. The steam powers steam turbines, which produce electricity. The different types of thermal power plants include Coal-Fired, Gas, Diesel or Liquid fuel, Geothermal, Biomass, and Waste Material-based thermal power plants. In India, Thermal power is mainly generated from coal, Lignite, Diesel, Naphtha, and Natural Gas.
List of Thermal Power Plants in India
List of Thermal Power Plants in India shows the major power plants in India with their location, type, and capacity in Megawatt (MW) as of 2023.
|
Thermal Power Plant |
State |
Capacity(MW) |
Type |
|
Vindhyachal |
Madhya Pradesh |
4760 |
Coal |
|
Mundra |
Gujarat |
4000 |
Coal |
|
Sasan |
Madhya Pradesh |
3960 |
Coal |
|
Adani Power Tiroda |
Maharashtra |
3300 |
Coal |
|
Talcher |
Odisha |
3000 |
Coal |
|
Rihand |
Uttar Pradesh |
3000 |
Coal |
|
Sipat |
Chattisgarh |
2980 |
Coal |
|
Chandrapur |
Maharashtra |
2920 |
Coal |
|
Adani Power Mundra |
Gujarat |
2640 |
Coal |
|
Anpara |
Uttar Pradesh |
2630 |
Coal |
|
Korba |
Chattisgarh |
2600 |
Coal |
|
Ramagundam |
Telangana |
2600 |
Coal |
|
Shree Singaji |
Madhya Pradesh |
2520 |
Coal |
|
Damodaram Sanjeevaiah |
Andhra Pradesh |
2400 |
Coal |
|
Tamnar |
Chattisgarh |
2400 |
Coal |
|
Kudgi |
Karnataka |
2400 |
Coal |
|
Kahalgaon |
Bihar |
2340 |
Coal |
|
Mejia |
West Bengal |
2340 |
Coal |
Major Thermal Power Plants in India
Major Thermal Power Plants in India are mainly coal-based and play a crucial role in India’s energy landscape. The major thermal power plants in India include Vindhyachal Thermal Power Plant (TPP), Mundra TPP, Sasan TPP, Tiroda TPP, Rihand TPP, etc. The major thermal power plants in India are discussed in detail below:
- Vindhyachal Thermal Power Station: It is India's largest thermal plant, located in Madhya Pradesh's Singrauli district. Constructed in 1982, it has a 4,760MW capacity and uses coal from the Nigahi mine.
- Mundra Thermal Power Station: It is India's second-largest, is located in Gujarat's Kutch district and has a capacity of 4,620MW.
- Operated by Adani Power, it comprises nine units and is primarily powered by imported Indonesian coal.
- Sasan Ultra Mega Power Plant: The Sasan Ultra Mega Power Plant in Singrauli, Madhya Pradesh, is among India's largest, with a 3,960MW capacity.
- Owned by Reliance Power, it features six 660MW units fueled by coal from the Moher and Moher-Amlohri mines.
- Tiroda Thermal Power Plant: The Tiroda thermal power plant in Maharashtra, India, is a 3,300MW coal-based facility owned by Adani Power Maharashtra.
- It operates five 660MW units and uses supercritical technology to source water from the Wainganga River. The plant has advanced pollution control systems.
- Rihand Thermal Power Station: The Rihand Thermal Power Station in Rihandnagar, Sonebhadra, Uttar Pradesh, has a 3,000MW capacity and six units, each generating 500MW, commissioned between 1988 and 2013.
- Coal is sourced from Madhya Pradesh's mines, and water is drawn from the Rihand Reservoir.
Thermal Power Plants in India Advantages
Thermal power plants in India are a major source of electricity, contributing significantly to the national power grid. Their benefits include a consistent energy supply, cost-effectiveness, job creation, and reliance on proven technology, among others. The advantages are listed below in detail:
- Reliable & Abundant Energy Source: Thermal power plants, which typically burn fossil fuels like coal, oil, or gas, can generate electricity consistently, making them a reliable energy source, particularly when compared to intermittent sources like Solar Energy or wind.
- Cost Effectiveness: Thermal power plants can be relatively cost-effective, especially when considering the initial investment and operational costs compared to other energy technologies.
- Flexibility in Location: Thermal power plants can be built in various locations as long as there is access to fuel and water for cooling, making them adaptable to different geographical contexts.
- Employment Generation: The construction and operation of thermal power plants create jobs in various sectors, including engineering, maintenance, and fuel handling.
- Thermal power plants in India directly employ a significant number of people, estimated at 3.2 to 4 lakh individuals. (Council On Energy, Environment and Water)
- Supports Economic Growth: The availability of electricity from thermal power plants is crucial for industrial operations, enabling manufacturing and other processes and thus contributing to economic growth.
- According to the National Electricity Plan document, the projected All India peak electricity demand and electrical energy requirement is 277.2 GW for the year 2026-27 and 366.4 GW for the year 2031-32.
- Less Space Requirement: Thermal Power Plants require less space to set up as compared to hydro power plants.
- Well-developed technology: The Technology of Thermal Power Plants is well developed and established due to years of operational experience and abundant infrastructure.
Thermal Power Plants in India Disadvantages
Thermal Power Plants in India pose several challenges like air pollution, impact on marine life, high maintenance costs, reliance on fossil fuels, huge water demand, etc. The disadvantages are listed below in detail:
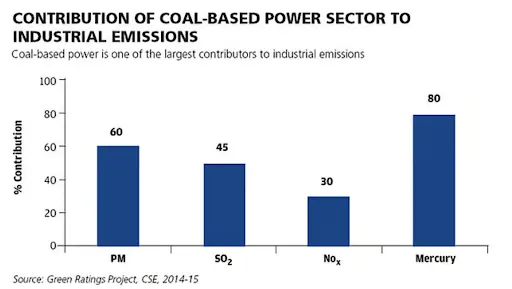
- Environmental Impact: Thermal power plants are major contributors to air pollution, releasing pollutants like particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
- According to the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA), thermal power plants emit ten times more kilotonnes of PM2.5 than crop residue burning, as well as more than 200 times more kilotonnes of sulfur dioxide, another harmful pollutant.
- Impact on Aquatic Life: Thermal power plants require large quantities of water for cooling, which can lead to thermal pollution of water bodies, harming aquatic life.
- Impact of Fly Ash: Thermal power plants release a high amount of fly ash, which can lead to significant air pollutants, causing respiratory issues, soil contamination, and heavy metal leaching into groundwater, affecting plant growth and aquatic ecosystems.
- High Maintenance Costs: Thermal power plants have higher operating costs compared to other electricity generation methods like hydro or Nuclear Energy power due to fuel costs and maintenance.
- Fuel Dependence: Over-reliance on fossil fuels, especially coal, makes thermal power plants vulnerable to price fluctuations and supply disruptions.
- Huge Water Demand: A Thermal power plant requires a large amount of water for cooling, which can strain water resources, especially in regions with water scarcity.
Thermal Power Plants in India Way Forward
Thermal power plants in India are crucial for maintaining grid stability and ensuring energy security by providing a reliable and consistent power supply. They complement intermittent renewable energy sources and reduce the risk of power outages and disruptions. The future of thermal power in India is expected to transition towards cleaner, more sustainable energy sources while maintaining a reliable and affordable power supply.
- To reduce the dependency on coal-based thermal power plants, India has planned to augment non-fossil fuel-based electricity generation capacity.
Thermal Power Plants in India UPSC PYQs
Q.1 To what factors can the recent dramatic fall in equipment costs and tariff of solar energy be attributed? What implications does the trend have for the thermal power producers and the related industry? (UPSC Mains 2015)
Q.2 Environmental impact assessment studies are increasingly undertaken before project is cleared by the government. Discuss the environmental impacts of coal-fired thermal plants located at Pitheads. (UPSC Mains 2014)
Q.3 With reference to coal-based thermal power plants in India, following statements:
(UPSC Prelims 2023)
- None of them uses seawater.
- None of them is set up in water-stressed district.
- None of them is privately owned.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Ans. (d)
Q.4 Consider the following statements: (UPSC Prelims 2020)
- Coal ash contains arsenic, lead, and mercury.
- Coal-fired power plants release sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen into the
environment.
- High ash content is observed in Indian coal.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (d)
Q.5 With reference to ‘fly ash’ produced by the power plants using coal as fuel, which of the following statements is/are correct? (UPSC Prelims 2015)
- Fly ash can be used in the production of bricks for building construction.
- Fly ash can be used as a replacement for some of the Portland cement contents of concrete. 3. Fly ash is made up of silicon dioxide and calcium oxide only, and does not contain any toxic elements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans. (a)
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Thermal Power Plants in India FAQs
Q1. How many thermal power plants are there in India?+
Q2. Where is the largest thermal power plant in India?+
Q3. Which is the 1st thermal power plant of India?+
Q4. Which fuel is used in a thermal power plant?+
Q5. What is the full form of NTPC?+
Tags: quest thermal power plants in india upsc economy notes