Mitochondrial Protein Import Latest News
Recently, researchers at Caltech University have uncovered new rules governing mitochondrial protein import, revising the long-standing understanding of how proteins are transported into mitochondria.
About Mitochondria
- Mitochondria are double-membraned organelles that generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the universal cellular energy currency.
- They originated over a billion years ago through endosymbiosis between a primitive archaeal cell and a bacterium.
- Over time, mitochondria transferred most of their genes to the host nucleus, making them dependent on the host cell for protein supply.
Traditional Model of Protein Import
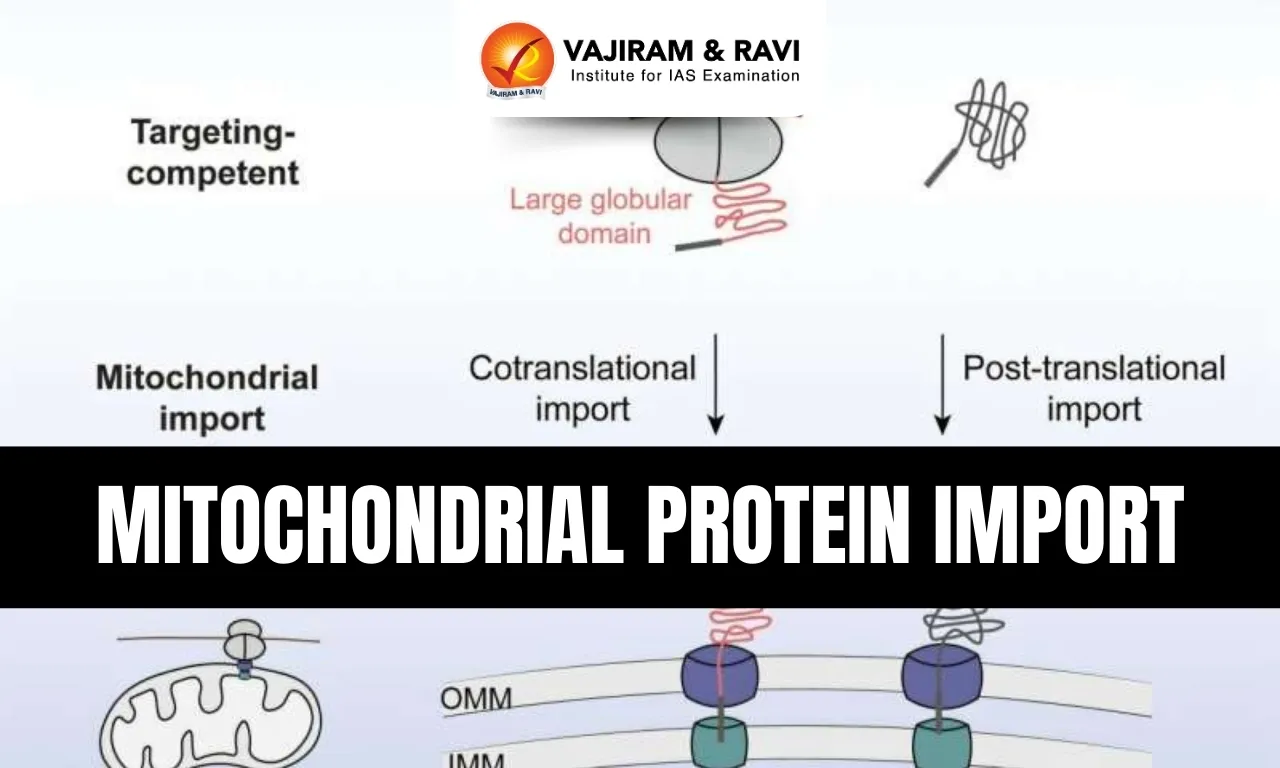
- Earlier, it was believed that mitochondrial proteins are imported only after translation is completed in the cytosol.
- Proteins were thought to fully synthesize on ribosomes before passing through mitochondrial membrane channels.
New Findings by Caltech Scientists
- Around 20% of mitochondrial proteins are cotranslationally imported, i.e., they are imported while still being synthesized by ribosomes.
- This mechanism mainly applies to large and structurally complex proteins that require assistance during folding.
- If these proteins fully fold in the cytosol, they risk forming irreversible structures that block import channels.
Mechanism of Cotranslational Import
- Such proteins contain a mitochondrial targeting sequence, but this alone is insufficient for cotranslational delivery.
- A second signal is required – the first large protein domain that emerges during translation.
- This domain acts like a “code to unlock the boarding pass”, ensuring the protein is guided into mitochondria early.
- Experiments confirmed that transplanting these domains onto other proteins rerouted them for cotranslational import.
Source: PHY
Mitochondrial Protein Import FAQs
Q1: Why are mitochondria dependent on the host cell for proteins?
Ans: Most mitochondrial genes were transferred to the nucleus during evolution, so proteins are now synthesised in the cytosol and then imported.
Q2: What is cotranslational import?
Ans: It is the process where mitochondrial proteins are imported during their synthesis, not after the ribosome finishes translation.
Q3: What signals guide proteins into mitochondria?
Ans: Two signals are essential: the mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) and the emergence of a large foldable domain during translation.