Bioremediation Latest News
Bioremediation offers a cheaper, scalable, and sustainable alternative, especially in a country like India where vast stretches of land and water are affected but resources for remediation are limited.
About Bioremediation
- Bioremediation literally means “restoring life through biology.”
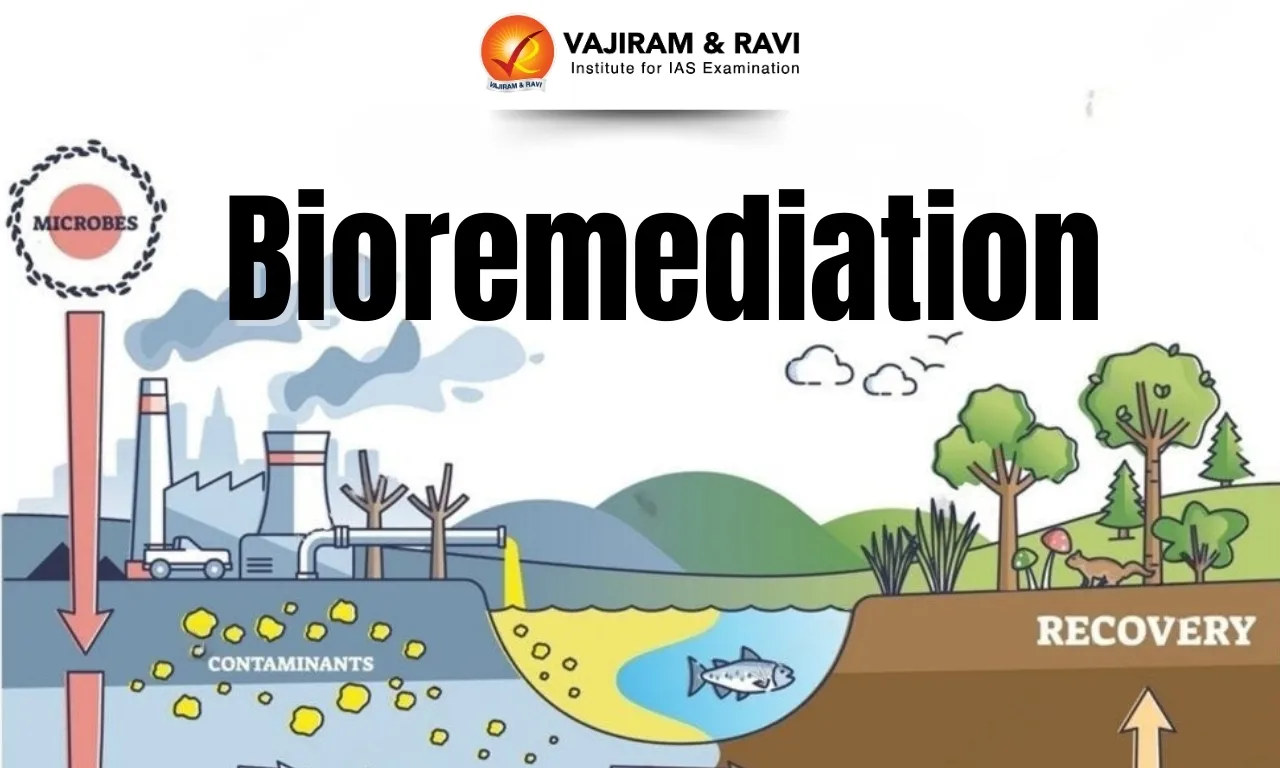
- It is the use of living organisms, primarily microorganisms, to degrade environmental contaminants into less toxic forms.
- It is used to clean up contaminated soil, air, and water.
- It harnesses microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, algae, and plants to sequester or transform toxic substances such as oil, pesticides, plastics, or heavy metals.
- These organisms metabolise these pollutants as food, breaking them down into harmless by-products such as water, carbon dioxide, or organic acids.
- In some cases, they can convert toxic metals into less dangerous forms that no longer leach into the soil or groundwater.
- Two Broad Types of Bioremediation:
- In situ bioremediation, where treatment happens directly at the contaminated site, such as when oil-eating bacteria is sprayed on an ocean spill;
- Ex situ bioremediation, where contaminated soil or water is removed, treated in a controlled facility, and returned once cleaned.
- For bioremediation to be effective, the right temperature, nutrients, and food also must be present.
- Proper conditions allow the right microbes to grow and multiply—and eat more contaminants.
Bioremediation Advantages
- It cleans up the environment naturally without the use of toxic chemicals. So, it is an environmentally friendly method.
- Contaminants are converted into water and harmless gases.
- It is cost-effective, as extensive equipment and labor are not needed.
- It is a permanent solution, as the degraded material cannot revert back to the previous one.
- It is a recommended method for removing oil stains.
Bioremediation Disadvantages
- It takes a large area and time from months to years.
- It is limited to the compounds which are degradable.
- It is not able to remove all kinds of impurities from the contaminated site. Like, some kind of inorganic contaminants cannot be treated with this bioremediation method.
- Some heavy metals cannot be completely broken down, resulting in toxic by-products.
Source: TH
Bioremediation FAQs
Q1: What does bioremediation use to degrade environmental contaminants?
Ans: Bioremediation use of living organisms, primarily microorganisms, to degrade environmental contaminants into less toxic forms.
Q2: Which organisms are commonly harnessed in bioremediation processes?
Ans: It harnesses microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, algae, and plants to sequester or transform toxic substances.
Q3: What is in situ bioremediation?
Ans: In situ bioremediation is a method where contaminants are treated directly at the site without removing the polluted soil or water.
Q4: Why is bioremediation considered an environmentally friendly method?
Ans: It cleans up the environment naturally without the use of toxic chemicals.