Plate tectonics is a geographical theory that covers the lithosphere, the outer layer of Earth and its division into large pieces that are known as tectonic plates. Tectonic plates move slowly beneath the Earth’s surface and are responsible for the formation of mountains, volcanoes and other geographical features that form and change over time. In this article, we are going to cover all about Plate Tectonic Theory.
The Plate Tectonics Theory evolved from Alfred Wegener’s early concept of continental drift, proposed in 1912. The modern, comprehensive version was developed during the 1950s and 1960s, with significant contributions from scientists like Harry Hess, who introduced seafloor spreading, W.J. Morgan, and Vine & Matthews, among others, ultimately formalizing the movement of Earth’s rigid plates.
Plate Tectonics Theory
A tectonic plate is a slab of solid rock that keeps shifting and causes changes in the lithosphere, that is the outermost layer of Earth. Tectonic plates are not static and move slowly over the asthenosphere, a semi-molten, ductile layer below the lithosphere that allows movement.
Tectonic Plates Types
Tectonic Plates are of the following types:
- Continental Plates: Consists of granitic rocks, light but thicker
- Oceanic Plates: Consists of basaltic rocks, dense but thin
- Mixed Pates: Include both continental and oceanic crust
A tectonic plate can be categorised as continental or oceanic depending on the dominant type of crust that it contains. Example-
- Pacific Plate- Oceanic Plate
- Eurasian Plate- Continental Plate
Plate Tectonics Theory Significance
The Plate Tectonics Theory was given by Alfred Weneger in the mid 20th century. Plate- Tectonics is accepted as the most reasonable theory for large-scale Earth processes. The theory explains-
- The origin and breakup of oceans and continents
- Formation of mountains due to collision of plates
- Occurrence of earthquakes due to fault lines
- Eruption of volcanoes at subduction zones and mid-ocean ridges
- This helps in understanding the dynamic surface of Earth
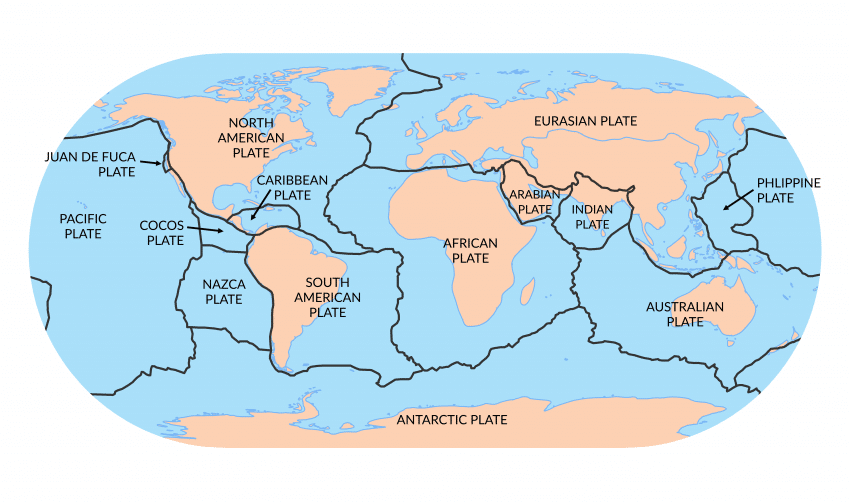
Plate Tectonics Major and Minor Divisions
The lithosphere layer of Earth is divided into seven major and minor plates:
Major Tectonic Plates:
- Pacific Plate
- Eurasian Plate
- North American Plate
- South American Plate
- African Plate
- Indo-Australian Plate
- Antarctic Plate
Minor Tectonic Plates:
- Cocos Plate – Between Central America & Pacific Plate
- Nazca Plate – Between South America & Pacific Plate
- Arabian Plate – Covers much of the Middle East
- Philippine Plate – Between Asia & Pacific
- Caroline Plate – North of New Guinea
- Fuji Plate – Northeast of Australia
Plate Tectonics Diagram
The following diagram below explains the Theory of Plate Tectonics:
Forces Driving Plate Tectonics Movement
Plate Tectonics movement is caused by the energy of heat in the Earth’s interior. These forces include:
- Asthenosphere Flow: Movement of tectonic plates due to convection currents in the semi-fluid asthenosphere.
- Heat sources include radioactive decay of elements (uranium, thorium, potassium) and heat residual from Earth’s formation.
- Convection Cells: Hot mantle material rises, spreads, cools and sinks leading to circular flow that pushes and pulls plates.
- This idea, proposed by Arthur Holmes (1930s), laid the foundation for Harry Hess’ theory of seafloor spreading in the 1960s.
Plate Tectonics Boundaries
Plate Tectonics boundaries can be classified into three types:
- Divergent Boundaries (Constructive)
- Plates move apart, and new crust forms from rising magma.
- Example: Mid-Atlantic Ridge (North American Plate separating from Eurasian Plate).
- Convergent Boundaries (Destructive)
- Plates collide, leading to subduction or mountain-building.
- Oceanic–Oceanic Convergence: One oceanic plate subducts beneath the other Volcanic island arcs (e.g., Philippines, Indonesia).
- Oceanic–Continental Convergence: Denser oceanic plate subducts beneath continental plate Volcanic mountains (e.g., Andes).
- Continental–Continental Convergence: Both plates collide Fold mountains (e.g., Himalayas, Alps).
- Transform Boundaries (Conservative)
- Plates slide past each other horizontally → causes earthquakes.
- Example: San Andreas Fault in California.
Plate Tectonics and Continental Evolution
- Alfred Wegener’s Theory of Continental Drift (1912) says that all continents were once a part of a supercontinent that is Pangaea.
- Over the years, through the studying of seafloor spreading and paleomagnetism, it was confirmed that continents were separated by tectonic plates.
- Continents move constantly, collide, break apart and reshape the globe.
- Example: The Indian subcontinent drifted from near Antarctica and collided with Asia, forming the Himalayas.
Last updated on January, 2026
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 Postponed for CSE & IFS which was scheduled to be released on 14 January 2026.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Plate Tectonics Theory FAQs
Q1. What is plate tectonic theory?+
Q2. Who proposed the plate tectonic theory?+
Q3. What is the 3 plate tectonic theory?+
Q4. How many types of plate tectonics are there?+
Q5. What are the transform boundaries of Plate tectonics?+
Tags: plate tectonics theory