Folding and faulting are important geological processes caused by tectonic forces acting within the Earth’s crust. Both processes are responsible for shaping major landforms such as mountains, plateaus, and valleys.
Understanding the Difference Between Folding and Faulting is essential for grasping the fundamentals of structural geology and geomorphology.
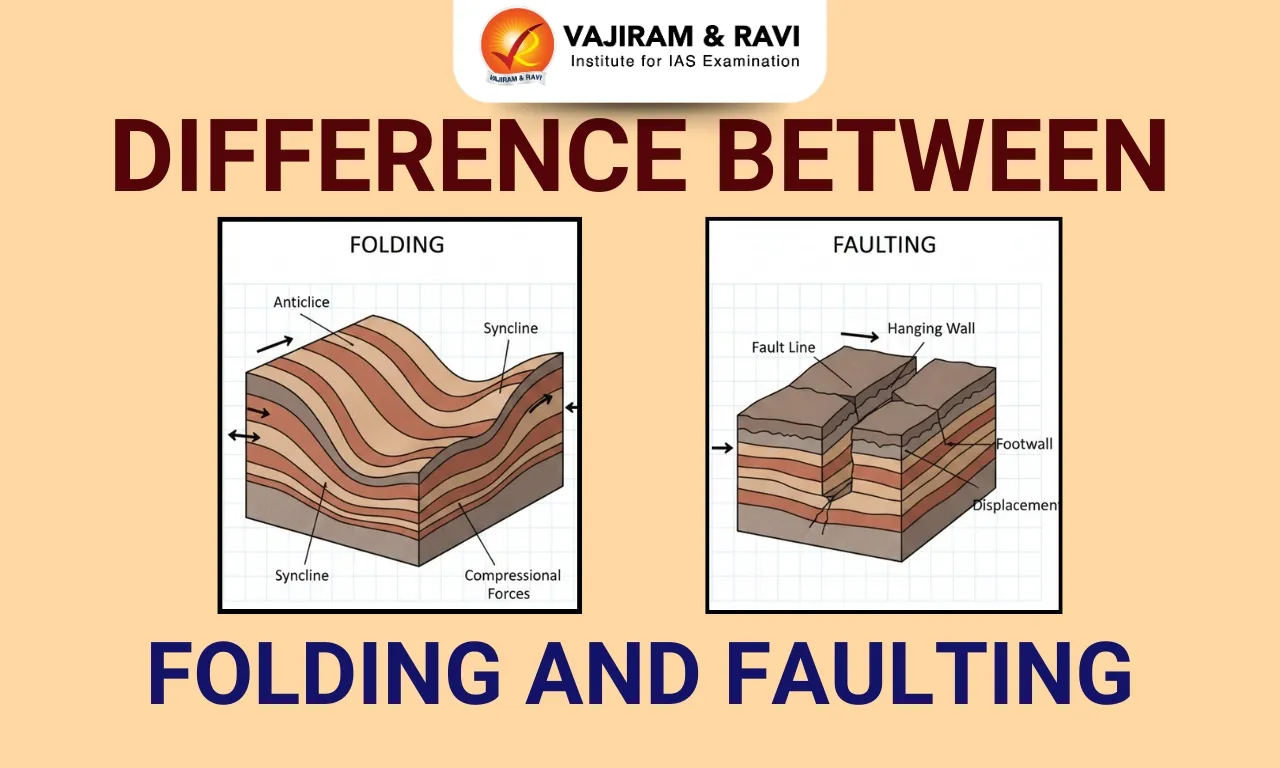
What is Folding?
Folding is a geological process in which rock layers bend or warp due to compressional forces acting deep within the Earth’s crust. These forces usually occur at convergent plate boundaries where tectonic plates move towards each other. Instead of breaking, the rock layers deform plastically, forming wave-like structures.
Folding commonly occurs in sedimentary rocks that are relatively soft and flexible under high temperature and pressure conditions. Major fold structures include anticlines (upward folds) and synclines (downward folds).
What is Faulting?
Faulting is the process by which rocks in the Earth’s crust break and move along a fracture called a fault due to intense tectonic forces. When the stress exceeds the strength of rocks, they crack and slip instead of bending. Faulting can result from compressional, tensional, or shearing forces.
This process leads to the formation of distinct landforms such as rift valleys, block mountains, and escarpments.
Difference Between Folding and Faulting
The table below provides a detailed comparison of folding and faulting, with each point explained briefly.
| Difference Between Folding and Faulting | ||
| Basis of Comparison | Folding | Faulting |
|
Nature of Process |
Folding involves bending of rock layers without breaking due to compressional forces. |
Faulting involves the breaking of rock layers followed by displacement along fractures. |
|
Type of Stress |
Mainly caused by compressional stress acting horizontally on rock strata. |
Can be caused by compressional, tensional, or shearing stresses. |
|
Rock Behavior |
Rocks behave plastically and deform under high pressure and temperature. |
Rocks behave brittlely and crack when stress exceeds their strength. |
|
Depth of Occurrence |
Generally occurs deep inside the Earth’s crust where rocks are ductile. |
Occurs at relatively shallow depths where rocks are rigid and brittle. |
|
Landforms Produced |
Produces fold mountains, anticlines, synclines, and complex fold systems. |
Produces block mountains, rift valleys, fault scarps, and grabens. |
|
Earthquake Association |
Folding rarely causes earthquakes as deformation is gradual. |
Faulting is directly associated with earthquakes due to sudden rock movement. |
Examples of Fold and Fault Landforms
Fold Landforms:
Major fold mountains include the Himalayas, Alps, Andes, and Rockies. These landforms are the result of prolonged compressional forces that folded thick sedimentary rock layers over millions of years.
Fault Landforms:
Important fault-related landforms include the Rhine Rift Valley, Narmada–Tapi Rift Valley, Sierra Nevada Block Mountains, and the Great Rift Valley of Africa. These features formed due to vertical or horizontal displacement along faults.
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the first week of March 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Difference Between Folding and Faulting FAQs
Q1. Why does folding not cause earthquakes frequently?+
Q2. Which type of rocks are most suitable for folding?+
Q3. Can folding and faulting occur together?+
Q4. What is the main reason faulting leads to earthquakes?+
Q5. Which process is responsible for rift valleys?+