About Stomata
- Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for gas exchange.
- They are typically found in plant leaves but can also be found in some stems.
- Stomata allow a plant to take in carbon dioxide, which is needed for photosynthesis.
- They also help to reduce water loss by closing when conditions are hot or dry.
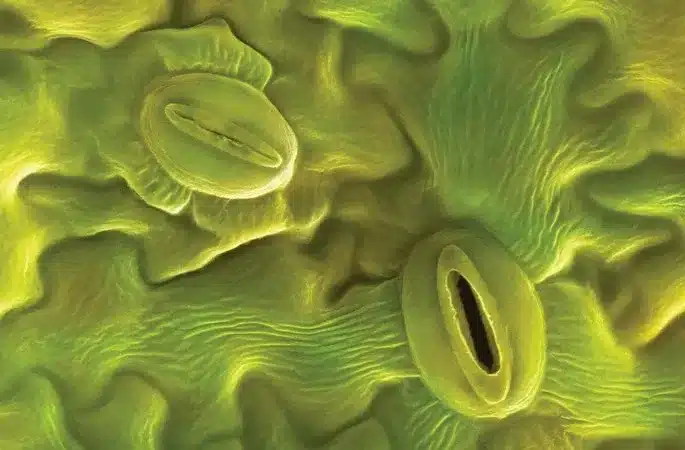
- Stomata look like tiny mouths which open and close as they assist in transpiration.
- Plants that reside on land typically have thousands of stomata on the surfaces of their leaves.
- The majority of stomata are located on the underside of plant leaves, reducing their exposure to heat and air current.
- In aquatic plants, stomata are located on the upper surface of the leaves.
- A stoma (singular for stomata) is surrounded by two types of specialized plant cells that differ from other plant epidermal cells. These cells are called guard cells and subsidiary cells.
- Guard cells are large, crescent-shaped cells, two of which surround a stoma and are connected to at both ends.
- A stomate opens and closes in response to the internal pressure of guard cells.
- These cells enlarge and contract to open and close stomatal pores.
- Guard cells work to control excessive water loss, closing on hot, dry, or windy days and opening when conditions are more favourable for gas exchange.
- Guard cells also contain chloroplasts, the light-capturing organelles in plants.
- Subsidiary cells, also called accessory cells, surround and support guard cells.
- They act as a buffer between guard cells and epidermal cells, protecting epidermal cells against guard cell expansion.
- For most plants, dawn triggers a sudden increase in stomatal opening, reaching a maximum near noon, which is followed by a decline because of water loss.
Q1) What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process used by plants, algae and some bacteria to turn sunlight into energy. The process chemically converts carbon dioxide (CO2) and water into food (sugars) and oxygen. The chemical reaction often relies on a pigment called chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color.
Source: Discovery of amino acid unveils how light makes stomata open in plants
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India