What’s in today’s article?
- Why in News?
- The Yemen Civil War (Background, Beginning)
- News Summary Regarding Peace Talks in Yemen
Why in News?
- After eight years of crushing civil war in Yemen, a new round of talks this week has raised a glimmer of hope for a breakthrough in one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises.
Background of the Yemen Civil War:
- The wave of protests known as the Arab Spring did not take long to arrive in Yemen after the Tunisian Revolution (2011–2012).
- Yemen, only unified since 1990, was a poor country with a government widely acknowledged to be corrupt, with a large number of weapons in private hands. It had deep divisions that persisted between the north and south.
- By 2011, the country was already facing challenges from al Qaeda-linked militants and separatists in the south and Zaydi Shia Muslim rebels in the north.
The Beginning of the Civil war:
- In September 2014, the Houthi insurgency (predominantly a Iran-backed Zaydi Shia force) transformed into a full-blown civil war as Houthi fighters swept into the capital of Sana’a.
- The rebels continued to apply pressure until the internationally recognised government was ousted in January 2015.
- The Houthis declared themselves in control of the Yemeni government, dissolving the Parliament, and installing an interim Revolutionary Committee.
- The then President (Hadi) escaped to Aden and declared himself Yemen’s legitimate president and proclaimed Aden as the country’s temporary capital.
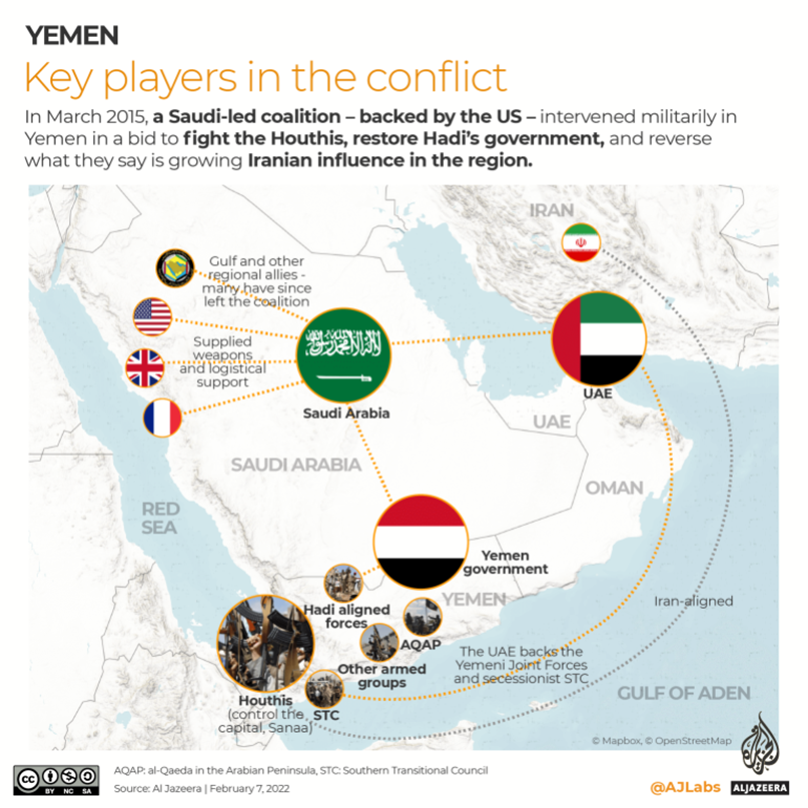
- The Saudi-led coalition intervened in 2015 in an attempt to restore the (Hadi) government, launching a devastating bombing campaign that lasted years.
Image Caption: Key Players in Yemen Conflict
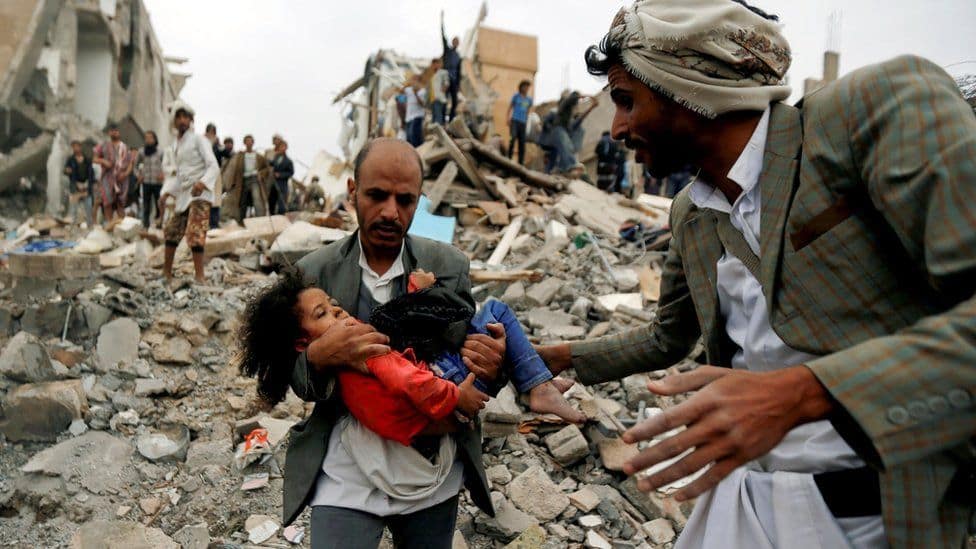
The world’s worst humanitarian crises:
- Even before the war, Yemen was the poorest Arab country.
- But the conflict mired the Yemenis into one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises and pushed the country to the brink of famine.
- The UN estimates the war had killed 377,000 people as of the end of 2021, both directly and indirectly through hunger and disease – 70% of those deaths are children.
- About 24 million people – 80% of Yemen’s population – are in need of humanitarian aid.
News Summary Regarding Peace Talks in Yemen:
- What has changed now? A surprise rapprochement/resumption of harmonious relations between two regional powers, Saudi Arabia and Iran – who fed a proxy conflict that worsened the war.
- Who is at the talks? The negotiations in Yemen’s capital, Sana, bring together Saudi Arabia and the Houthis.
- What are they trying to achieve?
- Negotiators are seeking the reinstatement of a truce and a complete withdrawal of foreign forces from Yemen.
- The negotiators also want to pave the way for broader talks to resolve Yemen’s multifaceted political conflict and repair its demolished economy.
- Why does the détente between Saudi Arabia and Iran matter?
- Both Riyadh and Tehran are keen to prove that their diplomatic efforts were instrumental in bringing calmness to Yemen.
- Saudi officials are eager to end their military involvement in Yemen, which has been expensive and damaging to the kingdom’s international reputation.
- Will these talks end Yemen’s conflict? Without genuine support within the country, among the Yemenis themselves, a political resolution cannot take root.
Q1) What is the Arab spring?
The Arab Spring was a series of anti-government protests, uprisings and armed rebellions that spread across much of the Arab world in the early 2010s. It began in Tunisia in response to corruption and economic stagnation.
Q2) What is the Houthi movement?
The Houthi movement is an Islamist political and armed organisation that emerged in North Yemen in the 1990s. The Houthi movement is a predominately Zaidi Shia force, whose leadership is drawn largely from the Houthi tribe, that have a complex relationship with Yemen’s Sunni Muslims.
Source: What do peace talks in Yemen mean for its 8-year war? | Aljazeera
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the second week of April 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India