Who is a President, and what is his/her constitutional position in Indian Polity?
The President of India is the head of state and the first citizen of India.
- As per the Constitution of India, the President is the supreme commander of the Indian Armed Forces and has the power to appoint the Prime Minister and other members of the Union Council of Ministers, as well as to dismiss them.
- The President acts as a figurehead and represents the nation’s unity. The President’s powers are largely ceremonial, with real executive power vested in the Prime Minister and Cabinet.
- The President also has the power to appoint judges to the Supreme Court and high courts and Governors of states.
How is the President of India elected?
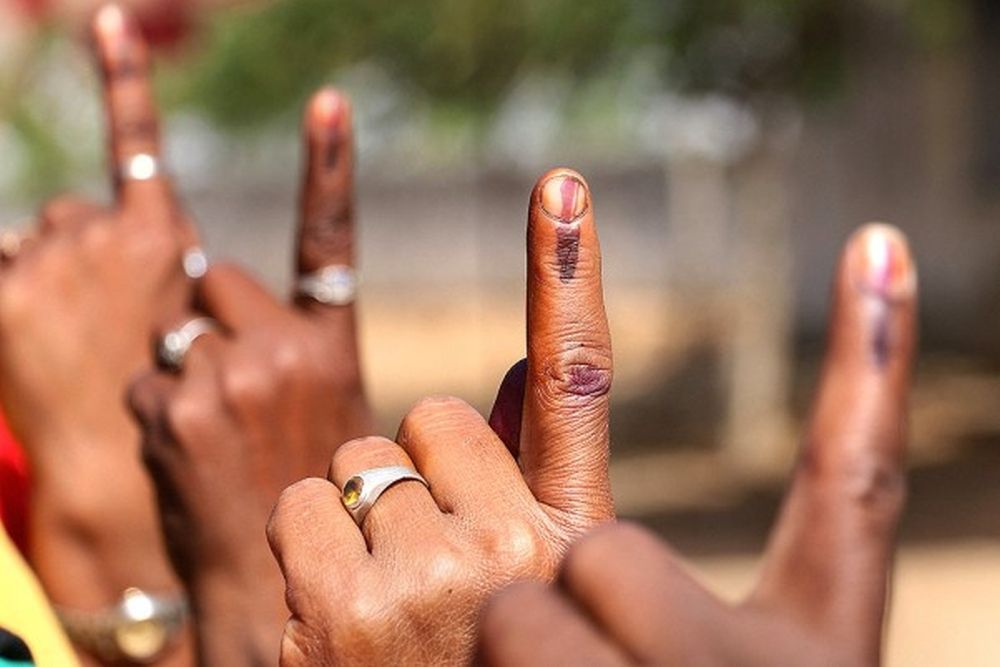
- The President is elected by the members of an electoral college consisting of the elected members of both the Houses of Parliament and the elected members of the Legislative Assemblies of States and the Union Territories of Delhi and Pondicherry.
- Therefore, those nominated to both Houses of Parliament, state legislative assemblies, state legislative councils (if applicable), and the Legislative Assemblies of Delhi and Puducherry are not eligible to vote in the presidential election.
- Members of the electoral college vote for the President in a system of proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote, where each member has a single vote that can be transferred to other candidates in a sequence of preferences. The candidate who receives the majority of votes in the electoral college is elected as the President of India.
- Process of Election: The process of electing the President of India is as follows:
- The Election Commission of India announces the date for the presidential election and invites nominations from eligible candidates.
- Candidates must be a citizen of India, at least 35 years old, and eligible to be a member of the Lok Sabha (the lower house of the Indian Parliament).
- A Candidate must be supported by 50 proposers and 50 seconders who are MP/MLA members of the electoral college.
- The Election Commission scrutinizes the nominations and publishes a list of valid candidates.
- Members of the electoral college, which is made up of elected members of the Indian Parliament and the Legislative Assemblies of the Indian states and Union Territories with legislative assembly, cast their votes using a system of proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote.
- The votes are then counted, and the candidate who receives the majority of votes is declared elected as the President of India.
- The President-elect takes the oath of office and assumes the responsibilities of the President of India.
What are the constitutional provisions relating to the office of the President of India?
| Article | Description |
| Article 52 | There shall be a President of India |
| Article 53 | The executive power of the Union shall be vested in the President |
| Article 54 | The President shall be elected by the members of an electoral college consisting of the elected members of both Houses of Parliament; and the elected members of the Legislative Assemblies of the States |
| Article 55 | Manner of election of President |
| Article 56 | The President shall hold office for a term of five years |
| Article 57 | A person who holds, or who has held, office as President shall, subject to the other provisions of this Constitution, be eligible for re-election to that office |
| Article 58 | Qualifications for election to the office of the President |
| Article 59 | Conditions of the office of the President |
| Article 60 | Oath to the office of President |
| Article 61 | Procedure for impeachment of the President |
| Article 62 | Provisions related to the term and vacancy of the President |
Qualifications
To be eligible to run for President, a person must meet the following criteria:
- Be a citizen of India.
- Be at least 35 years old.
- Meet the qualifications to be a member of the Lok Sabha.
- Not hold any office of profit under the Union or state government or any local or other public authority. Exceptions are made for the sitting President or Vice-President, the Governor of any state, and the ministers of the Union or any state.
Oath for the Office of President
Before taking office, the President must take an oath in which he/she swears to
- to faithfully execute the office;
- to preserve, protect and defend the Constitution and the law;
- to devote himself to the service and well-being of the people of India.
Conditions of Office
Moreover, The Constitution sets the following conditions for the President’s term in office:
- He should not be a member of either House of Parliament or a House of the state legislature. If any such person is elected as President, he is deemed to have vacated his seat in that House on the date on which he enters upon his office as President.
- He should not hold any other office of profit.
- He is entitled, without payment of rent, to the use of his official residence (the Rashtrapati Bhavan).
- He is entitled to such emoluments, allowances, and privileges as may be determined by Parliament.
- His emoluments and allowances cannot be diminished during his term of office.
Term and Vacancy
- Term: The President serves a term of five years from the date they take office. However, they can resign anytime by sending a resignation letter to the Vice-President. Additionally, they can be removed from office through the process of impeachment before the completion of their term.
- The President can remain in office until their successor takes over and is eligible for re-election for any number of terms. However, in the United States, a person cannot be elected as President more than twice.
- Vacancy: A vacancy in the office of the President can happen in the following ways:
- On the expiry of his tenure of five years.
- By his resignation.
- On his removal by the process of impeachment.
- By his death.
- Otherwise, for example, when he becomes disqualified to hold office or his election is declared void.
How is the President of India impeached?
The President can be removed from office through a process of impeachment for “violation of the Constitution,” although the Constitution does not specify what constitutes such a violation.
- Impeachment proceedings can be initiated by either House of Parliament, with the charges being signed by one-fourth of the members of the House.
- The President is given 14 days’ notice before the proceedings begin and has the right to appear and be represented during the investigation. If a resolution is passed by a two-thirds majority of both Houses, the President is removed from office.
- An impeachment is a semi-judicial process in Parliament. Nominated members of either House of Parliament can participate in impeachment proceedings, even though they cannot vote in the presidential election.
- Members of state legislative assemblies and the Union Territories of Delhi and Puducherry, who can vote in the presidential election, do not participate in impeachment proceedings.
- To date, no President has ever been impeached.
Last updated on April, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Admit Card 2025 is expected to release in first week of May for CSE Prelims Exam 2025.
→ The UPSC Prelims 2025 is scheduled to be conducted on 25th May 2025 and UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ Apply once through it and aspirants can apply for various government exams conducted by UPSC.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi
President of India FAQs
Q1. What happens in case of the death, resignation, or removal of the President of India?+
Q2. Can the President of India dissolve the Lok Sabha?+
Tags: president of india quest