La Nina Latest News
Climate change is intensifying, and the cooling effects of La Niña may weaken in a warmer future, climate scientists warn, citing current heat trends across much of the country.
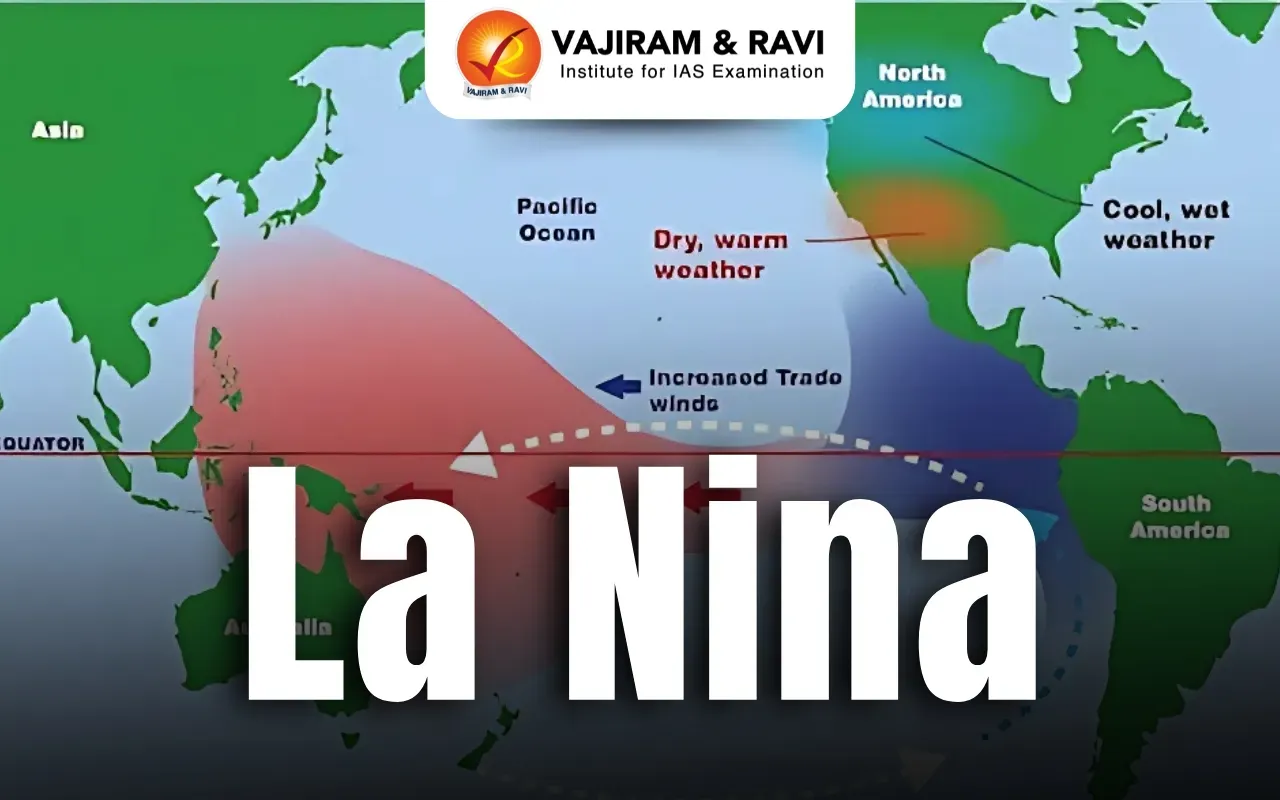
About La Nina
- La Niña is a climate pattern that describes the cooling of surface-ocean waters along the tropical west coast of South America.
- La Niña is considered to be the counterpart to El Niño, which is characterized by unusually warm ocean temperatures in the equatorial region of the Pacific Ocean.
- Together, La Niña and El Niño are the “cold” (La Niña) and “warm” (El Niño) phases of the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). ENSO is series of linked weather- and ocean-related phenomena.
- La Niña events are indicated by sea-surface temperature decreases of more than 0.5 degrees Celsius (0.9 degrees Fahrenheit) for at least five successive three-month seasons.
La Nina Causes
- La Niña is caused by a build-up of cooler-than-normal waters in the tropical Pacific, the area of the Pacific Ocean between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- Unusually strong, eastward-moving trade winds and ocean currents bring this cold water to the surface, a process known as upwelling. Upwelling can cause a drastic drop in sea-surface temperature.
La Nina Effects
- Impact on Air Pressure and Rainfall: La Niña lowers air pressure over the western Pacific, leading to increased rainfall. Southeast Asia experiences stronger summer monsoons, benefiting agriculture in northwest India and Bangladesh.
- Risk of Flooding in Australia: While La Niña supports agriculture in South Asia, strong events can cause severe flooding in northern Australia due to excessive rainfall and low-pressure systems.
- Global Rainfall Patterns: La Niña brings more rain to southeastern Africa and northern Brazil. In contrast, it increases air pressure over the central and eastern Pacific, causing dry conditions.
- Drier Conditions in Some Regions: Regions like the west coast of tropical South America, the Gulf Coast of the US, and the pampas of South America experience reduced rainfall and dry spells during La Niña.
- Boost to the Fishing Industry: Upwelling caused by La Niña brings cold, nutrient-rich waters to the surface, supporting plankton growth. This benefits fish populations and predators like sea bass.
- Duration and Seasonal Peak: La Niña events usually last between one and three years, whereas El Niño typically lasts less than a year. Both tend to peak during the Northern Hemisphere winter.
La Nina FAQs
Q1. What is the meaning of La Niña?
Ans. La Niña is a climate pattern causing cooler-than-normal sea-surface temperatures in the tropical Pacific, affecting global weather patterns.
Q2 How does La Niña affect India?
Ans. La Niña strengthens the Indian monsoon, increasing rainfall in northwest India and Bangladesh, benefiting agriculture but sometimes causing floods.
Q3. What is the difference between La Niña and El Niño?
Ans. La Niña causes cooler Pacific waters and increased rainfall, while El Niño causes warmer waters and disrupts global weather patterns.
Q4. What is worse, El Niño or La Niña?
Ans. El Niño generally causes more severe global weather disruptions, but La Niña can lead to destructive floods in certain regions.
Source: ET
Last updated on June, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi