What’s in today’s article?
- Why in News?
- About Olive Ridley Turtles
- Population of Olive Ridleys in the Indian Ocean
- Threats to Olive Ridleys’ Existence
- Conservation Measures for Olive Ridleys
- Legal Protection for Olive Ridleys
- News Summary
Why in News?
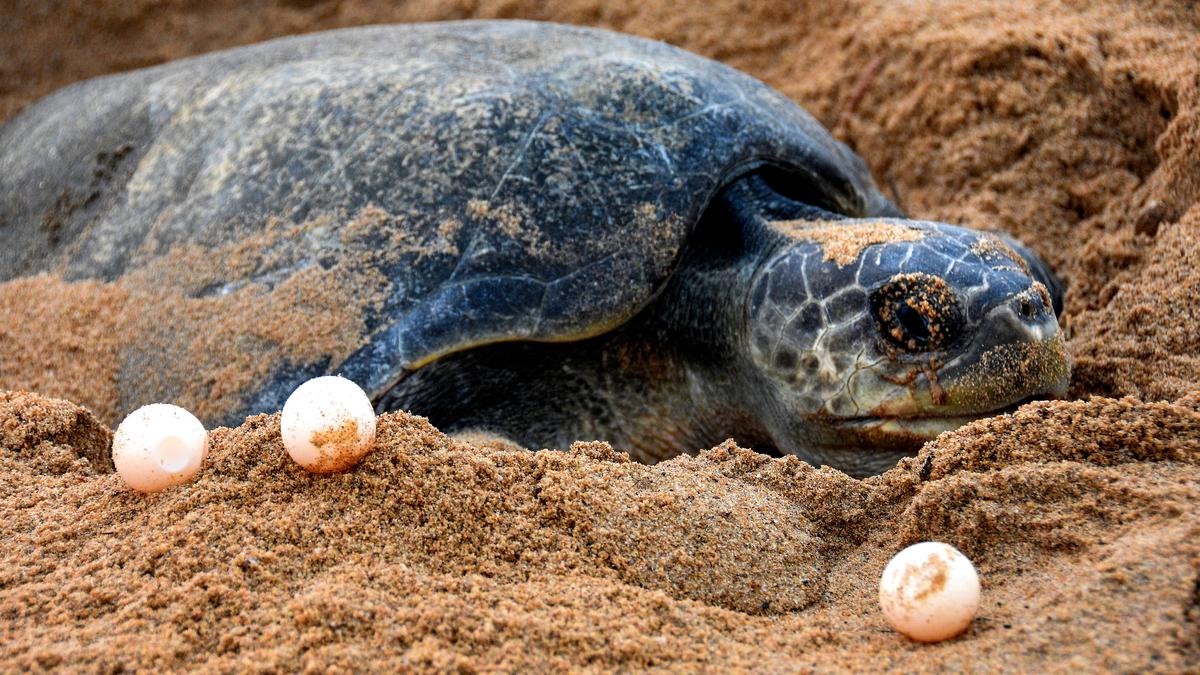
- About 6.37 lakh Olive Ridley sea turtles have arrived for mass nesting at Rushikulya coast this year, setting a new record for the beach in Odisha’s Ganjam district.
About Olive Ridley Turtles
- The olive ridley gets its name from the olive green colour of its heart-shaped shell.
- The species is among the smallest of the world’s sea turtles and is found primarily in the tropical regions of the Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic oceans.
- They are carnivores, and feed mainly on jellyfish, shrimp, snails, crabs, molluscs and a variety of fish and their eggs.
- These turtles spend their entire lives in the ocean, and migrate thousands of kilometres between feeding and mating grounds in the course of a year.
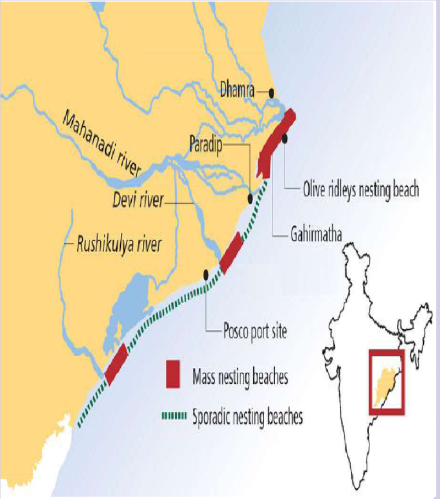
Population of Olive Ridleys in the Indian Ocean
Image Caption: Olive Ridleys in the Indian Ocean
- In the Indian Ocean, three arribada beaches occur in Odisha, India (Gahirmatha, Devi River mouth, and Rushikulya) with an estimated +100,000 nests per year.
- ‘Arribada’ is a term used for olive ridley turtles and kemps ridley turtles wherein thousands of females come together on the same beach to lay eggs.
- Interestingly, females return to the very same beach from where they first hatched, to lay their eggs.
- After about 45-65 days, the eggs begin to hatch, and these beaches are swamped with crawling Olive-ridley turtle babies, making their first trek towards the vast ocean.
- It is estimated that approximately 1 hatchling survives to reach adulthood for every 1000 hatchlings that enter the sea waters.
- The coast of Odisha is the largest mass nesting site for the olive-ridley, followed by the coasts of Mexico and Costa Rica.
Threats to Olive Ridleys’ Existence
- According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), there has been between a 30 to 50 percent reduction in global population size.
- Although some nesting populations have increased in the past few years or are currently stable, the overall reduction in some populations is greater than the overall increase in others.
- The number of olive ridleys are greatly reduced from historical estimates (for example, 10 million olive ridleys in the Pacific Ocean), due to overexploitation for turtle meat and eggs.
- Though international trade in these turtles and their products is banned under CITES Appendix I, they are still extensively poached for their meat, shell and leather, and their eggs.
- Olive-ridleys face serious threats across their migratory route, habitat and nesting beaches, due to human activities such as –
- Turtle unfriendly fishing practices,
- Development and exploitation of nesting beaches for ports, and
- Tourist centres.
- The most severe threat they face is the accidental killing of adult turtles through entanglement in trawl nets and gill nets due to uncontrolled fishing during their mating season around nesting beaches.
Conservation Measures for Olive Ridleys
- To reduce accidental killing in India, the Odisha government has made it mandatory for trawls to use Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs), a net specially designed with an exit cover which allows the turtles to escape while retaining the catch.
- Operation Olivia –
- Every year, the Indian Coast Guard’s “Operation Olivia”, initiated in the early 1980s, helps protect Olive Ridley turtles as they congregate along the Odisha coast for breeding and nesting from November to December.
- Metal Tags –
- Since 2021, the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) in collaboration with Wildlife Wing of Odisha’s forest department started tagging olive ridley turtles with the help of metal tags.
- These are non-corrosive metal tags which enable scientists to chart the movements of olive ridleys and also know the areas they visit in order to protect the species and their habitats.
Legal Protection for Olive Ridleys
- Olive ridley turtles enjoy following legal protection –
- IUCN Status – Vulnerable
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 – Schedule I
- CITES – Appendix I
News Summary
- About 6.37 lakh Olive Ridley sea turtles have arrived for mass nesting at Rushikulya coast this year (between February and March), setting a new record for the beach in Odisha’s Ganjam district.
- Last year, 5.5 lakh Olive Ridley turtles had come to Rushikulya for mass nesting.
- This is attributed to emergence of new beaches for laying of eggs near the Podampetta area on the coast of Odisha.
- Also, the beaches remained unaffected as there were no extreme weather events such as cyclone and heavy rain and turtles ascended perfectly sloped beaches at Rushikulya river mouth
Q1) What is the difference between Turtle and Tortoise?
Tortoises have more rounded and domed shells where turtles have thinner, more water-dynamic shells. Turtle shells are more streamlined to aid in swimming. One major key difference is that tortoises spend most of their time on land and turtles are adapted for life spent in water.
Q2) What is IUCN?
The International Union for Conservation of Nature is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education.
Source: Record 6.37 lakh Olive Ridley turtles arrive at Odisha’s Rushikulya beach for mass nesting | WWF India
Last updated on December, 2025
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is scheduled to be released on January 14, 2026.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Mains Question Paper 2025 is out for Essay, GS 1, 2, 3 & GS 4.
→ UPSC Mains Indian Language Question Paper 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Mains Optional Question Paper 2025 is now out.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi